Kidney Transplant Recipient Adherence Measured by Proportion of Days Covered Is Associated with Late Biopsy Proven Acute Rejection.
UW Health, Madison, WI.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D306
Keywords: Biopsy, High-risk, Kidney transplantation, Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Late Breaking
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, June 14, 2016
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Halls C&D
While medication non-adherence is a known risk factor for late “biopsy proven acute rejection (BPAR),” the Pharmacy Quality Alliance definition of “proportion of days covered (PDC)” had not been examined as a tool to identify patients at risk for late BPAR.
This analysis combined transplant outcomes from the “UW (University of Wisconsin)” Transplant Database and pharmacy billing files from the UW Specialty Pharmacy Program. Patients included had a primary kidney transplant between 3/10/2006 and 6/30/2012 and 360 days of follow-up. Inclusion required at least 3 mycophenolic acid fills during the study period including one within 15 days before or after date of discharge and one within 100 days of the end of the study period to demonstrate persistence. Late BPAR is defined as BPAR occurring more than 90 days post-transplant. PDC is capped at 100% and calculated as percent of days medication was available during patient-specific 360-day period using time arrays adjusted prospectively for overlapping days supply and truncated at the end of the study period. Primary statistical analysis includes logistic regression.
A total of 387 patients met inclusion and exclusion criteria. The incidence of late BPAR in the cohort is 4.9% (19/387). Mean PDC is 91.9%, standard deviation 0.14 (Figure 1). 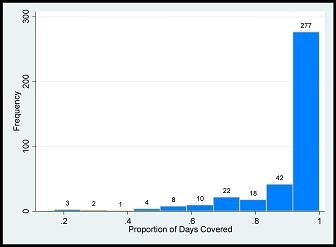 Higher PDC is associated with lesser odds of late BPAR (OR 0.03, p = 0.004) while higher number of readmissions is associated with greater odds of late BPAR (OR 1.46, p = 0.032) after adjusting for all covariates (Table 1).
Higher PDC is associated with lesser odds of late BPAR (OR 0.03, p = 0.004) while higher number of readmissions is associated with greater odds of late BPAR (OR 1.46, p = 0.032) after adjusting for all covariates (Table 1).
| Variable (comparator) | Odds ratio | p-value |
| Proportion of days covered | 0.03 | 0.004 |
| Age | 0.99 | 0.828 |
| Female (male) sex | 0.65 | 0.426 |
| Black (white) race | 1.17 | 0.848 |
| Other (white) race | 2.50 | 0.207 |
| Diabetes (other) kidney disease | 0.47 | 0.349 |
| Transplants number | 0.84 | 0.505 |
| Brain death (living) donor | 1.32 | 0.752 |
| Cardiac death (living) donor | 0.45 | 0.317 |
| Panel reactive antibody | 1.00 | 0.786 |
| Readmissions number | 1.46 | 0.032 |
PDC is significantly and strongly associated with late BPAR in this cohort despite a low incidence of late BPAR and a mean PDC exceeding a threshold of 90%.
CITATION INFORMATION: Hofmeyer B, Look K, Fose J, Pulvermacher A, Djamali A, Hager D. Kidney Transplant Recipient Adherence Measured by Proportion of Days Covered Is Associated with Late Biopsy Proven Acute Rejection. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hofmeyer B, Look K, Fose J, Pulvermacher A, Djamali A, Hager D. Kidney Transplant Recipient Adherence Measured by Proportion of Days Covered Is Associated with Late Biopsy Proven Acute Rejection. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/kidney-transplant-recipient-adherence-measured-by-proportion-of-days-covered-is-associated-with-late-biopsy-proven-acute-rejection/. Accessed March 5, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
