Kidney Transplant Outcomes in Recipients Older Than 70: A Single Center Experience
Indiana University Health, Indianapolis, IN.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B225
Keywords: Elderly patients, Graft survival, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Obesity/Elderly/Frail
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, May 3, 2015
Session Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Age is no longer considered a contraindication to renal transplantation. To date, little is known in regards to the grafts and patients outcomes in elderly (age≥70) population.
We retrospectively evaluated the graft and patient outcomes in 102 kidney transplant recipients older than 70 years who underwent kidney transplantation from 2001 to 2010.
Patients were divided into two groups, 70-74 and ≥75 years (G1 n=64 and G2 n=38). Categorical variables were analyzed using ANOVA and Chi-square tests. The 1, 3 and 5 years graft and patient survival between G2/G1 were evaluated using logistic regression analysis, and the effects of co-morbidities on outcomes were analyzed using Cox-regression.
During a median follow up period of 51 months (0-143) , 35 (34.7%) patients died.. Overall, graft survival at 1, 3, 5 years was 89%, 76.8%, and 60.8% respectively, while patient survival was in 90%, 78.9% and 60.8%. No statistically significant difference was observed between G2 and G1 groups in graft failure (P = 0.063, P = 0.283, P = 0.925) or death (P = 0.124, P = 0.695, P = 0.925) at 1, 3, 5 years respectively. G2 group (N=38) received more extended criteria kidneys (ECD) compared to G1 (15.8% vs 3.2%, p=0.023).
Patients who died with functioning graft mean survival was 32 months in G1 and 29 months in G2 group respectively.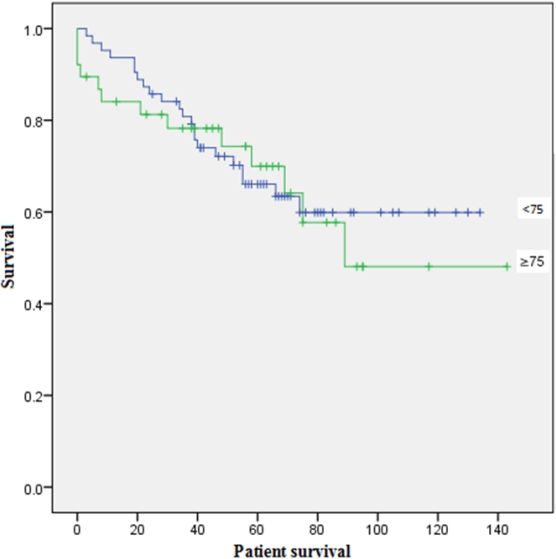
Overall actuarial graft and patient survival rates were similar between the two groups (p=0.6, p=0.796 respectively). G1 patients with CAD (Coronary Artery Disease) or receiving ECD had worse graft and patient outcomes [(CAD, HR: 2.44, p= 0.04 and HR: 2.48, p= 0.035), (ECD, HR: 5.25, p= 0.027 and HR: 5.33, p= 0.026) respectively]. In G2, diabetic patients had worse graft outcome (HR: 3.08, p= 0.045) and showed a trend towards worse patient outcome (HR: 2.7, p= 0.08),
Kidney transplant in elderly patients above age 70 with longstanding DM and CAD may not improve survival.
This study highlights the importance of a careful selection of patients receiving renal transplantation, and addresses the effects of co-morbid conditions on both graft and patient outcomes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yaqub M, Sharfuddin A, Mujtaba M, Mishler D, Taber T, Goggins W, Akl NKassis. Kidney Transplant Outcomes in Recipients Older Than 70: A Single Center Experience [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/kidney-transplant-outcomes-in-recipients-older-than-70-a-single-center-experience/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
