Lack of Drug-Drug Interaction between Maribavir and Voriconazole
I. H. Song1, K. Ilic2, J. Wu3
1Quantitative Clinical Pharmacology, Shire, a Takeda Company, Lexington, MA, 2Rare Disease TAU, Shire, a Takeda Company, Lexington, MA, 3Biostat, Shire, a Takeda Company, Lexington, MA
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A-176
Keywords: Cytomeglovirus, Drug interaction, Pharmacokinetics
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: All Infections (Excluding Kidney & Viral Hepatitis)
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Maribavir is being evaluated in Phase 3 trials for the treatment of cytomegalovirus infections in transplant recipients. These patients often take numerous concomitant medications, including the anti-fungal drug voriconazole. Therefore, potential drug interactions between maribavir and voriconazole, a cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2C19 substrate, were evaluated.
*Methods: In this Phase 1 study, healthy adult subjects received voriconazole 400 mg every 12 hours (q12h) on Day -5 and 200 mg q12h from Day -4 to Day 7; subjects were randomized to receive maribavir 400 mg or placebo (5:1 ratio) q12h from Day 1 to Day 7. Serial blood samples were collected on Days -1 and 7 to determine plasma concentrations of voriconazole and its major metabolite, voriconazole-N-oxide. Pharmacokinetic (PK) parameters for voriconazole and its metabolite were estimated using noncompartmental methods and compared between Day -1 (voriconazole alone) and Day 7 (voriconazole+maribavir) using ANOVA. Safety assessments included adverse events, physical examinations, ECGs, vital signs, and laboratory results.
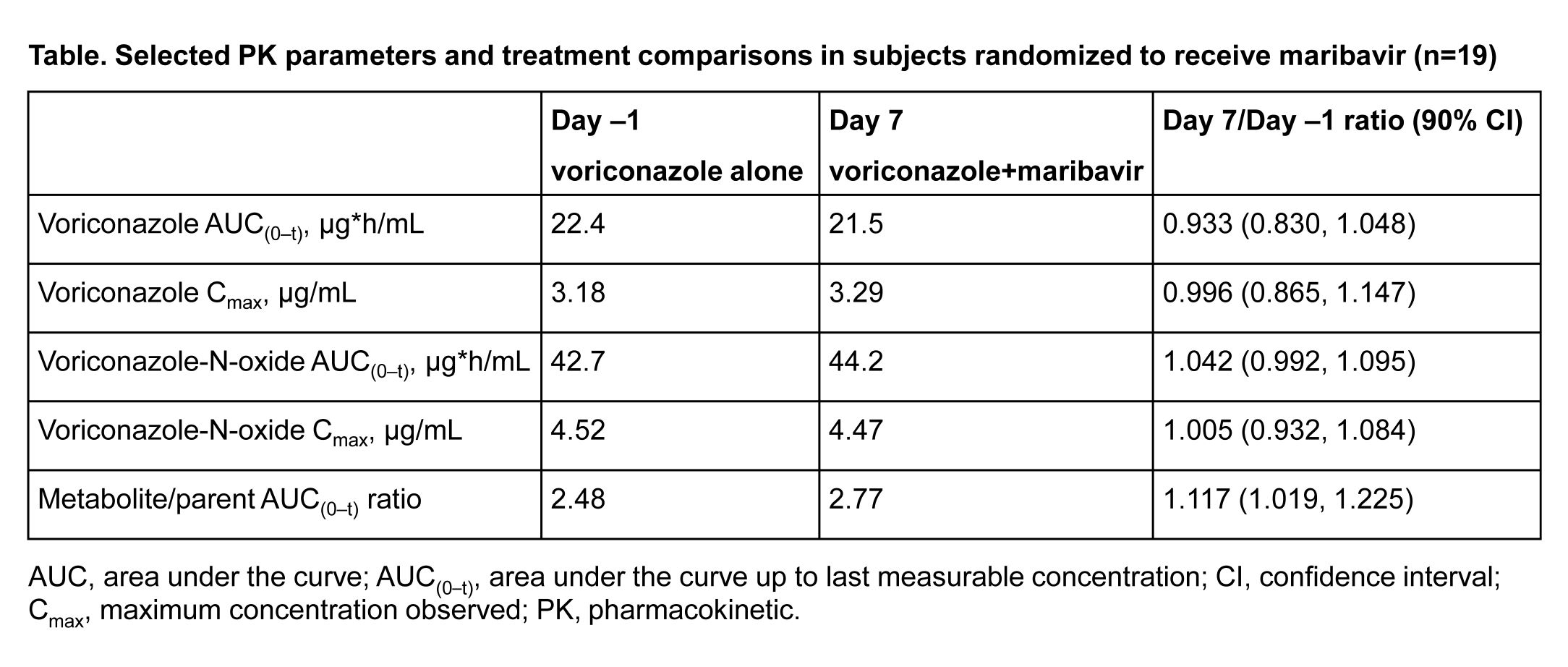
*Results: A total of 23 healthy subjects (52% male) completed the study: 19 subjects received maribavir and 4 received placebo. PK of voriconazole and its metabolite were not affected by maribavir (table). Oral maribavir 400 mg q12h was generally well tolerated when co-administered for 7 days with oral voriconazole 200 mg q12h. In subjects who received maribavir, dysgeusia was the most frequently reported treatment-emergent adverse event and occurred in 10 (53%) subjects.
*Conclusions: Co-administration of maribavir (400 mg q12h) had no effect on the PK of voriconazole or voriconazole-N-oxide. Maribavir and voriconazole can be safely co-administered at clinically relevant doses without adjustment. Using voriconazole-N-oxide/voriconazole area under the curve as an isozyme marker, repeated doses of maribavir did not change the activity of CYP2C19; therefore, maribavir is not likely to affect the PK of drugs that are substrates of CYP2C19.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Song IH, Ilic K, Wu J. Lack of Drug-Drug Interaction between Maribavir and Voriconazole [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/lack-of-drug-drug-interaction-between-maribavir-and-voriconazole/. Accessed February 19, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress