New Everolimus Administration Targeting the Prevention of the Development of Antibody-Mediated Rejection Considering the Comparison of Growth and Survival in IgG and IgM Memory B Cells
1Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine, Suita, Japan, 2Fujita Health University, Toyoake, Japan
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B-106
Keywords: B cells, Immunosuppression, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Kidney Immunosuppression: Novel Regimens and Drug Minimization
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Some reports indicated that immunoglobulin (Ig) M antibodies corresponding to donor-specific antigen in addition to IgG antibodies are closely involved in the activation of humoral immunity against transplanted grafts.Therefore, it is expected that immunosuppression targeting both donor antigen-specific IgG and IgM memory B cell (mBC) survival and growth will play important roles in the prevention of antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) development.
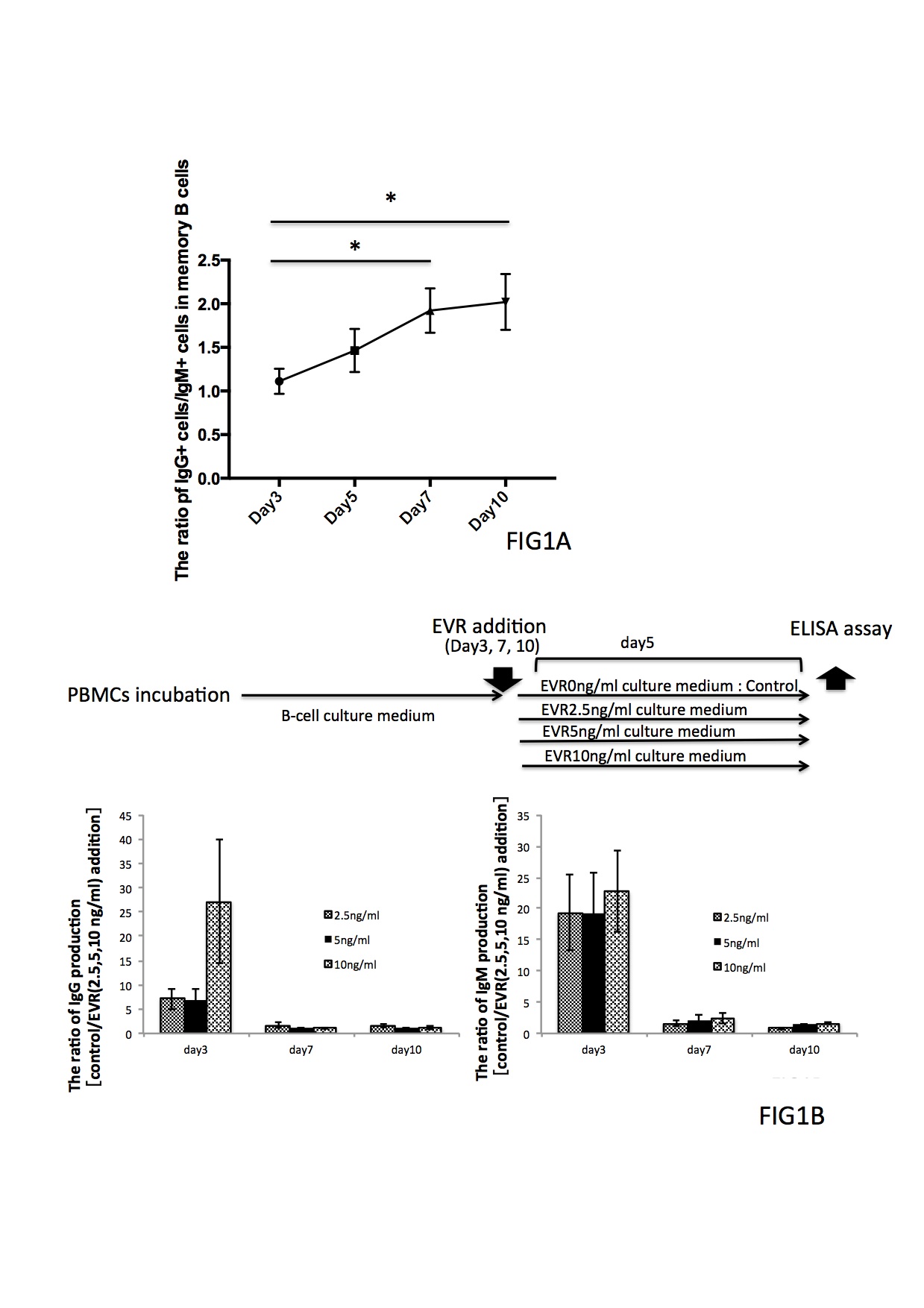
*Methods: mBCs were separated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells obtained from healthy donors (n = 5) via negative selection and incubated with IL-21, IL-4, CpG-ODN, CD40 ligand, PHA-L, and PMA containing AffiniPure F(ab’)2 Fragment Goat Anti-Human IgM, Fc5μ fragment-specific or AffiniPure F(ab’)₂ Fragment Goat Anti-Human IgG, and F(ab’)₂ fragment specific for B cell receptor cross-linking in vitro. We compared the effects of everolimus (EVR; 2.5, 5, and 10 ng/mL) on IgM mBC survival, proliferation, and differentiation into plasma cell and IgG in vitro.Additionally, change in the ratio of IgG-/IgM-positive mBCs during culture and addition time during which IgG/IgM antibody production is more efficiently suppressed were examined.
*Results: EVR inhibited IgM mBC survival, proliferation, and differentiation into IgM-producing plasma cells more strongly compared with IgG in vitro findings.In addition, the ratio of IgG-/IgM-positive cells in mBCs were remarkably increased from day 3 to day 7 of in vitro culture (Fig1-A).EVR (2.5, 5, or 10 ng/ml) addition on day 3 of incubation, as opposed to day 7 or day 10, considerably suppressed both IgG and IgM antibody productions compared with EVR (0 ng/ml) addition (Fig1-B).
*Conclusions: Class switching of IgM in mBCs has been reported to be induced by the reduction of immunosuppression or activation of antigen-antibody reaction in vivo. Therefore, our findings indicate that compared with conventional administration, EVR administration before or immediately after transplantation might prevent AMR development more efficiently.However, differences in the EVR susceptibility for IgM/IgG mBC growth and survival under in vitro and in vivo conditions should be further examined in a larger cohort.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Matsuda Y, Imamura R, Tezuka H, Takahara S. New Everolimus Administration Targeting the Prevention of the Development of Antibody-Mediated Rejection Considering the Comparison of Growth and Survival in IgG and IgM Memory B Cells [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/new-everolimus-administration-targeting-the-prevention-of-the-development-of-antibody-mediated-rejection-considering-the-comparison-of-growth-and-survival-in-igg-and-igm-memory-b-cells/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress