Infusion of Human Factor 7a Restores Circulating Platelets and Prevents TMA in Pig-to-Baboon Liver Xenotransplantation
Transplantation Biology Research Center, Massachusetts General Hospital/Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B291
Keywords: Liver transplantation, Xenotransplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Vascularized Composite Tissue Allografts and Xenotransplantation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, May 3, 2015
Session Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Background
We sought to determine the effects of exogenous administration of human coagulation factors in a pig-to-baboon model of liver xenotransplantation (LXT).
Methods
LXT was performed in a standard bicaval fashion using GalT-KO donors. Post-LXT, baboons received bolus (2.5 mL/kg) administration of a human prothrombin concentrate complex (PCC)(n = 2), or a continuous infusion (1 mcg/kg/hr) of activated Factor 7a (n = 3), or no exogenous clotting factors (control, n=1).
Results
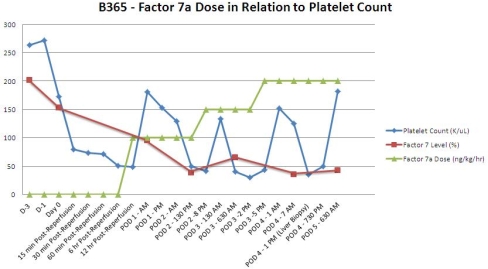
Circulating platelet levels were maintained in recipients given human PCC. Recipient platelets were noted to increase with escalating doses of Factor 7a (with the exception of B368 which had thrombocytopenia pre-LXT). In contrast, the control recipient (B274) had persistent post-reperfusion thrombocytopenia despite receiving exogenous platelets. Hepatic thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA) was noticeably absent in recipients receiving Factor 7a.
Conclusion
Exogenous administration of clotting factors appears to restore circulating platelets post-reperfusion in a clinically
relevant LXT model. This effect is most profound with a continuous escalating dose of Factor 7a, and may prevent TMA.
| Recipient | Coagulation Factor | Survival (Days) | Platelet Count (k/mL) Baseline | Platelet Count (k/mL) Reperfusion | Platelet Count (k/mL) POD 1 | Platelet Count (k/mL) Terminal | Liver Histology |
| B274 | None | 6 | 224 | 52 | 78 | 18 | (POD 2) Centrilobular hemorrhagic necrosis; Thrombotic microangiopathy |
| B353 | Human PCC | 2 | 216 | 144 | 144 | 147 | (Necropsy) Massive congestion. Thrombi in portal tracts |
| B356 | Human PCC | 4 | 252 | 128 | 151 | 73 | (POD 2) Arteries with intimal inflammation; Focal necrosis; Thrombi in small arteries and veins |
| B368 | Factor 7a | 7 | 24 | 18 | 13 | 9 | (POD 4) Minimal inflammation (5%); Patchy necrosis (5%); No thrombi |
| B365 | Factor 7a | 6 | 172 | 71 | 181 | 182 | (POD 4) Mild inflammation around portal tracts; Centrilobular necrosis (10%); Concern for rejection; No thrombi |
| B381 | Factor 7a | 6 | 154 | 42 | 32 | 260 | (POD 4) Intact hepatic architecture; Minimal focal necrosis; No thrombi |
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Shah J, Navarro-Alvarez N, Yeh H, Elias N, Ligocka J, Markmann J, Hertl M, Sachs D, Vagefi P. Infusion of Human Factor 7a Restores Circulating Platelets and Prevents TMA in Pig-to-Baboon Liver Xenotransplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/infusion-of-human-factor-7a-restores-circulating-platelets-and-prevents-tma-in-pig-to-baboon-liver-xenotransplantation/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
