Low Dose Thymoglobulin Has No Disadvantages to Standard Higher Dose: A Report of the Midwest Pediatric Nephrology Consortium
1LSU Health, New Orleans, LA, 2Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Baton Rouge, LA, 3Children's National Medical Center, Washington, DC, 4Wayne State University, Detroit, MI, 5University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY, 6Nationwide Children's Hospital, Colombus, OH, 7University of Utah SOM, Salt Lake City, UT, 8Levine Children's Hospital, Charlotte, NC, 9University of Tennessee, Memphis, TN, 10Washington University, St. Louis, MO
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C218
Keywords: Immunosuppression, Induction therapy, Pediatric
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Kidney: Pediatrics
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 3, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: What is not known is whether a lower Thymoglobulin (ATG) induction dose provides safe and effective immunosuppression compared to a “standard” higher dose in pediatric kidney transplants.
*Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of all isolated first-time pediatric <21 year old kidney transplant recipients who received ATG induction between 1-1-2010 and 12-31-2014 at 9 Midwest pediatric nephrology consortium centers. We compared 24-month outcome measures of PTLD occurence, patient and graft survival, as well as 12-month outcome measures of graft function (eGFR), acute rejection, donor specific antibody (DSA), neutropenia, viral infections (CMV, EBV, BK virus) and body mass index (BMI) change over time across 2 ATG cumulative induction doses: standard =/> 7.5 mg/kg and low <7.5 mg/kg using logistic regression and survival analysis.
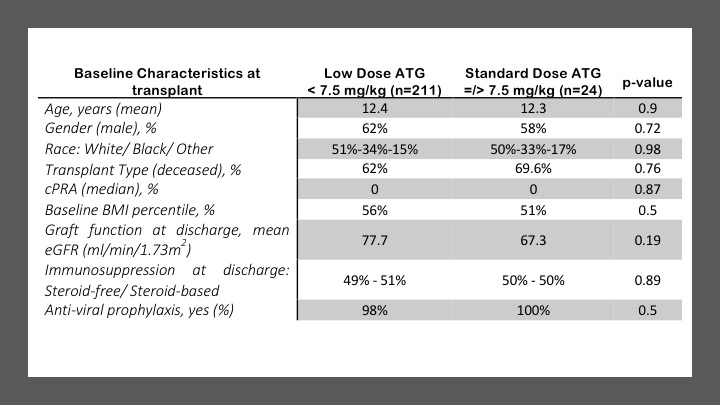
*Results: Two-hundred forty patients were included with data on cumulative ATG dose exposure available for 235 patients. Mean administered cumulative ATG dose (in mg/kg) was 5.4 +/- 1.6 (SD). This was lower than the intention-to-treat ATG dose of 6.4 +/- 1.4 mg/kg. Baseline features of the low and standard ATG dose groups are shown in Figure.
By 12 months, ATG dose group had no significant impact on the occurrence of neutropenia, positive DSA, or positive viral PCR for CMV, EBV, or BKV (p-values 0.86, 0.23, and 0.66 respectively). Graft function was similar with mean eGFR of 72 (low dose ATG) vs. 66 (standard dose ATG) ml/min/1.73m2, p-value 0.24. Higher ATG dose exposure was associated with significantly higher BMI% change from baseline by 12 mo (+21% vs. +8%, p-value 0.009). By 24 months, graft survival (97.5% vs. 97%) and occurrence of PTLD (1% vs. 0%) were similar between the low dose and standard dose ATG groups (p-values 0.8 and 0.4, respectively), however, the standard dose group had one death event (p-value 0.003) attributed to urosepsis.
*Conclusions: Lower ATG cumulative induction dose <7.5 mg/kg provided safe and effective outcomes in this multi-center pediatric kidney transplant cohort and was associated with significantly less BMI increase from baseline by 12 months.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ashoor I, Beyl R, Gupta C, Jain A, Kiessling S, Patel H, Sherbotie J, Jr DJWeaver, Zahr R, Dharnidharka V. Low Dose Thymoglobulin Has No Disadvantages to Standard Higher Dose: A Report of the Midwest Pediatric Nephrology Consortium [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/low-dose-thymoglobulin-has-no-disadvantages-to-standard-higher-dose-a-report-of-the-midwest-pediatric-nephrology-consortium/. Accessed March 6, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress