MicroRNA-375 and -200c Are a Set of Novel Biomarkers That Can Predict Islet Autotransplantation Outcome.
1Islet Cell Laboratory, Baylor Research Institute, Dallas, TX
2Transplant Division, Department of Surgery, VCU Medical Center, Richmond, VA
3Baylor Simmons Transplant Institute, Dallas, TX.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A78
Keywords: Islets, Pancreatitis
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Clinical Pancreas Transplantation and All Islet Cell Transplantation Topics
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 11, 2016
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Halls C&D
Introduction: Total pancreatectomy with islet autotransplantation (TPIAT) is an effective treatment for refractive chronic pancreatitis to relieve pain and retain endocrine function. Patient selection is difficult in the absence of reliable markers that predict transplant outcome. Here we analyzed a set of microRNAs in circulation that can predict islet yield and endocrine function following TPIAT.
Methods: Thirty one TPIAT patients at our center with a follow up of >1y were analyzed. miR-7, miR-200a, miR-200c, miR-320 and miR-375 before were measured at admission. Plasma microRNAs and preoperative patient characteristics were analyzed to predict post-digestion islet count as isolation outcome, and exogenous insulin amount and C-peptide level as transplantation outcome with multivariate regression model. Results: Circulating miR-375, BMI and [Delta]C-peptide were correlated with post-digestion islet count in univariate analysis (p = 0.039, < 0.001 and = 0.007, respectively). MiR-200c, BMI and [Delta]C-peptide were significantly correlated with C-peptide level at one- year post-TPIAT (p = 0.0002, p = 0.006, p = 0.001, respectively). Moreover miR-200c, age, HbA1c, and [Delta]C-peptide were significantly correlated with exogenous insulin amount at one-year post-TPIAT in the univariate model (p < 0.001, = 0.049, < 0.001 and < 0.001, respectively).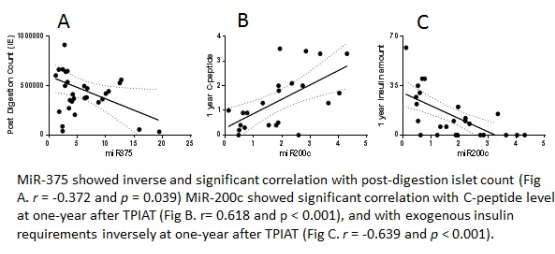
Conclusion: Circulating miR-200c and HbA1c were selected as independent predictors for insulin requirements one-year post-TPIAT after multivariate regression analysis (miR200c; t=-3.76, p=0.0011, HbA1c; t=3.53, p=0.0019, respectively. Adjusted R2=0.66). Preoperative circulating miR-375 was correlated with islet isolation outcome and miR-200c should be a novel biomarker to predict endocrine function post-TPIAT.
CITATION INFORMATION: Yoshimatsu G, Kanak M, Takita M, Prathab Balaji S, Chang C, Lawrence M, Levy M, Onaca N, Kim P, Naziruddin B. MicroRNA-375 and -200c Are a Set of Novel Biomarkers That Can Predict Islet Autotransplantation Outcome. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yoshimatsu G, Kanak M, Takita M, Balaji SPrathab, Chang C, Lawrence M, Levy M, Onaca N, Kim P, Naziruddin B. MicroRNA-375 and -200c Are a Set of Novel Biomarkers That Can Predict Islet Autotransplantation Outcome. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/microrna-375-and-200c-are-a-set-of-novel-biomarkers-that-can-predict-islet-autotransplantation-outcome/. Accessed February 26, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
