National Landscape of the Utilization of Living Donor Liver Allografts in Redo Liver Transplantation
Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 869
Keywords: Liver transplantation, Living donor, Organ Selection/Allocation, Retransplantation
Topic: Clinical Science » Liver » 55 - Liver: Recipient Selection
Session Information
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: To examine the use of living donor liver allografts in patient’s requiring redo liver transplantation.
*Methods: Using data from SRTR 2009-2020, we evaluated the number of living donor liver allografts used in re-do liver transplants (RLT) and the number of transplant centers performing living donor RLTs. Characteristics of living and deceased donor RLT recipients were compared using Chi-square and Wilcoxon rank-sum tests, as appropriate. Cox proportional hazards models were used to compare post-transplant mortality and all-cause graft failure between living and deceased donor RLT recipients.
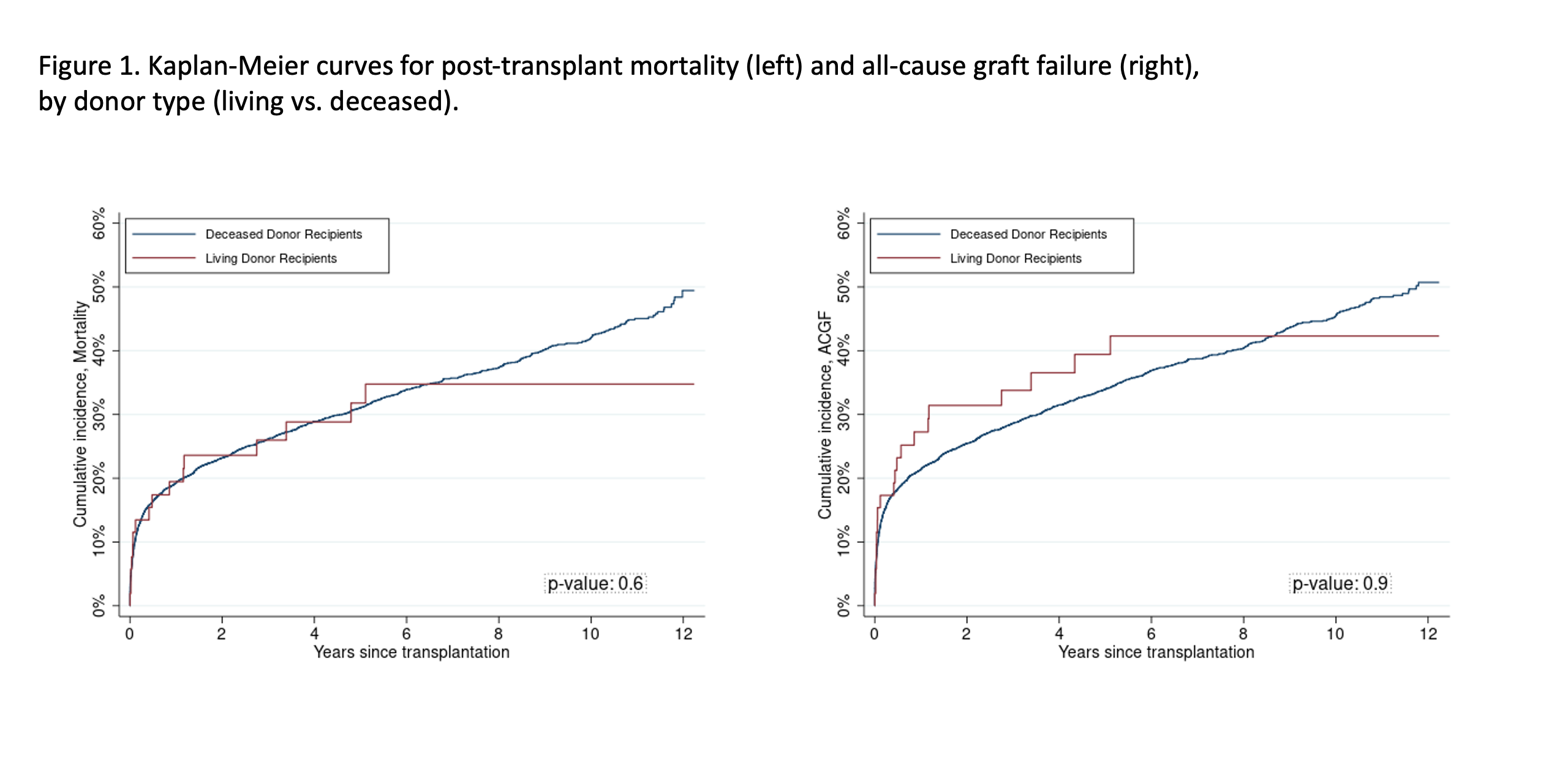
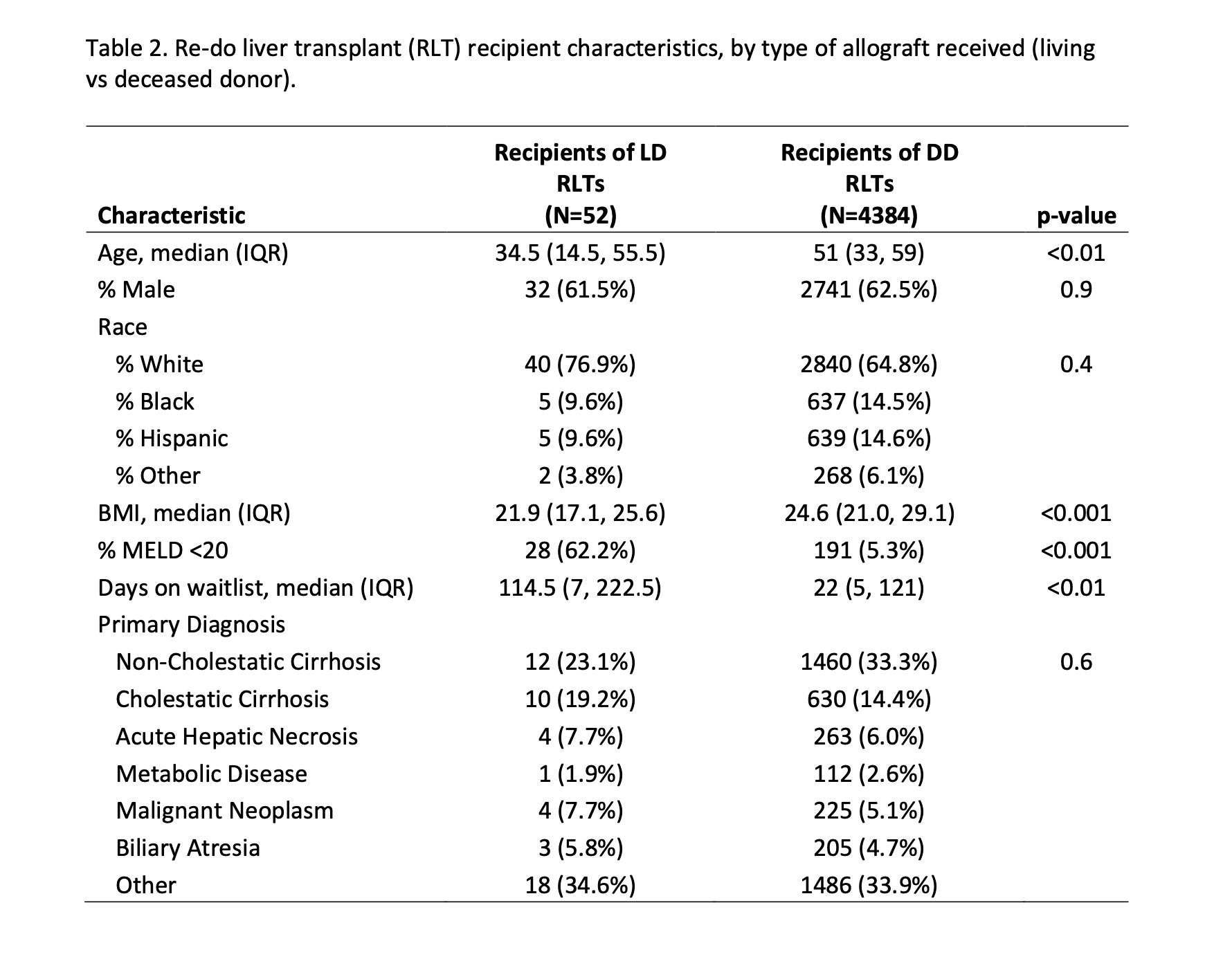
*Results: Between 2009 and 2020, 4,436 RLTs were performed in the United States, of which 1.2% (n=52) utilized allografts from living donors. During that time, an average of 4.3 (SD= 1.8) living donor liver allografts were utilized for RLT each year. An average of 3.6 transplant centers performed living donor RLTs per year during the study period. Compared to recipients of deceased donor RLTs, recipients of living donor RLTs more often had a MELD <20 (62.2% vs 5.3%, p<0.001), spent more days on the waitlist (Median [IQR] 114.5 [7, 222.5] vs 22 [5, 121], p<0.01) and had a lower BMI (Median [IQR] 21.9 [17.1, 25.6] vs 24.6 [21.0, 29.1], p<0.001). There were no differences in primary diagnosis between living and deceased donor recipients. No differences were observed in patient or graft survival between living and deceased donor recipients (HR, Mortality: 1.05(0.67, 1.63); HR, ACGF: 0.88(0.54, 1.44)).
*Conclusions: Our findings suggest that using living donor liver allografts in re-do transplantation is an uncommon practice in the United States. Further investigation into the clinical context in which living donor allografts can be successfully used for candidates requiring re-do liver transplants is necessary to help future decision-making when accepting organs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
López JI, Nijhar K, Mitchell J, Zeiser LBowles, Key K, Asamoah-Mensah A, Thomas A, Haneda R, Romano SK, Huang J, Massie A, Cameron AM, Segev DL, King EA. National Landscape of the Utilization of Living Donor Liver Allografts in Redo Liver Transplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/national-landscape-of-the-utilization-of-living-donor-liver-allografts-in-redo-liver-transplantation/. Accessed February 24, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress