Outcome of Induction Therapies in Low Sensitized Renal Transplant Recipients with Two HLA DR Mismatch in Tacrolimus Era
1Medicine, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC, 2Medicine, Cairo University, Cairo, Egypt, 3Medicine, Royal Stoke, Royal Stoke, United Kingdom
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A-006
Keywords: HLA antigens, Induction therapy, Outcome, Panel reactive antibodies
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Kidney Immunosuppression: Induction Therapy
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: A mismatch for two HLA DR antigens portends high immunological risk in renal transplant recipients (RTRs). Induction therapies with both rabbit Anti-thymocyte Globulin (r-ATG) and IL-2 Receptor Antagonist (IL-2RA) have resulted in marked reduction of acute allograft rejection rates and improved graft survivals. Nevertheless, the relative value of induction therapies in low sensitized RTRs with 2HLA-DR antigen mismatch in the era of tacrolimus-mycophenolate mofetil maintenance immunosuppression remains insufficiently understood.
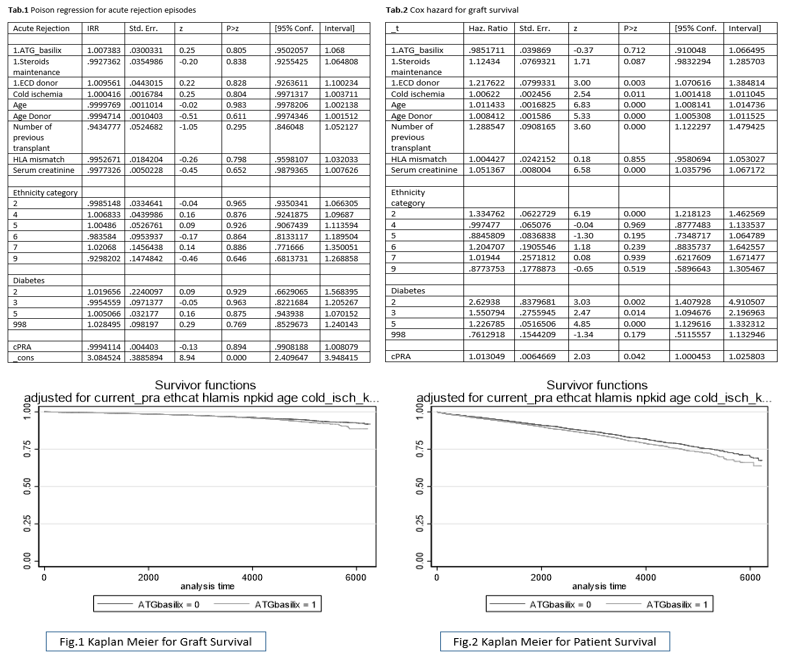
*Methods: Using data from the United States Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network, all low sensitized (PRA <20%) RTRs with 2HLA-DR antigen mismatch who were maintained on tacrolimus and mycophenolate mofetil immunotherapy between 2000 and 2017 were retrospectively reviewed. Data including age, sex, gender, ethnicity, functional status, diabetes, body mass index, cold ischemia time, number of previous transplants, panel reactive antibodies, donor type, donor age, HLA-mismatches, number of acute rejection episodes, induction therapies, maintenance immunotherapy, recipients and graft survival were collected. Based on induction therapies administered, RTRs were divided into 2 groups: r-ATG and IL-2RA groups. Poisson regression analysis was used to assess effect of induction therapies on acute rejection episodes (Tab.1). For survival analysis, estimates were adjusted to zero values of specified variables. Cox hazard regression analysis for adjusted data was used to assess effect of different induction therapies on patient and graft survival.
*Results: Out of 7,056 patients, 3,379 received IL2-RA while 3,677 received r-ATG for induction. There were no significant differences between both groups in terms of early post-operative acute rejection episodes (OR 1.00; 95% CI: 0.95 – 1.068, P=0.805), graft survival (OR 0.98, 95% CI: 0.91 – 1.06, P=0.712) or patient survival (OR 1.03, 95% CI: -0.949 – 1.12, P=0.43). Adjusted Kaplan Meier curves for graft and patient survivals were similar (Fig. 1, 2).
*Conclusions: This study revealed no significant difference in patient and graft survival when utilizing r-ATG vs IL-2RA in low sensitized (PRA<20%) RTRs with 2HLA-DR mismatch in the tacrolimus-based maintenance immunosuppression era. Therefore, IL2-RA is a safe non-inferior alternative to r-ATG induction therapy in this group of patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Soliman K, Fulop T, Osman A, Ali H. Outcome of Induction Therapies in Low Sensitized Renal Transplant Recipients with Two HLA DR Mismatch in Tacrolimus Era [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/outcome-of-induction-therapies-in-low-sensitized-renal-transplant-recipients-with-two-hla-dr-mismatch-in-tacrolimus-era/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress