Novel Personalized Immune-Monitoring Assay for Predicting Operational Tolerance by Using Humanized Mouse Model.
Y. Fukasaku,1 R. Goto,1 Y. Ganchiku,1 M. Zaitsu,1 M. Watanabe,1 N. Kawamura,1 Y. Koshizuka,1 K. Yamashita,2 T. Shimamura,3 A. Taketomi.1
1Gastroenterological Surgery I, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan
2Transplant Surgery, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan
3Division of Organ Transplantation, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 86
Keywords: Immunosuppression, Living-related liver donors, Tolerance
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Predicting Tolerance and Rejection
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, April 30, 2017
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:18pm-3:30pm
Presentation Time: 3:18pm-3:30pm
Location: E351
Background: Biomarkers and immune-monitoring assays predicting operational tolerance in transplant recipients have not been established. Our aim was to develop an immune-monitoring assay to address tailoring immunosuppression (IS) of transplant recipients who can be weaned off IS. Methods: 2.5×106 hu-PBMCs were injected intraperitoneally into NSG mice. Hu-PBMCs were obtained from humanized mice 21 days after reconstitution. The allo-reactivity by MLR and lymphocyte population were evaluated before and after reconstitution. Results: In healthy volunteers (n=5), the percentages of hu-CD3+ T cells were significantly increased after reconstitution (59.2±3.0 to 86.5±3.1%, mean±SEM, P<0.01). In particular, CD45RA–CD62Llo effector memory T cells were predominantly reconstituted (CD4+; 25.5±6.6 to 55.8±4.6%, P<0.05, CD8; 8.6±2.0 to 30.1±4.3 %, P<0.01). Consequently, the allo-reactivities (Stimulation index) were boosted after reconstitution (Fig.1a).The similar trends of both reconstituted cell populations and the allo-reactivities were observed in hu-PBMCs from living donor liver transplant recipients. Of note donor-hyporesponsiveness of hu-PBMCs from the recipients who achieved operational tolerance, were maintained after reconstitution (n=4, Fig.1b). Meanwhile the reactivities to donor and 3rd party antigens of hu-PBMCs from the recipients treated with IS, differed after reconstitutionamong individuals (n=6, Fig.1b).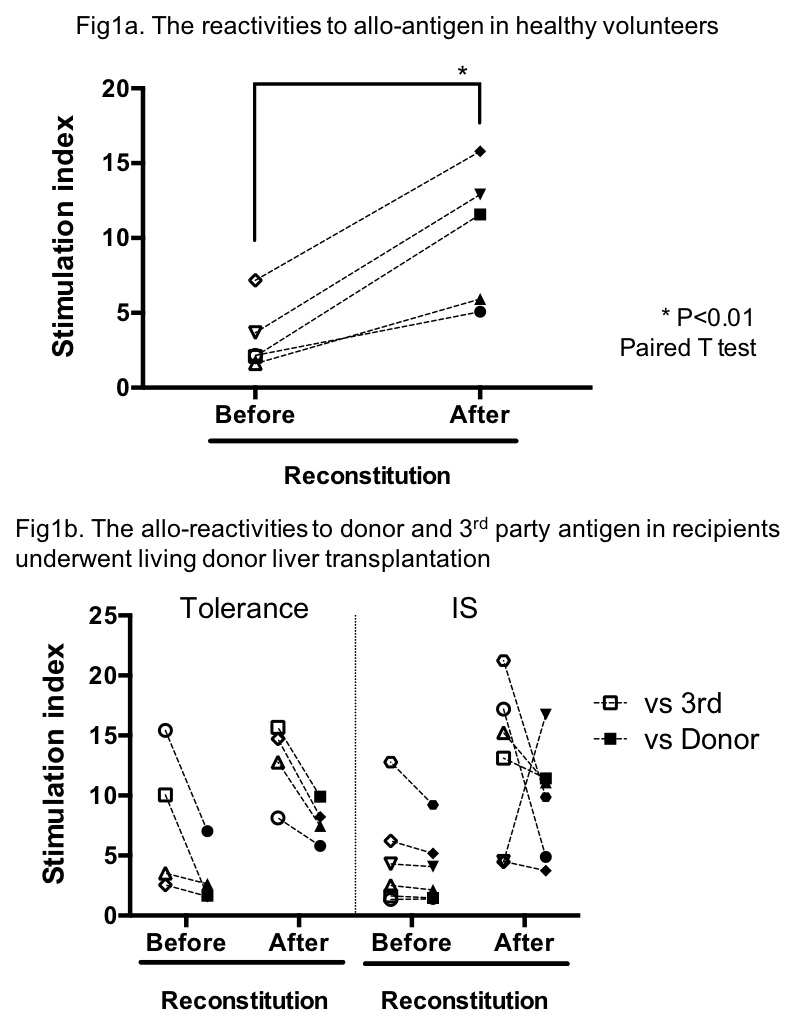 As hu-PBMCs in humanized mice for 21 days possibly mimic the completely weaned off IS status, it is probable that the cases in whom donor-hyporesponsiveness retained after reconstitution being similar to operational tolerant cases, may wean off IS in clinical settings. Conclusion:A novel immune-monitoring assay exploring the capability of immune response to alloantigens without IS in humanized mice, may be used to identify recipients who have successfullyachieved operational tolerance.
As hu-PBMCs in humanized mice for 21 days possibly mimic the completely weaned off IS status, it is probable that the cases in whom donor-hyporesponsiveness retained after reconstitution being similar to operational tolerant cases, may wean off IS in clinical settings. Conclusion:A novel immune-monitoring assay exploring the capability of immune response to alloantigens without IS in humanized mice, may be used to identify recipients who have successfullyachieved operational tolerance.
CITATION INFORMATION: Fukasaku Y, Goto R, Ganchiku Y, Zaitsu M, Watanabe M, Kawamura N, Koshizuka Y, Yamashita K, Shimamura T, Taketomi A. Novel Personalized Immune-Monitoring Assay for Predicting Operational Tolerance by Using Humanized Mouse Model. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fukasaku Y, Goto R, Ganchiku Y, Zaitsu M, Watanabe M, Kawamura N, Koshizuka Y, Yamashita K, Shimamura T, Taketomi A. Novel Personalized Immune-Monitoring Assay for Predicting Operational Tolerance by Using Humanized Mouse Model. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/novel-personalized-immune-monitoring-assay-for-predicting-operational-tolerance-by-using-humanized-mouse-model/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
