Is Dual Allocation Successful at Higher Remuzzi Scores? Outcomes of Dual Kidney Transplants at Remuzzi Scores of 8 or Greater
1Department of Transplantation, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI, 2Department of Transplantation, Piedmont Transplant Center, Atlanta, GA, 3Department of Statistics, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B-036
Keywords: Allocation, Donors, marginal, Graft survival, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Kidney Deceased Donor Selection
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: The Remuzzi score (RS) is a histologic assessment of donor kidneys based on degree of glomerulosclerosis, arterial narrowing, interstitial fibrosis, and tubular atrophy. The RS can guide allocation of renal allografts for single (SKT) or dual (DKT) kidney transplantation. Outcomes of DKT using kidneys with combined RS of 5-12 have been demonstrated to be similar to SKT with score <5. Previous reports recommend DKT with combined RS of up to 12; however, the outcomes of DKT with allografts with combined RS > 12 remain unknown. The purpose of this analysis was to determine whether outcomes after DKT are impacted by higher RS.
*Methods: We performed a single-center retrospective review of 65 recipients of DKT 2000-2015. Biopsy data was complete on 60 (92.3%). The analysis was divided by RS: low (2-5, n=10), intermediate (6-8, n=29), and high (9-14, n=21). Mean estimated glomerular filtration rates (eGFR) were compared using ANOVA. Kaplan-Meier estimates were used to determine graft survival (GS) and patient survival (PS) and compared with log rank test.
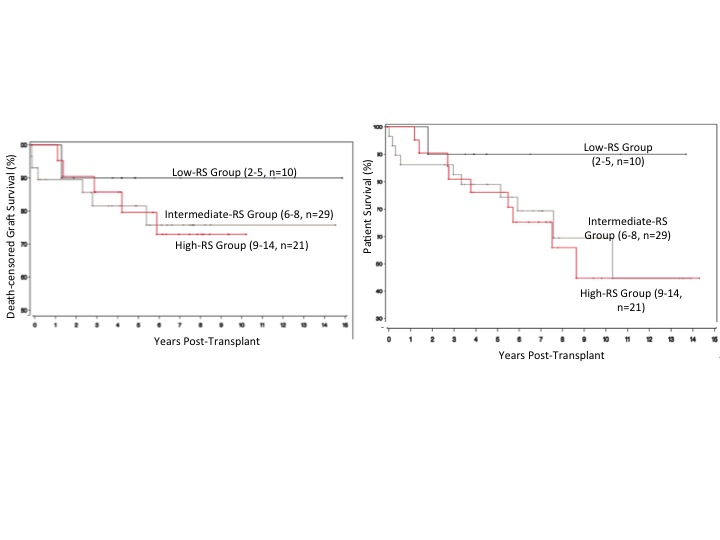
*Results: The eGFR increased in the low and intermediate RS groups at 3 and 5 years but did not improve in the high RS group (Table 1). Death-censored graft survival appeared better in recipients of low RS kidneys at 3 years but similar between intermediate and high RS (90.0% low RS; 75.7% intermediate RS; 73.0% high RS; p=0.77; Fig. 1). Patient survival was again higher in the low-risk group after 3 years but similar in the intermediate- and high-risk group (p=0.37) for up to 10 years.
*Conclusions: The use of kidneys with high RS for DKT is safe and effective, with similar death-censored GS and PS in intermediate and high RS. At 5 years, eGFR is higher in intermediate RS recipients than high RS recipients; intermediate-RS recipients may develop better filtration ability over time than high-RS recipients. Despite having lower filtration, the high-risk group has similar GS and PS outcomes and is therefore appropriate for use.
| GFR | 1 year | 3 years | 5 years |
| Low | 59.3 (±10.9) | 65.3 (±14.8) | 67.7 (±14.6) |
| Intermediate | 51.1 (±17.5) | 54.9 (±17.0) | 63.5 (±16.2) |
| High | 51.5 (±21.7) | 50.1 (±21.2) | 53.4 (±24.2) |
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fleetwood V, Kensinger C, Papageorge C, Aufhauser D, Leverson G, Welch B, Foley D, Pasha P. Is Dual Allocation Successful at Higher Remuzzi Scores? Outcomes of Dual Kidney Transplants at Remuzzi Scores of 8 or Greater [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/is-dual-allocation-successful-at-higher-remuzzi-scores-outcomes-of-dual-kidney-transplants-at-remuzzi-scores-of-8-or-greater/. Accessed March 7, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress