Long-Term Clinical Outcomes in ABO Incompatible Kidney Transplantation in Patients with High Baseline Anti-A/B Antibody Titer
1Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 2Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Incheon St. Mary's Hospital, Incheon, Korea, Republic of
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 801
Keywords: Graft survival, Isoantibodies, Kidney transplantation, Outcome
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » 39 - Kidney Living Donor: Long Term Outcomes
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney Living Donor: Long Term Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Saturday, June 4, 2022
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: ABO incompatible (ABOi) kidney transplantation (KT) has been considered to overcome donor shortage. We investigated the long-term clinical outcomes in ABOi KT in patients with high baseline anti-A/B antibody titer.
*Methods: We retrospectively included 260 patients who had undergone ABOi KT from May, 2009 to November, 2020. One hundred and eighty-one patients with a baseline immunoglobulin G (IgG) titer of ≥1:128 were assigned to the high-titer group and 79 patients with a baseline titer of ≤1:64 were assigned to the low-titer group. We used a protocol composed of rituximab, plasmapheresis, and intravenous immunoglobulin (RTX/PP/IVIG). We compared the clinical outcomes of the two groups.
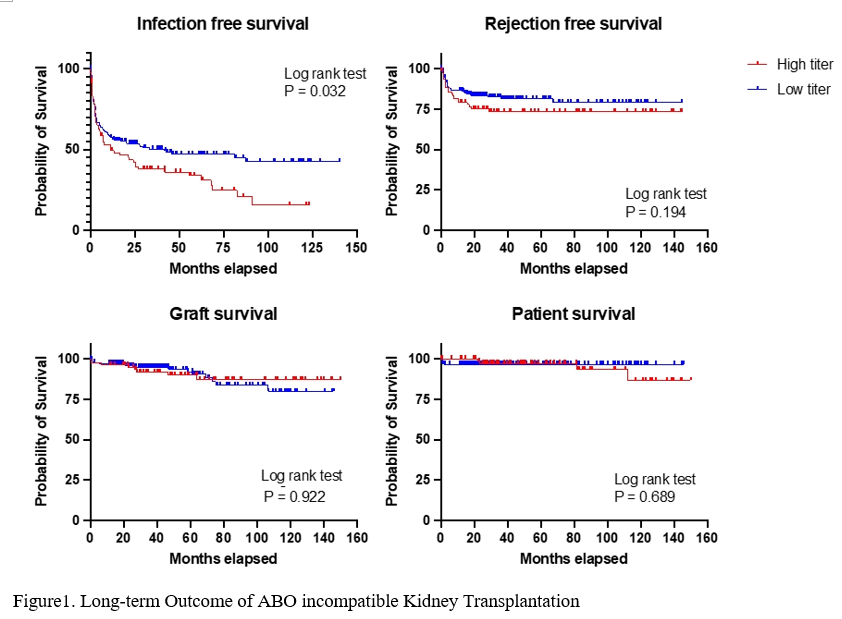
*Results: The median follow-up periods were 56.57 months (high-titer group) and 38.77 months (low-titer group) (p = 0.003). The high-titer group required more sessions of PP/IVIG than the low titer group (7.75±3.10, 3.59±1.91, p < 0.001, respectively). Patient survival at 5 years was 93.50% in high-titer and 96.70% in low-titer group (p = 0.689). Graft survival at 5 years was 87.20% in high-titer and 95.80% in low-titer group (p = 0.922). During the follow-up period to one year, antibody titer remained higher in the high-titer group. And serum creatinine showed no difference between two groups up to 6 years (p for interaction = 0.730). No significant differences were detected in the graft survival rate, patient survival rate and rejection-free survival rate between two groups. However, the infection-free survival rate was significantly lower in the high-titer group (p = 0.032). The incidence of bacterial infection was higher in high-titer group (46.84% vs. 27.07%, p = 0.002).
*Conclusions: Patients with high baseline anti-A/B IgG isoagglutinin titers had equally successful long-term outcomes as those with low titers. However, ABOi KT in the high-titer group may require greater caution compared to the low-titer group because of the higher tendency of infection.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Eum S, Lee H, Ko E, Yoon H, Shin S, Yang C, Chung B. Long-Term Clinical Outcomes in ABO Incompatible Kidney Transplantation in Patients with High Baseline Anti-A/B Antibody Titer [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/long-term-clinical-outcomes-in-abo-incompatible-kidney-transplantation-in-patients-with-high-baseline-anti-a-b-antibody-titer/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress