Outcomes in Highly Sensitized Kidney Transplant Recipients Receiving DCD Organs
1Pharmacy, Temple University Hospital, Philadelphia, PA, 2Temple University, Philadelphia, PA, 3Surgery, Temple University Hospital, Philadelphia, PA
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 839
Keywords: Donors, non-heart-beating, Kidney transplantation, Panel reactive antibodies, Sensitization
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » Kidney Deceased Donor Selection
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney Deceased Donor Selection
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Highly sensitized (HS) patients experience longer wait times for kidney transplantation despite prioritization by the Kidney Allocation System. Kidney transplants performed from donors defined as donation after circulatory death (DCD) have been shown to decrease wait times for most patient populations. However, concern for increased rejection during delayed graft function (DGF) causes hesitancy in using DCD kidneys in HS patients. In this study, we evaluate the outcomes of HS kidney transplant (KT) recipients who received a DCD kidney.
*Methods: KT recipients who received DCD organs from 2015-2018 were studied using the United Network for Organ Sharing database. Patients were divided into three groups for analysis; calculated panel-reactive antibody (cPRA) 0% (Group 1), 1-89% (Group 2), and 90-100% (Group 3). Data analysis was performed with the SPSS software. Survival analysis was performed using a Cox regression and Kaplan-Meier model.
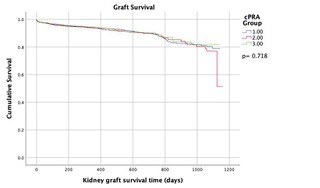
*Results: 7,854 KT recipients received DCD kidneys. Patients were divided into three groups: cPRA 0% (n= 4,598), cPRA 1-89% (n= 2,233), and cPRA 90-100% (n= 1,023). There was no significant difference in baseline characteristics (see Table 1). The mean KDPI in Group 3 was lower compared to other groups (51% vs. 50% vs. 44%; p<0.001). Rabbit antithymocyte globulin induction was used for most patients (58% vs. 66% vs. 75%). The incidence of DGF was similar between groups (41% vs. 42%. vs. 42%; p= 0.45). A higher number of patients in Group 3 were treated for rejection within 12 months (4.2% vs. 4.1% vs. 6.1%; p=0.003). No differences in graft failure (7.1% vs. 7.1 % vs. 6.7%; p=0.905) and patient survival (95% vs. 95% vs. 96%; p=0.449) were noted. A Cox regression model identified KDPI as a significant factor, independent of cPRA, impacting graft survival (OR 3.76; 95% CI: 2.61-5.41).
| cPRA 0% N= 4,598 | cPRA 1-89% N= 2,233 | cPRA 90-100% N =1,023 | |
| Recipient age (years), mean + SD | 54.1 + 13.1 | 53.1 + 13 | 49.5 + 13 |
| Donor age (years), mean + SD | 38.5 + 14.6 | 37.8 + 14.4 | 35.1 + 13.1 |
| Recipient gender (male), n (%) | 3072 (66.8) | 1490 (66.7) | 696 (68) |
| Recipient ethnicity, n (%) White; Black | 1891 (41.1); 1390 (30.2) | 855 (38.3); 735 (32.9) | 443 (43.3); 299 (29.2) |
| Donor ethnicity, n (%) White; Black | 3687 (80.2); 347 (7.5) | 1777 (79.6); 187 (8.4) | 758 (74.1); 78 (7.6) |
| Days on dialysis prior to transplant, mean + SD | 1907.3 + 1110.3 | 1941.6 + 1107 | 1798.3 + 1455.5 |
| EPTS, mean + SD | 53.14 + 29.77 | 51.02 + 29.39 | 45.89 + 28.52 |
*Conclusions: DCD kidney transplantation provides HS patients with comparable long term graft survival with an acceptable incidence of treated rejection within 12 months. Notably, KDPI had a larger influence on graft survival than the recipient’s cPRA. This study supports an increased use of DCD kidneys in HS patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Diamond A, Rodrigues L, Carlo ADi, Karhadkar S. Outcomes in Highly Sensitized Kidney Transplant Recipients Receiving DCD Organs [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/outcomes-in-highly-sensitized-kidney-transplant-recipients-receiving-dcd-organs/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress