Kidney Donation After Brain Death Followed by Circulatory Death Confers Comparable Outcomes with Kidney Donation After Brain Death.
1Renal Transplantation, Lingnan Hospital, The Third Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
2Urology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun, China
3Renal Transplantation, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou Traditional Chinese Medicine University, Guangzhou, China
4Renal Transplantation, The Third Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, China
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C32
Keywords: Donation, Graft survival, Kidney transplantation, Renal dysfunction
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Deceased Donor Issues II: DCD, DGF, AKI, En-Bloc
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, May 1, 2017
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall D1
The shortage of donor organs is an obstacle to meet the growing need of grafts. Although using DBD donors is the best available strategy, brain death is not accepted by the whole world, which hinders the extend of donor pool. A unique donation classification, namely donation after brain death followed by circulatory death (DBCD), is established by China, which is promising to overcome the obstacle of donor sources. DBCD has a controlled procurement process, and can maximally reduce warm ischemia time. However, the outcomes of DBCD have not been studied. We carried out a multi-center cohort study to analyze outcomes of kidney transplantation from DBCD, compared with DBD.In our study, 523 recipients (383 DBCD and 140 DBD) were enrolled, and followed-up from 2012 to 2015. Donor procurement was approved by Human Organ Transplantation and Ethic Committee. For DBCD, a planned withdrawal of life-sustaining support and subsequent execution of cardiac death were processed after brain death.  Recipient and graft survivals and incidences of DGF and AR were measured. One-year survivals of graft and recipient from DBCD were similar with DBD.
Recipient and graft survivals and incidences of DGF and AR were measured. One-year survivals of graft and recipient from DBCD were similar with DBD. 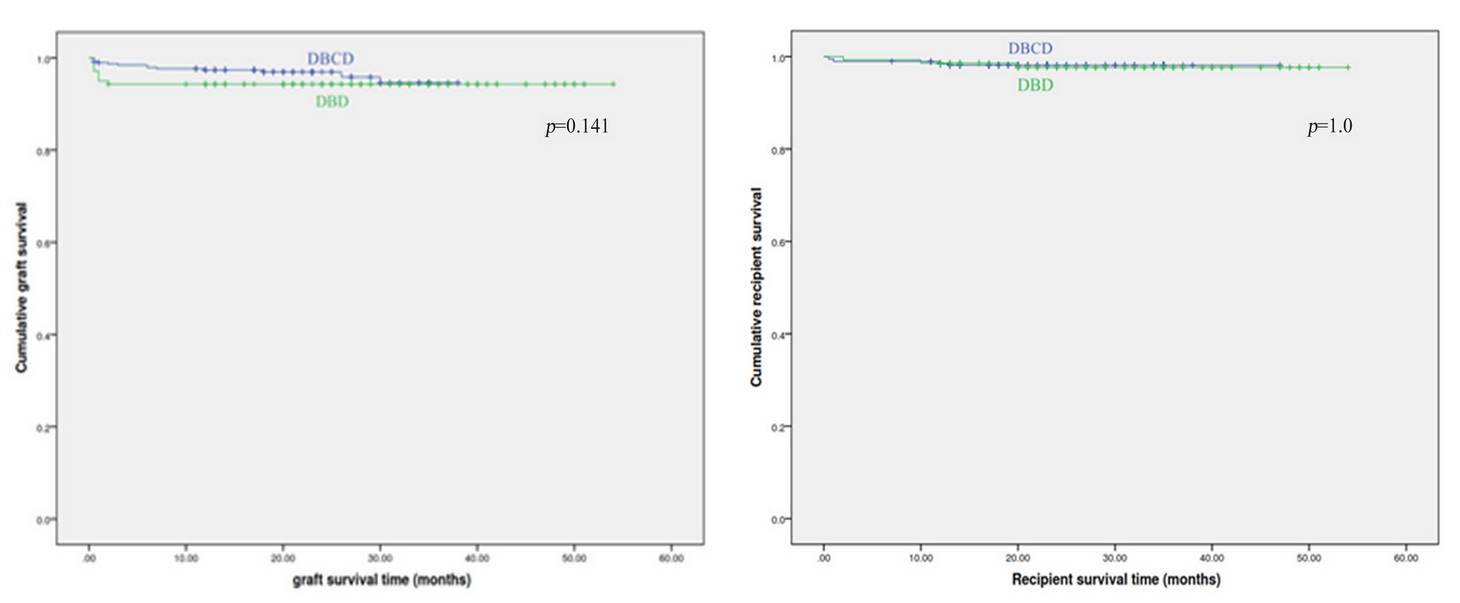 Additionally, recipient from DBCD was equivalent to develop DGF and AR, compared with DBD. In conclusion, kidney transplantation from DBCD confers comparable outcomes with DBD. This finding paves an alternative way to enlarge graft pool.
Additionally, recipient from DBCD was equivalent to develop DGF and AR, compared with DBD. In conclusion, kidney transplantation from DBCD confers comparable outcomes with DBD. This finding paves an alternative way to enlarge graft pool.
CITATION INFORMATION: Sun Q, Sun Q, Zhou H, Cao R, Lin M, Hua X, Hong L, Huang Z, Na N, Cai R, Wang G, Meng F. Kidney Donation After Brain Death Followed by Circulatory Death Confers Comparable Outcomes with Kidney Donation After Brain Death. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sun Q, Sun Q, Zhou H, Cao R, Lin M, Hua X, Hong L, Huang Z, Na N, Cai R, Wang G, Meng F. Kidney Donation After Brain Death Followed by Circulatory Death Confers Comparable Outcomes with Kidney Donation After Brain Death. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/kidney-donation-after-brain-death-followed-by-circulatory-death-confers-comparable-outcomes-with-kidney-donation-after-brain-death/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
