Nivolumab After Sorafenib Failure in Liver Recipients with HCC Recurrence
Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea, Republic of
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1100
Keywords: Malignancy, Outcome, Rejection
Topic: Clinical Science » Liver » 56 - Liver: Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Other Malignancies
Session Information
Session Name: Liver: Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Other Malignancies
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Sunday, June 5, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
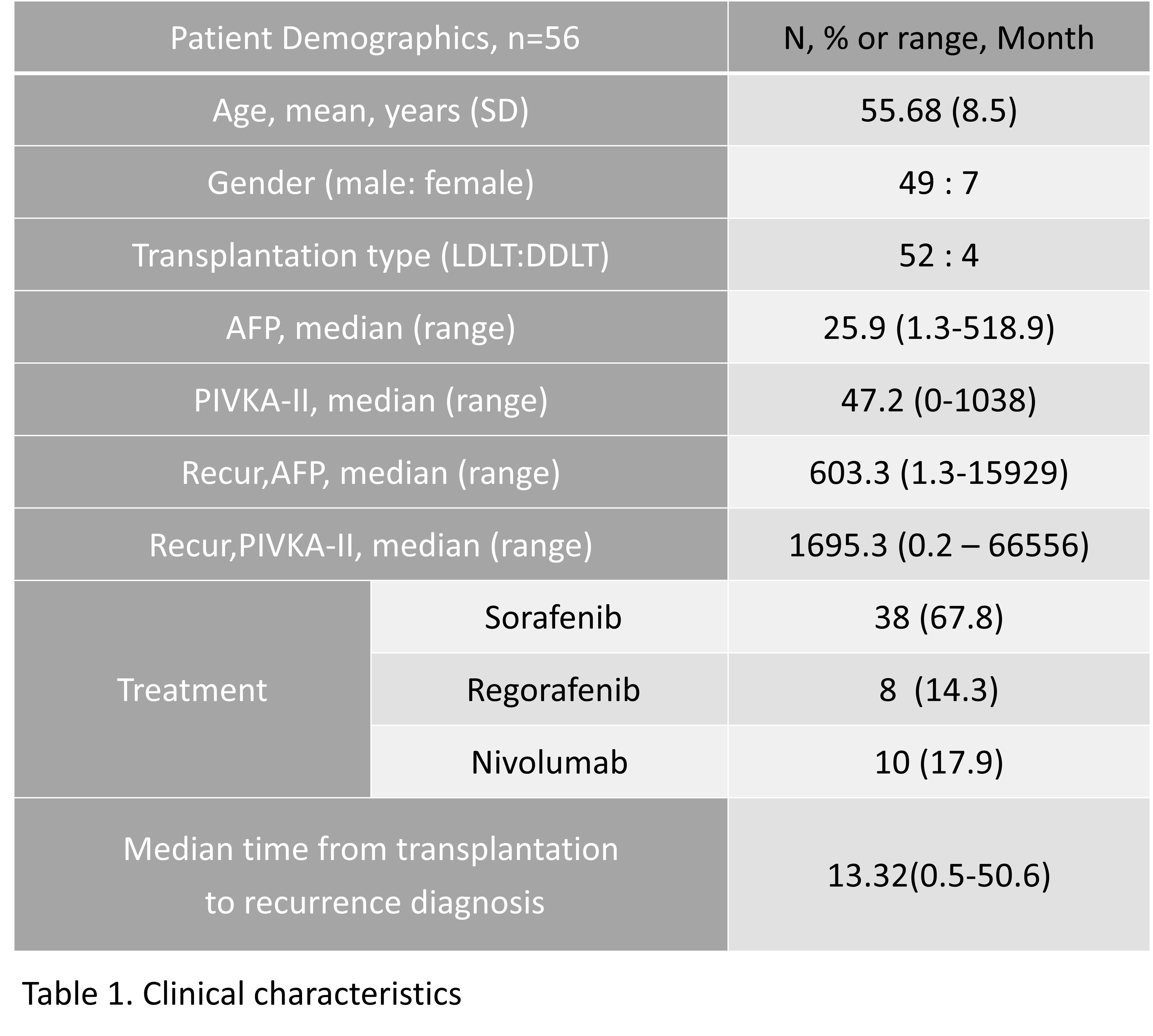
*Purpose: Several treatments have recently been known for hepatocellcular carcinoma (HCC) who have failed to treat sorafenib. Immune checkpoint inhibitors have proven to be effective, but data on the safety and efficacy of liver transplant recipients are limited. We aimed to report the effect of nivolumab after failure of sorafenib treatment in patients with recurrent HCC after liver transplantation.
*Methods: This study retrospectively evaluated patients who failed sorafenib for recurrent HCC treatment after liver transplantation in a single center from March 2007 to December 2018. Patients with recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation who received regorafenib or nivolumab after sorafenib treatment failure were included.
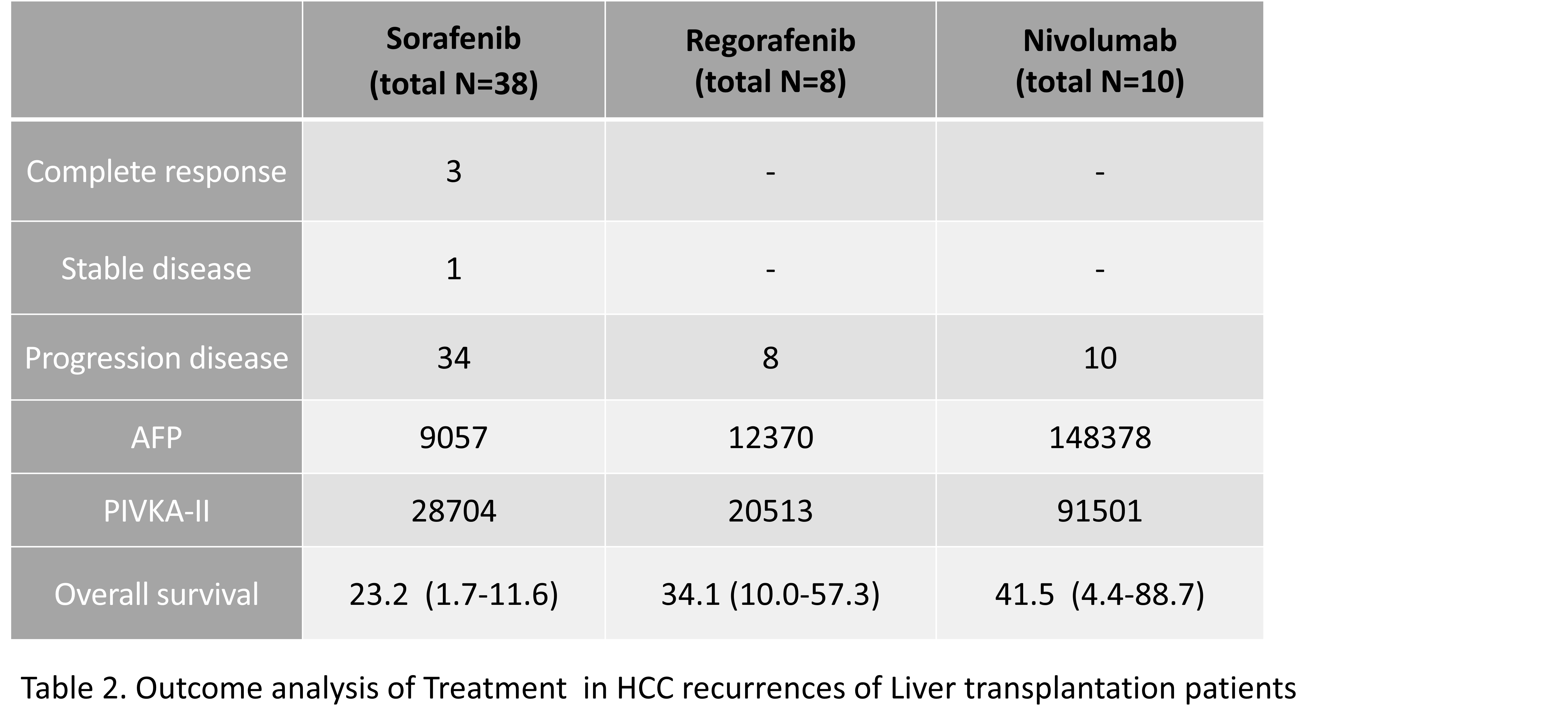
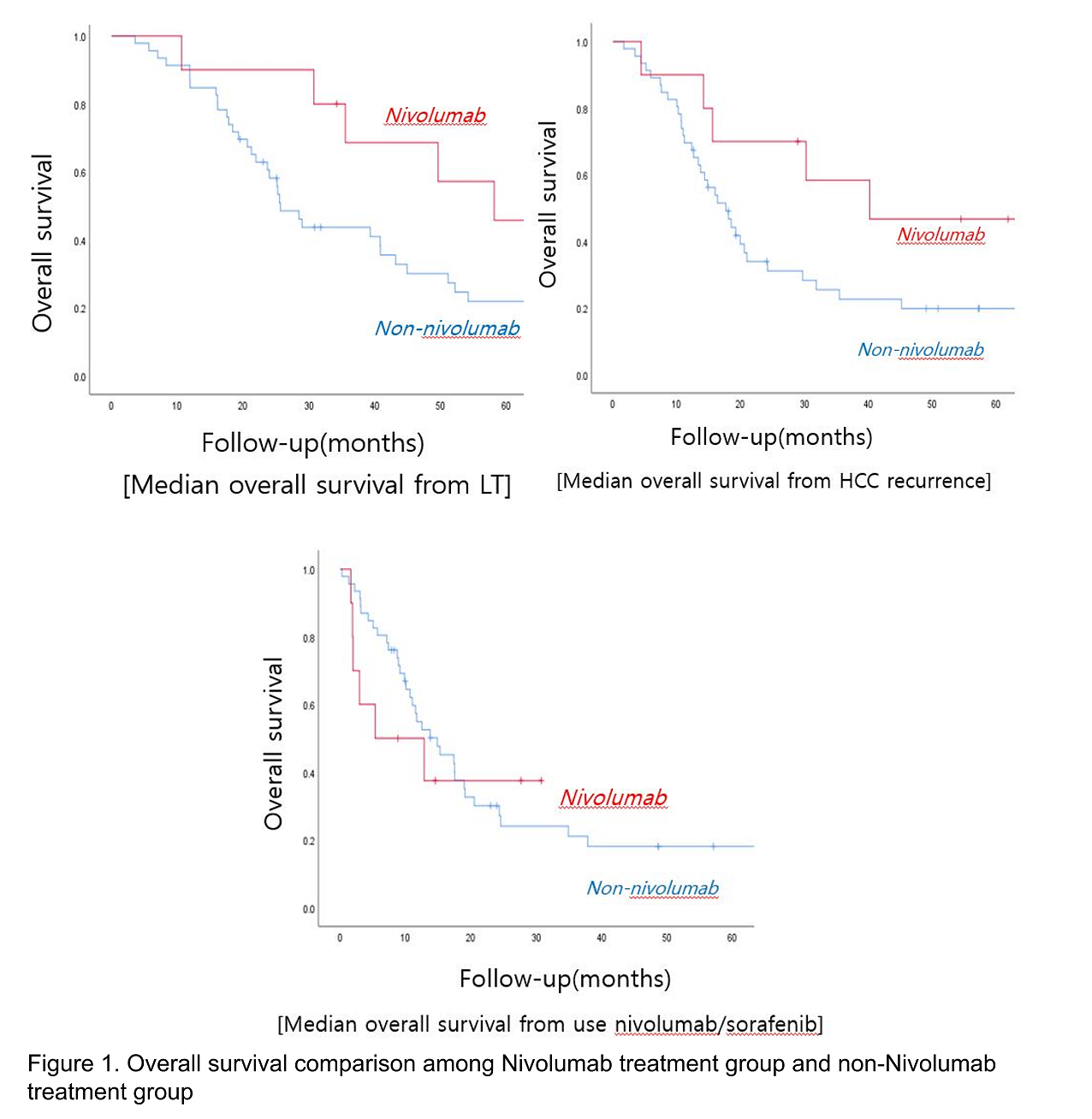
*Results: Of the 53 study patients, 8 received regorafenib and 10 received nivolumab. (Table 1) The median OS was 17.7 (95% confidence interval [CI], 13.1-22.2) months in the non-nivolumab group and 40 (95% CI, 7.6-72.8) months in the nivolumab group(P = 0.143 by log rank test). (Table 2)There were no significant differences between groups. The mean duration of nivolumab was 5.3 months (interquartile range, 0.8-6.3 months). All 10 patients receiving nivolumab failed to control HCC progression and 6 patients (60%) died during a median follow-up period of 2.4 months (interquartile range, 1.8-7.2 months) from the onset of nivolumab. (Figure 1) All of these deaths were caused by cancer progression, which can be attributed to transplant failure due to acute rejection.
*Conclusions: When administering nivolumab in liver transplant patients, it is important to be aware of the risk of cancer progression and rejection. The use of ICI in transplant patients remains challenging with current strategies and more research is needed to modulate immunosuppressants and prevent transplant rejection.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kwon J. Nivolumab After Sorafenib Failure in Liver Recipients with HCC Recurrence [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/nivolumab-after-sorafenib-failure-in-liver-recipients-with-hcc-recurrence/. Accessed March 11, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress