Kidney Transplantation from Uncontrolled Donation after Circulatory Death, Good Outcomes after Very Long Time
1Department of Nephrology, Hospital Universitario 12 de Octubre, Madrid, Spain
2Department of Nephrology, Hospital Evangelico, Montevideo, Uruguay.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D132
Keywords: Donors, Graft survival, non-heart-beating, Renal function
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Kidney Donor Selection / Management Issues
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, June 5, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Introduction: Kidney transplantation (KT) is the best renal replacement therapy but the shortage of organ is the main limitation. Uncontrolled Donation after Circulatory Death (uDCD) increases the available organs with similar outcomes than donors after brain death (DBD). The long-term outcome of uDCD compared to standard criteria donors after DBD KT is unknown.
Methods: We compared the long-term follow-up (10 y) of all uDCD KT procured since June 2005 to December 2013 (n=237) with a cohort of first KT of DBD performed between 2004 and 2014 (237) in the same institution. We review renal function, graft and recipient survival. We studied factors related with graft survival.
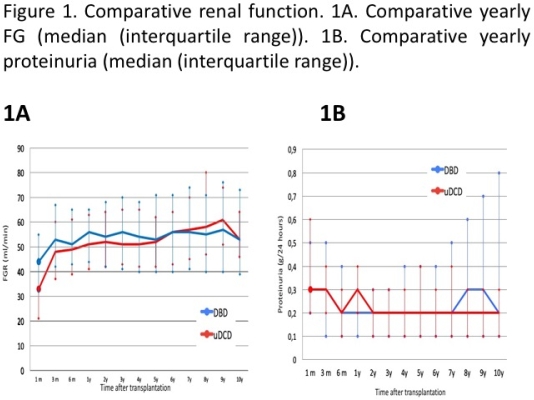
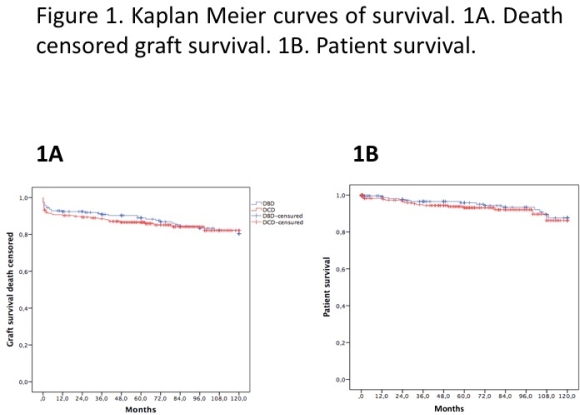
Results: Primary non-function was similar between both groups (uDCD 6.8% vs. 4.2%, p=0.16). Despite the higher delayed graft function (DGF) in uDCD (73.4% vs. 46.4%, p<0.01), renal function was similar between the two groups in the follow-up with exception the first six months (FG 51±17 ml/min vs 55±19 ml/min, p=0.04), Figure 1. Graft and recipient survival were equivalent in both groups after 10 years (82% vs. 80%, p=0.6 and 86% vs 88%, p=0.45, respectively), Figure 2. In multivariable analysis, proteinuria > 0.5 g/day after 3, 6 and 12 months (HR 5.1 CI 1.2-5.4, p<0.05) and GFR < 45 ml/min (HR 6.2 CI 1.8-21.5, p<0.05) had a deleterious impact in uDCD donors (HR 2.5 CI 1.01-6.3, p=0.04) while DGF had any impact (p>0.05).
Conclusions: KT from uDCD has similar renal function, graft and recipient survival than DBD after long-term of follow-up. Proteinuria and GFR are the main factors related with graft survival.
CITATION INFORMATION: Molina M., Cabrera J., Gonzalez E., Hernandez A., Natalia P., Andres A. Kidney Transplantation from Uncontrolled Donation after Circulatory Death, Good Outcomes after Very Long Time Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Molina M, Cabrera J, Gonzalez E, Hernandez A, Natalia P, Andres A. Kidney Transplantation from Uncontrolled Donation after Circulatory Death, Good Outcomes after Very Long Time [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/kidney-transplantation-from-uncontrolled-donation-after-circulatory-death-good-outcomes-after-very-long-time/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress