Original KDRI Predicts Kidney Graft Failure in a Brazilian Cohort.
1Kidney Transplant Unit, Hospital das Clínicas, University of São Paulo School of Medicine, São Paulo, SP, Brazil
2Psychobiology Department, Universidade Federal de São Paulo, São Paulo, SP, Brazil
3Renal Transplant Unit, Hospital das Clinicas of the University of Sao Paulo Medical School, São Paulo, SP, Brazil.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B192
Keywords: Donors, Graft failure, Kidney transplantation, marginal, Risk factors
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Kidney Transplantation: KDPI, HCV/Matching, Donor Age
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 12, 2016
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Halls C&D
Current US allocation system for kidney transplantation (KT) is based on KDRI (Kidney Donor Risk Index). In Brazil, it is still based on HLA-compatibility; donor characterization is restricted to the dichotomy of standard (SCD) or expanded criteria donor (ECD). This study aimed to analyze KDRI power to predict graft failure in a brazilian population. All 1224 deceased donor KT in the 2005-2014 period in a single center were considered. Exclusion criteria: recipient's age <18 years, multiorgan transplant, missing/invalid donor height or weight and previous KT. Final analysis included 942 patients; mean follow-up time was 1093 days (±910). Recipient's mean age was 50 years (±12.8), 52.4% male, 26.5% black, 20.6% diabetic nephropathy, 25.9% sensitized, 15.7% vascular access failure; mean dialysis time was 54.2 months (±44). Donor's mean age was 46.4 years (±130), of which 31.3% were ECD, and stroke was the cause of death in 59.8%. There were no cardiac-death, HCV+ donors, double nor en-bloc kidneys. Median KDRI was 1.31 (higher then in Rao study, 1,05); 6.2% of patients were in the original 1st “quintile” (KDRI <0.79) and 35.7% in the 5th “quintile” (KDRI>1.45). ECD and SCD kidneys distribution through KDRI ranges demonstrated that some ECD kidneys have reasonably good estimated quality likewise as SCD kidneys. A crude Cox regression was performed with all KDRI compounding (plus recipient) factors and adjusted Cox regression proved to be independently associated with graft failure: stroke as cause of death (HR 1.24, CI95% 1.03-1.38), DR-MM (HR 1.22, 1.03-1.43) and donor age (for each year: HR 1.02, 1.01-1.03). Extreme quintiles graft survival in 5 years were significant different (Log Rank, p<0.05) 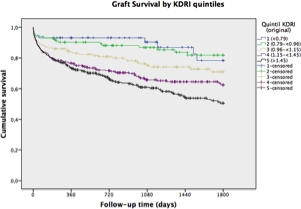 . KDRI ability to discriminate graft loss summarized in C-statistics 0.62 (CI95% 0.59-0.66) was very similar to the original study (0.60). In conclusion, the development of our own donor risk index based in our population might be the future for allocation and a helpful tool in kidney acceptance decision making.
. KDRI ability to discriminate graft loss summarized in C-statistics 0.62 (CI95% 0.59-0.66) was very similar to the original study (0.60). In conclusion, the development of our own donor risk index based in our population might be the future for allocation and a helpful tool in kidney acceptance decision making.
CITATION INFORMATION: Reusing Jr. J, Nihei C, Lino de Souza A, David-Neto E, Ventura C. Original KDRI Predicts Kidney Graft Failure in a Brazilian Cohort. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jr JReusing, Nihei C, Souza ALinode, David-Neto E, Ventura C. Original KDRI Predicts Kidney Graft Failure in a Brazilian Cohort. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/original-kdri-predicts-kidney-graft-failure-in-a-brazilian-cohort/. Accessed March 14, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
