Modern Medicine Needs Modern Technology Tools
Ochsner Foundation Hospital, New Orleans, LA
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1670
Keywords: Biopsy, Kidney, Outcome, Rejection
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » 34 - Kidney: Acute Cellular Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney: Acute Cellular Rejection
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Tuesday, June 7, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: Dd-cfDNA has been used as a non-invasive biomarker for allograft injury and has been shown to detect subclinical rejection with higher predictive power compare to serum creatinine level. Here, we show the value of dd-cfDNA in detecting early allograft rejection while other indicators showed stable allograft function.
*Methods: Ochsner uses AlloSure for a surveillance for the high-risk patients.
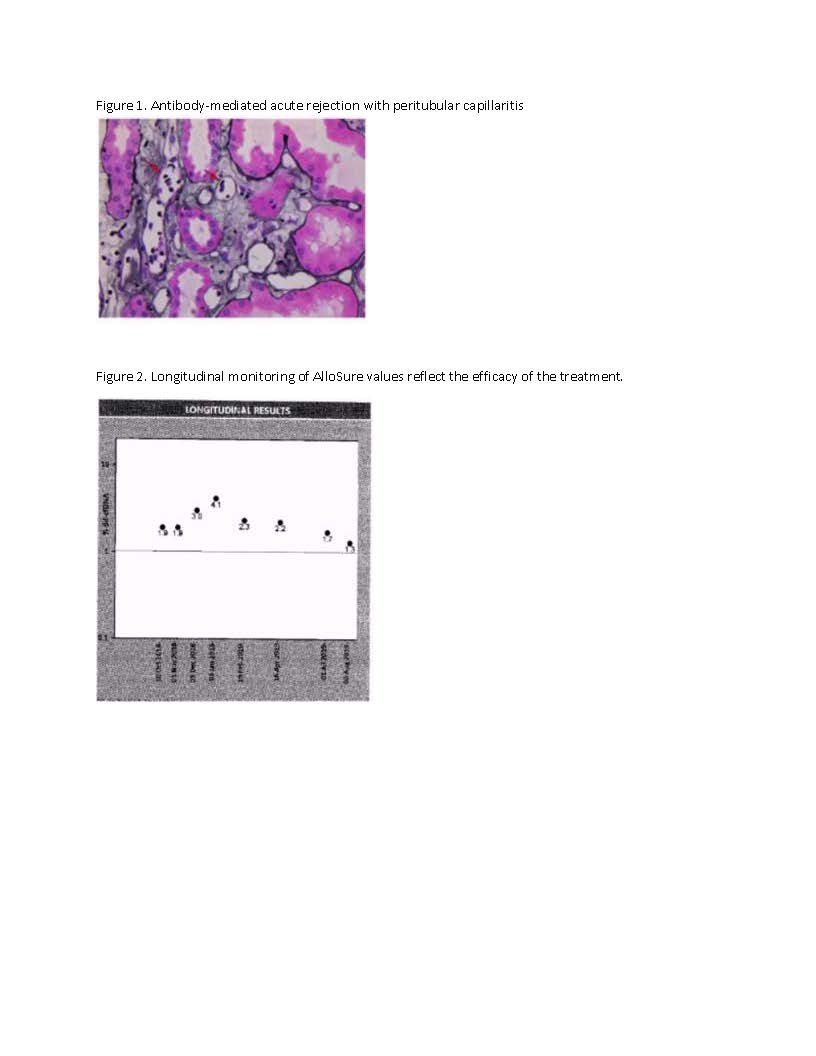
*Results: Thirty-two years old Caucasian female with ESRD secondary to HIV infection underwent deceased-donor renal transplant. Serum creatinine level had been stable at 1.1mg/dL to 1.2mg/dL post-transplant. This patient was monitored using AlloSure for 1-,2-,3-,4-,6- and 9-month post-transplant. AlloSure values for month 1 to 6 were <0.21, which indicates stable allograft function. However, at 9-month post-transplant, AlloSure value went up to 4.5%, which indicates possible allograft injury, while serum creatinine level remained stable at 1.2 mg/dL with low level of class 2 DSA. Despite stable creatinine level and low level of DSA, we initiated biopsy because of sharp increase in AlloSure value. Biopsy revealed acute TCMR and acute vascular rejection. The second case is a 33 years-old Caucasian female with history of previous renal transplant. Serum creatinine level was stable at 1.0-1.3 mg/dL and AlloSure values in month 1 and 2 were < 0.21% and 0.32%, respectively. At month 3, AlloSure value went up to 0.78% with negative DSA. We initiated biopsy based on increase in AlloSure values and it revealed acute ABMR (Figure 1). The third case is a 56 years-old male with history of ESRD secondary to hypertension. He developed acute renal failure (Cr went up from 1.2 mg/dl to 1.7 mg/dL) few months after kidney transplant and his kidney biopsy showed acute ABMR and TCMR which were treated. He was placed on monthly AlloSure surveillance at 1-year post-transplant. The first AlloSure value was 1.9%, which indicates possible allograft injury. Monthly monitoring showed increase trend in AlloSure value up to 4.1% while Cr remained stable at 1.2 mg/dL-1.3 mg/dL. At that point, biopsy was performed, and it revealed acute ABMR and chronic active antibody rejection. Patient was treated for ABMR and monthly Tocilizumab for chronic active antibody mediated rejection for 6 months. AlloSure values reflected the efficacy of treatment with downward trending values (Figure 2).
*Conclusions: When other indicators are normal/stable, AlloSure was able to detect early rejection. All three cases demonstrated the value of AlloSure as a monitoring tool for detection of early allograft rejection.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Soltani ZS, Soltani S. Modern Medicine Needs Modern Technology Tools [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/modern-medicine-needs-modern-technology-tools/. Accessed March 14, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress