Novel Role of Qa-1, a Murine Homolog of HLA-E, in Controlling Follicular Helper T Cells During Humoral Alloimmunity
1Medicine, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA, 2Immunology, Dana Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, MA
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 611
Keywords: Alloantibodies, Major histocompatibility complex (MHC), Mice, knockout, Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Lymphocyte Biology: Signaling, Co-Stimulation, Regulation
Session Type: Oral Abstract Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:45pm
 Presentation Time: 3:27pm-3:39pm
Presentation Time: 3:27pm-3:39pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) is a major challenge in prolonging allograft survival. Limited insight into the humoral alloimmunity hinders the development of therapeutic strategies. We showed that a non-classical MHC called Qa-1 (HLA-E in human) is highly expressed on follicular helper T cells (TFH) during rejection. Qa-1 transduces dichotomous signaling on regulatory CD8 T cells (CD8 Treg) by binding either 1) T cell receptor (TCR) that activates, or 2) NKG2A receptor that inhibits CD8 Treg lytic function. Using transgenic mice B6.Qa-1D227K (D227K), which harbor a mutation that specifically inhibits binding of Qa-1 to CD8 TCR, we showed the critical role of CD8 Treg in controlling TFH and AMR.
*Methods: BALB/c heart allografts were transplanted into B6 (WT) or D227K recipients with either single- or multiple-doses of CTLA4-Ig for mechanistic and survival analysis. For mechanistic, recipients’ spleens, serum and allografts were analyzed for immunophenotype, donor-specific antibody (DSA) and histopathology. Tconv (CD25+CD4+) isolated from either WT or D227K and CD8 Treg (CD44+CXCR5+CD8+) from naive WT were either 1) co-cultured with stimulation, or 2) adoptively trasnferred to RAG1-/- hosts, for in vitro and in vivo suppression assay.
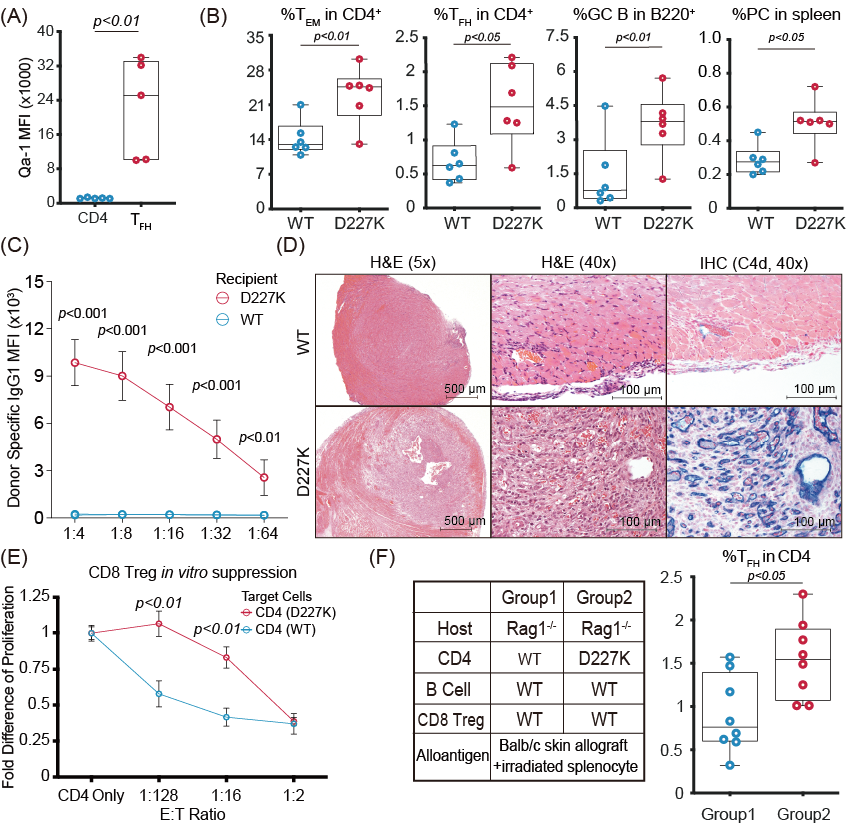
*Results: We showed that Qa-1 is highly upregulated on TFH compared to whole CD4+T cells (18.5-fold, P<0.001) [Fig. (A)]. D227K recipients showed increased frequency of TFH, isotype-switched B cells and plasmacytes compared to WT recipients (fold difference: 2.0, 2.5, 2.2 and P<0.05, 0.01, 0.05, respectively) [Fig. (B)]. These findings were associated with 11-fold higher DSA in D227K compared to WT (P<0.001) [Fig. (C)]. Allografts from D227K showed severe structural damage, vessel injury and strong C4d deposition, in contrast to allografts from WT [Fig. (D)]. Tolerance induction was abrogated in D227K recipients (allograft survival: 25 days vs 98 days, D227K vs WT respectively, P<0.001). Finally, CD4+ T cells isolated from WT but not D227K were sensitive to killing by CD8 Treg in vivo [Fig. (E)] and in vitro [Fig. (F)].
*Conclusions: We showed that 1) disrupting the CD8 Treg function unleashes TFH leading to severe AMR, while 2) killing of activated CD4+ T cells and TFH by CD8 Treg is Qa-1-dependent both in vivo and in vitro. We will extend theses findings by specifically inhibiting the Qa-1-NKG2A receptor interaction to enhance killing of TFH by CD8 Treg, thus protecting allografts from AMR.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Choi JY, Eskandari SK, Cai S, Assaker J, Sulkaj I, Allos H, Alhaddad J, Chu P, Kim H, Cantor HI, Azzi JR. Novel Role of Qa-1, a Murine Homolog of HLA-E, in Controlling Follicular Helper T Cells During Humoral Alloimmunity [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/novel-role-of-qa-1-a-murine-homolog-of-hla-e-in-controlling-follicular-helper-t-cells-during-humoral-alloimmunity/. Accessed February 27, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress