Outcomes of Second Kidney Transplantation Compared Primary Transplantation According to Donor Specific Antibody.
1Department of Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
2The Research Institute for Transplantation, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D17
Keywords: Antibodies, Graft survival, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Antibody Mediated Rejection: Session #2
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, June 14, 2016
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Halls C&D
Background:
Re-transplantation is associated with an improved overall survival of patients with a failed renal allograft. Some studies showed the outcomes of retransplantation are than those of primary procedures. But outcome of second transplantation according to Donor Specific Antibody (DSA) is not established.
Objectives: The aim of study was to know outcomes of re-transplantation and primary transplantation in kidney recipients according to DSA.
Methods: Medical records of 1333 Kidney recipients between Jan. 2006 and Dec. 2015 was retrospectively reviewed. Pediatric recipients and recipients who underwent multi-organ transplantation were excluded. Patients was divided into four group according to DSA at transplantation.
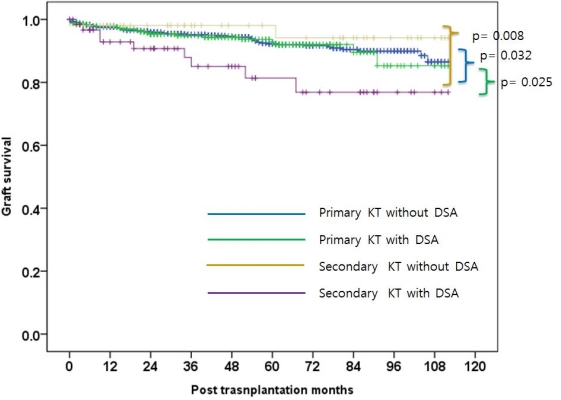
Results: 1218 kidney recipients underwent primary transplantation (PT) and 115 kidney recipients underwent re-transplantation (RT). There was no significantly difference in age and gender between PT and RT. The portion of deceased donor kidney transplantation (DDKT) was higher in RT than PT. (45.2% vs. 25.9%, p <0.001). The rate of delayed graft function was higher in RT than PT (15.7% vs. 9.2%, p = 0.032). Graft survivals of PT at 1 year, 3years, 5 years were 95.1%, 90.9% and 92.4%, respectively and that of RT at 1 year, 3years, 5 years were 95.4%, 91.3% and 89.5%, respectively. (p= 0.225) However, graft survival of RT with DSA is lower than that of PT without DSA, PT with DSA and RT without DSA (p= 0.008, 0.032 and 0.025, respectively)
Conclusion: DSA at transplantation in kidney recipients who were considered RT is poor prognosis factor in graft survival. Thus, DSA should be checked and monitored in RT.
CITATION INFORMATION: Lee J, Lee K, Lee J, Song S, Lee J, Kwon S.-K, Joo D, Huh K, Kim M, Kim S, Kim Y. Outcomes of Second Kidney Transplantation Compared Primary Transplantation According to Donor Specific Antibody. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lee J, Lee K, Lee J, Song S, Lee J, Kwon S-K, Joo D, Huh K, Kim M, Kim S, Kim Y. Outcomes of Second Kidney Transplantation Compared Primary Transplantation According to Donor Specific Antibody. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/outcomes-of-second-kidney-transplantation-compared-primary-transplantation-according-to-donor-specific-antibody/. Accessed March 7, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
