Multicenter Banff Fibrosis Trial: Comparing Visual Assessment of Interstitial Fibrosis in Kidney Biopsies to Computer-Based Image Analysis and Organ Function, The
Emory University, Atlanta
University of Alberta, Edmonton, Canada
Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston
Meeting: 2013 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C1318
Interstitial fibrosis (IF) in renal biopsies is a valuable correlate for organ function, provides prognostic information and is a potential end point in trials.
From 15 allograft and 15 native kidney biopsies sections were stained with trichrome, PAS, and Collagen III immunohistochemistry; and virtual microscopy scans were prepared for scoring. Trichrome, PAS, and Collagen III slides were assessed by 27 pathologists for the extent of interstitial inflammation (ti) and IF following two different definitions (figure 1): (A) the % cortex surface occupied with fibrous tissue, analogous to a computer-based image analysis. (B) the % cortex which has abnormal fibrosis. Reproducibility was assessed using kappa statistics. The results were correlated with image analysis of collagen III and to organ function (GFR).
Using the trichrome stain, better correlations with the image analysis results were obtained using approach B, i.e. estimating the % abnormal cortex (Table 1). Identical correlations were seen for visual assessment of collagen III using approach A. A stronger inverse association between IF and GFR was seen with the trichrome stain compared to the PAS stain, using either A or B methods, but similar to how image analysis correlated with function. Tubular atrophy and the Banff total i-score correlated less well with the collagen III stain and GFR. Independent of the approach and the stain, reproducibility between observers for assessing IF was weak (kappa <0.25).
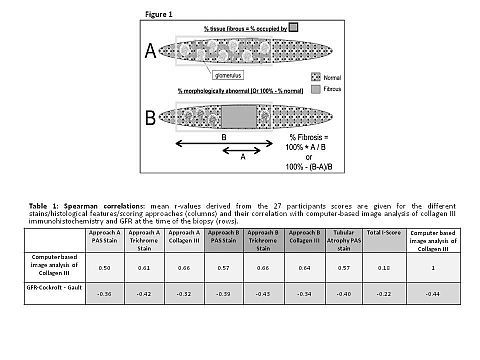
These results indicated that trichrome and collagen III stains are similar but superior to the PAS stain in assessing IF. Visual assessment of IF in trichrome or collagen III stains correlates with organ function as well as computer-based image analysis. However, significant variability between observers, even with the same stained images, argues that computer based image analysis might be a more robust approach for standardized IF assessment in renal biopsies.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Farris A, Chan S, Climenhaga J, Colvin R, Mengel M. Multicenter Banff Fibrosis Trial: Comparing Visual Assessment of Interstitial Fibrosis in Kidney Biopsies to Computer-Based Image Analysis and Organ Function, The [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13 (suppl 5). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/multicenter-banff-fibrosis-trial-comparing-visual-assessment-of-interstitial-fibrosis-in-kidney-biopsies-to-computer-based-image-analysis-and-organ-function-the/. Accessed July 9, 2025.« Back to 2013 American Transplant Congress
