New Factors Predicting Delayed Graft Function: A Multi-Center Cohort Study Based on Kidney Donation after Brain Death Followed by Circulatory Death
1The Third Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
2The First Affiliated Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun, China
3The Third Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, China.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D130
Keywords: Donation, Graft function, Kidney transplantation, Risk factors
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Kidney Donor Selection / Management Issues
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, June 5, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Background. Delayed graft function (DGF) is a common complication following kidney transplantation that exerts an adverse impact on graft outcomes. Donation after brain death followed by circulatory death (DBCD), a novel donation pattern, is supposed to correlate with high incidence of DGF. However, little information is available about factors associated with DGF in DBCD.
Methods. 383 kidney transplants from DBCD donation in three institutions were enrolled. The associations of DGF with clinical characteristics of recipients and donors were quantified.
Results. The incidence of DGF in this study was 19.3%. Lower incidence of DGF was found in recipients using ATG as induction (8.6% for ATG vs 53.3% for anti- interleukin-2 receptor antibody, P<0.05), which was an independent protective factor for DGF (odds ratio [OR]=0.48; 95% CI 0.27-0.86). Two novel explicative variables were recognized as independent risk factors of DGF, including using vasoactive drugs (OR=3.15; 95% CI 1.39-7.14) and cardio- pulmonary resuscitation (OR =2.51; 95% CI 1.05- 5.99), which contributed significantly to higher risk of DGF(P<0.05). Prolonged warm ischemia time(>18 minutes) (OR =2.42; 95% CI 1.36-4.32), was also of predicted value for DGF in DBCD. A predicted model of DGF was developed based on the identified four factors, and achieved an area under the receiver operating curve of 0.89 when combined with current DGF prediction parameters.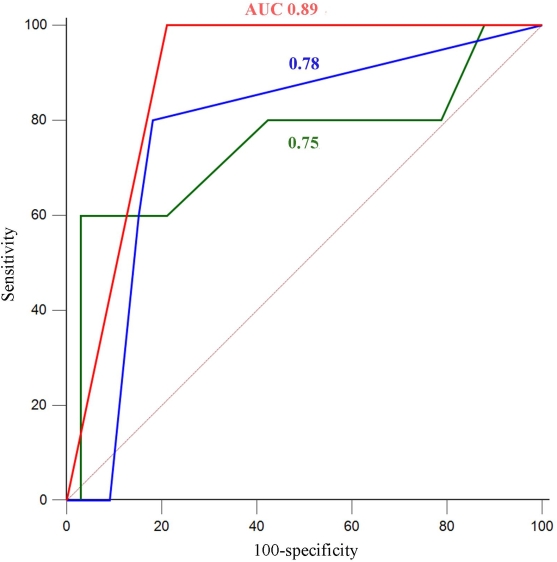
Conclusions. The novel factors, confirmed first in our study, will help to improve risk prediction of DGF and to determine optimal interventions to prevent DGF in clinical practice.
CITATION INFORMATION: Sun Q., Zhou H., Lin M., Hua X., Hong L., Huang Z., Na N., Cai R., Wang G., Sun Q. New Factors Predicting Delayed Graft Function: A Multi-Center Cohort Study Based on Kidney Donation after Brain Death Followed by Circulatory Death Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sun Q, Zhou H, Lin M, Hua X, Hong L, Huang Z, Na N, Cai R, Wang G, Sun Q. New Factors Predicting Delayed Graft Function: A Multi-Center Cohort Study Based on Kidney Donation after Brain Death Followed by Circulatory Death [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/new-factors-predicting-delayed-graft-function-a-multi-center-cohort-study-based-on-kidney-donation-after-brain-death-followed-by-circulatory-death/. Accessed March 12, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
