Long-Term Outcomes in Older Kidney Transplant Recipients from Older Donors
Nephrology and Kidney Transplantation, Hospital Clínic de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 838
Keywords: Elderly patients, Graft survival, Kidney, Kidney transplantation
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » Kidney Deceased Donor Selection
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney Deceased Donor Selection
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: The age of patients referred for kidney transplantation has increased progressively. However, the precise influence of age on hard outcomes after transplantation is controversial
*Methods: Single-centre, longitudinal retrospective study in which graft and recipient survival in a cohort of ≥75 years old kidney recipients were compared with a contemporary younger cohort aged 60-65 years.
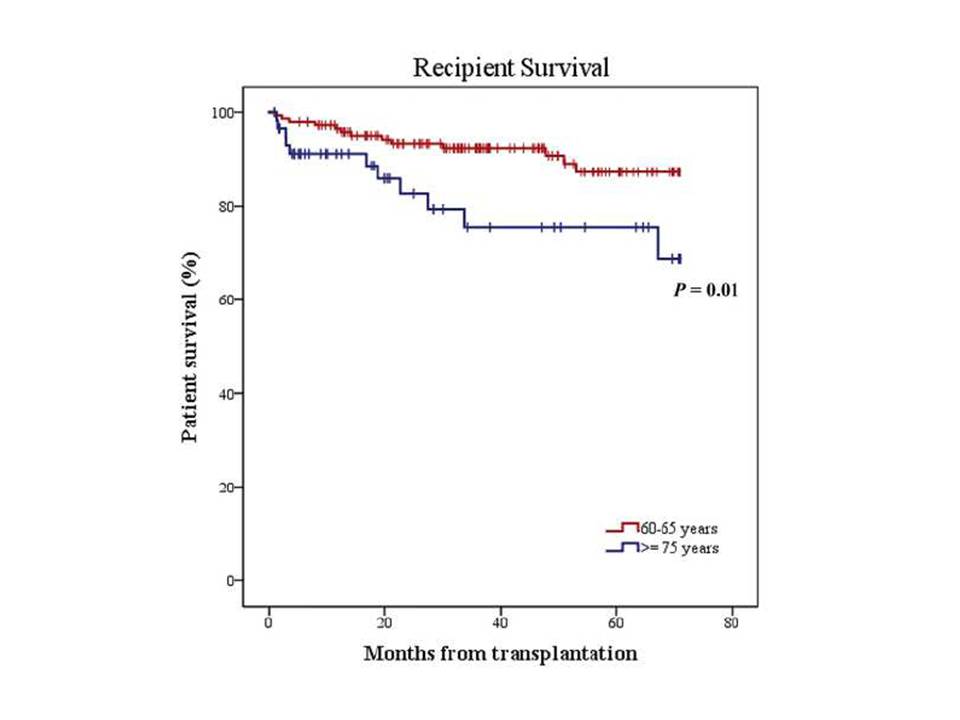
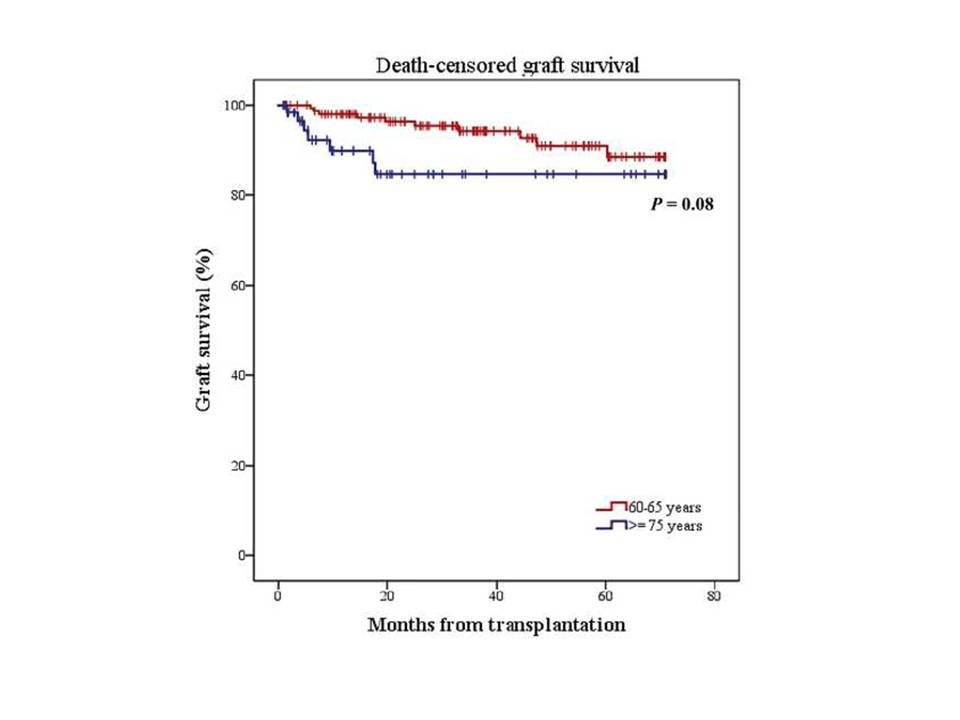
*Results: We included 149 recipients between 60-65 and 60 patients of ≥75 years old. No differences in baseline characteristics were observed except for the prevalence of diabetes mellitus (62 patients versus 9 patients respectively, p < 0.0001). One- and five-year recipient survival was lower in the older group (91% and 76% for the older and 96% and 87% for the younger group, P =0.01). In the multivariate analysis, recipient age was not associated with an increased risk of death. Donor after Circulatory Death (DCD), recipient Ischemic Heart Disease and Delayed Graft Function (DGF) were associated with an increased risk of death. One- and five-year death-censored graft survival did not significantly differ between both groups (90% and 85% for the older and 98% and 88% for the younger group, respectively, P =0.08). In the multivariate analysis age was no associated with graft loss (HR 2.84, 95%CI [0.77-8.12], P =0.09), although DGF was (HR 4.46, 95%CI [1.63-12.21], P =0.004). DCD donor (OR 2.88, 95%CI [1.07-7.78], P =0.03) and Deceased Donor Kidney Transplantation (OR 2.51, 95%CI [1.26-4.99], P =0.009) were risk factors for DGF.
*Conclusions: Recipient age should not be considered itself as an absolute contraindication for kidney transplant. With a judicious selection of the recipient and the donor, kidney transplantation can be safely performed in elderly patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cuadrado-Payán E, Montagud-Marrahi E, Casals-Urquiza J, Risco-Zevallos Jdel, Cucchiari D, Ventura-Aguiar P, Revuelta I, Piñeiro G, Esforzado N, Cofan F, Ugalde J, Campistol J, Oppenheimer F, Torregrosa J, Diekmann F. Long-Term Outcomes in Older Kidney Transplant Recipients from Older Donors [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/long-term-outcomes-in-older-kidney-transplant-recipients-from-older-donors/. Accessed March 11, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress