Outcomes of HIV+ Liver Transplant Recipients Compared to HCV+ or HIV+/HCV+ Co-Infected Recipients: The “Real World” Experience
D. Sawinski,1 G. David,2 E. Blumberg,3 P. Abt,4 R. Bloom,1 K. Forde.2
1Renal Division, Univ. of Penn, Philadelphia, PA
2Gastroenterology Division, Univ. of Penn, Philadelphia, PA
3Infectious Disease, Univ. of Penn, Philadelphia, PA
4Surgery, Univ of Penn, Philadelphia, PA.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 224
Keywords: Hepatitis C, HIV virus, Liver transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Liver Transplantation: Viral Hepatitis
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, May 4, 2015
Session Time: 2:15pm-3:45pm
 Presentation Time: 3:03pm-3:15pm
Presentation Time: 3:03pm-3:15pm
Location: Terrace IV
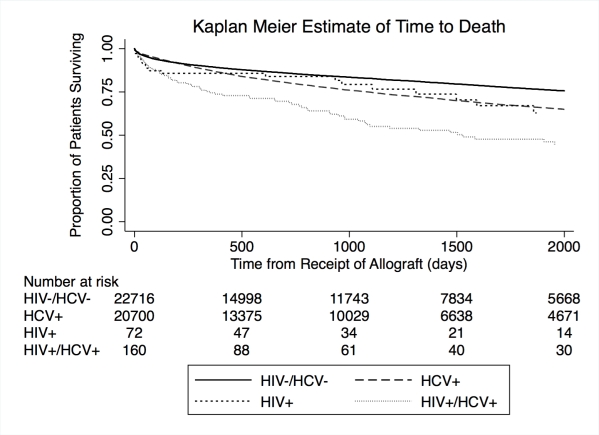
End stage liver disease is a frequent cause of mortality in patients with HIV. Though demonstrated in the NIH observational trial, the effectiveness of LT in HIV mono-infected and HIV/ HCV co-infected patients in the larger transplant population is not known. To determine the effect of HIV infection on outcomes in comparison to HCV mono-infected and HIV/ HCV uninfected LT recipients in the United States, we performed a retrospective registry study of first LT recipients from February 27, 2002 through December 31, 2013, stratified according to viral status: HCV (n=20,829), HIV (n=72) and HIV/HCV co-infected (n=160), with the HIV/HCV uninfected (n=22,926) as the reference. Patient and allograft survival were explored with Cox regression. In the multivariable analysis, patient and allograft survival in HIV patients did not differ significantly from the reference group and was better than that observed in the HCV or HIV/HCV co-infected groups. Transplantation at a center that participated in the NIH trial of LT in HIV+ patients did not confer an advantage for patient or allograft outcomes in HIV or HIV/ HCV co-infected LT recipients. A strategy of pre-transplant HCV viral eradication or preemptive post-transplant eradication should be explored as an approach to improve outcomes in HCV and HIV/ HCV co-infected LT recipients.
| NIH Study Center | Non NIH Study Center | |||||||
| variable | HR | p value | 95%CI | HR | p value | 95%CI | ||
| HIV-/HCV- | REF | REF | ||||||
| HCV+ | 1.56 | <0.001 | 1.43-1.71 | 1.52 | <0.001 | 1.45-1.60 | ||
| HIV+ | 1.65 | 0.09 | 0.93-2.92 | 1.03 | 0.95 | 0.43-2.47 | ||
| HIV+/HCV+ | 3.15 | <0.001 | 2.32-4.28 | 2.55 | <0.001 | 1.64-3.96 | ||
| Age | 1.02 | <0.001 | 0.92-1.10 | 1.02 | <0.001 | 1.01-1.02 | ||
| Male | 1.01 | 0.11 | 0.99-1.08 | 1.05 | 0.06 | 1.00-1.10 | ||
| Race | ||||||||
| White | REF | REF | ||||||
| Black | 1.13 | 0.05 | 1.00-1.28 | 1.35 | <0.001 | 1.26-1.46 | ||
| Latino | 0.88 | 0.05 | 0.77-1.00 | 0.94 | 0.07 | 0.87-1.01 | ||
| Asian | 0.78 | 0.03 | 0.62-0.98 | 0.82 | 0.01 | 0.72-0.94 | ||
| MELD | 1.01 | <0.001 | 1.01-1.02 | 1.01 | <0.001 | 1.00-1.01 | ||
| dialysis at txp | 1.59 | <0.001 | 1.48-1.78 | 1.46 | <0.001 | 1.32-1.61 | ||
| donor risk index | 1.62 | <0.001 | 1.48-1.78 | 1.56 | <0.001 | 1.48-1.65 | ||
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sawinski D, David G, Blumberg E, Abt P, Bloom R, Forde K. Outcomes of HIV+ Liver Transplant Recipients Compared to HCV+ or HIV+/HCV+ Co-Infected Recipients: The “Real World” Experience [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/outcomes-of-hiv-liver-transplant-recipients-compared-to-hcv-or-hivhcv-co-infected-recipients-the-real-world-experience/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
