MicroRNAs and Long Non-Coding RNAs as Potential Novel Biomarkers in Transplanted Patients with Candida Infection.
1Organ Transplantation Center, The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat -sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
2Gastroenterology Unit, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA
3Ophthalmology, Schepens Research Institute, Boston, MA
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B106
Keywords: Fungal infection, Gene expression, Infection, Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Bacteria, Fungi, Parasites
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, April 30, 2017
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall D1
There is an urgent need to develop sensitive and specific biomarkers for the early diagnosis of candida infection in transplanted patients. miRNAs and lncRNAs are endogenous RNAs thought to be involved in human disease and development. Little is known about their value in it.
Several miRNAs and lncRNAs' expression levels were examined in the blood samples of both normal and candida infected transplanted patients by RT-PCR. Furthermore, we examined the correlations of miRNAs and lncRNAs' expression with some traditional clinical tests (e.g. number of white blood cells, neutrophil percentage,etc.). Additionally, principle component analysis (PCA) and K-mean clustering were adopted to examine if the miRNAs and lncRNAs can separate normal and infected transplanted patients based on their expression.
miR-let-7c and NR_036506.1 are over-expressed in infected patients and their expression levels have significantly negative correlation with white blood cells counting number and neutrophil percentage(p<0.05), but have positive correlation with monocyte percentage in patients with candida infection(p<0.05). miR-let-7c and NR_027669.1 expression exhibit positive correlations, while NR_027669.1 and miR-154 expression exhibit negative correlations in infected group. Finally, PCA analysis demonstrated the expression patterns of miRNAs and lncRNAs are different between normal and candida infected patients.
Our selected miRNAs and lncRNAs are likely contributors to the immune response to candida infection. miR-let-7c and NR_027669.1 may be involved in the same/relative pathway of immunoreaction, the same as NR_027669.1 and miR-154. These selected RNAs will set the stage for more extensive studies to develop novel diagnostic assays for early candida infected detection and will help to help to distinguish normal patients from candida infected patients, paving the way for clinical diagnostics.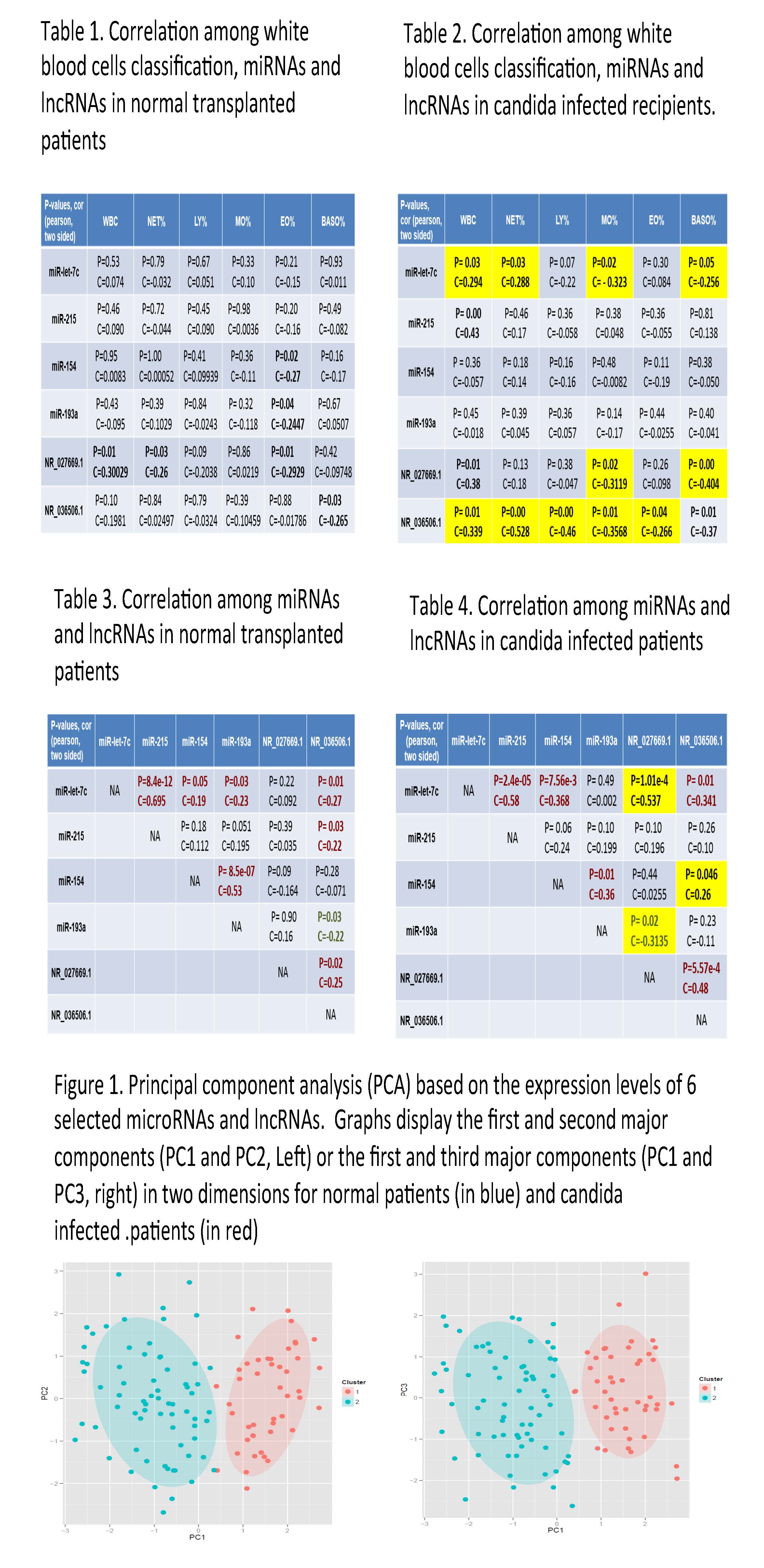
CITATION INFORMATION: Yang A, Zhou C, Li D, Ju W, Guo Z, Wu L, Hu A, Ma Y, Wang D, Zhu X, He X. MicroRNAs and Long Non-Coding RNAs as Potential Novel Biomarkers in Transplanted Patients with Candida Infection. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yang A, Zhou C, Li D, Ju W, Guo Z, Wu L, Hu A, Ma Y, Wang D, Zhu X, He X. MicroRNAs and Long Non-Coding RNAs as Potential Novel Biomarkers in Transplanted Patients with Candida Infection. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/micrornas-and-long-non-coding-rnas-as-potential-novel-biomarkers-in-transplanted-patients-with-candida-infection/. Accessed February 27, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
