Outcome Predictors with Perioperative Kidney Transplant Midodrine Usage
R. Watson1, S. Mullins2, S. Williams3, F. Fakhre4, K. Robichaux4, S. Mohammed4, M. Gosselin3, A. Kumar5, J. Buggs1, V. Bowers1
1Transplant Surgery, Tampa General Hospital, Tampa, FL, 2Florida A &M University, Tallahassee, FL, 3University of Tampa, Tampa, FL, 4University of South Florida, Tampa, FL, 5Morsani College of Medicine, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 224
Keywords: Adverse effects, Kidney transplantation
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » 35 - Kidney: Cardiovascular and Metabolic Complications
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney: Cardiovascular and Metabolic Complications II
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Monday, June 6, 2022
Session Time: 3:30pm-5:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:50pm-5:00pm
Presentation Time: 4:50pm-5:00pm
Location: Hynes Veterans Auditorium
*Purpose: Midodrine is an alpha-1 agonist drug commonly used to aid hypotension in kidney transplant patients. Little is described regarding outcomes with midodrine in kidney transplant patients. The purpose of this study was to determine any difference in outcomes for kidney transplant patients on midodrine. We also evaluated outcomes based on the timing of midodrine administration i.e., pre-transplant (Pre-TX), interdialytically (Inter-dial,) or post-transplant (Post-TX).
*Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study of consecutive adult (age 18 or older) kidney transplant recipients at a single center from January 2015 to December 2020.
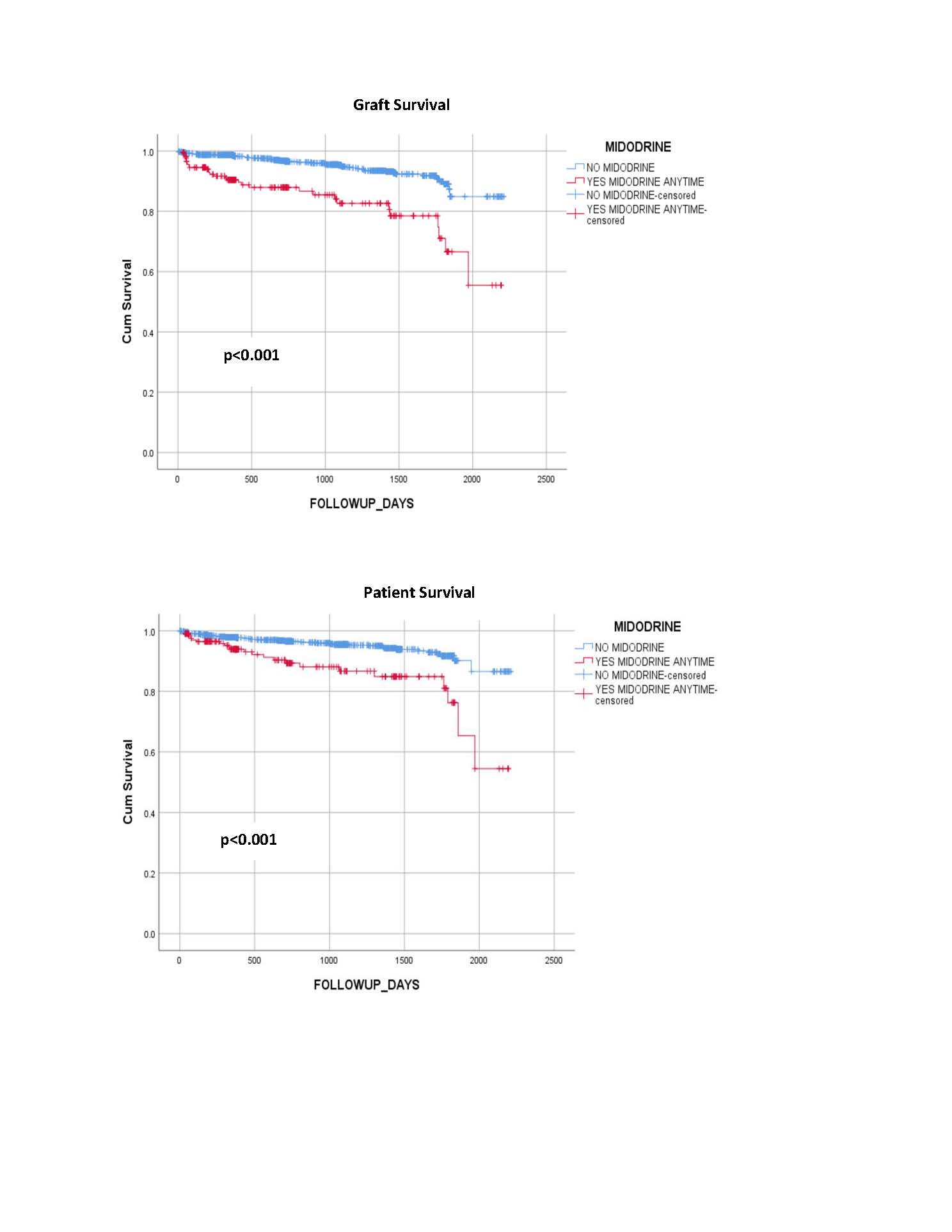
*Results: Of the 1,702 adult patients transplanted during the study period, 210 received midodrine. The two groups were similar in years of age (midodrine 53 vs 52 no midodrine p=0.493) and race (69% or 145 of 210 were White and received midodrine vs 73% or 1082/1492 were White and did not receive midodrine, p=0.141). There was overlap with the timing of midodrine administration with 84 Pre-TX, 53 Inter-dial, and 127 Post-TX. For all midodrine dosing times, the one-month discharge systolic blood pressure (mmHg) remained lower (PRE-TX 124 vs 140, p<0.001, Inter-dial 128 vs 140, p<0.001, and POST-TX 128 vs 140, p<0.001).The six-month diastolic blood pressure remained lower for all midodrine doses (PRE-TX 73 vs 76, p=0.009, Inter-dial 71 vs 76, p=0.001 and POST-TX 73 vs 76, p=0.001). The mean length of stay (days) was longer for all midodrine dosing times (PRE-TX 12 vs 7, p=0.003, Inter-dial 11 vs 7, p=0.118 and POST-TX 11 vs 7, p=0.001). Graft survival days (1684 vs 2068, p<0.001) and patient survival days (1793 vs 2080, p<0.001) were statistically less with midodrine. There was no difference in graft survival (p=.359) or patient survival (p=.539) when comparing the three dosing times for midodrine.
*Conclusions: In conclusion, the use of midodrine in dialysis patients receiving kidney transplantation is a marker for decreased blood pressure, a longer length of stay, and worse graft and patient survival. There was no difference in graft or patient survival based on the timing of the midodrine administration. This information should be considered in the listing and management of transplant patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Watson R, Mullins S, Williams S, Fakhre F, Robichaux K, Mohammed S, Gosselin M, Kumar A, Buggs J, Bowers V. Outcome Predictors with Perioperative Kidney Transplant Midodrine Usage [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/outcome-predictors-with-perioperative-kidney-transplant-midodrine-usage/. Accessed March 6, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress