Influence of Regulatory B Cells on B Cells
1Center for Transplant Science, MGH, Boston, MA, 2Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, 3Transplantation Surgery Research, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, 4Surgery, Mass General, Boston, MA, 5Sichuan Provincial People's Hospital, University of Electronic Sciences and Technology of China, Chengdu, China
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1229
Keywords: B cells
Topic: Basic Science » Basic Science » 04 - B-cell / Antibody /Autoimmunity
Session Information
Session Name: B-cell / Antibody /Autoimmunity
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Monday, June 6, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: Our previous study showed that Bregs-TLR, one type of previously studied Breg expanded in vitro, are capable of suppressing naïve B cell proliferation in the presence of LPS stimulation. Our previous result showed Bregs-TLR rescuing more LPS-stimulated B cells from apoptosis in vitro. However, less is known about how Bregs-TLR influence B cell activation and differentiation when LPS is absent. In the current study, we aim to explore the rescuing role of Bregs-TLR on naive B cells.
*Methods: Bregs-TLR were obtained after purified splenic B6 B cells were given CpG ODN1668 (TLR9 agonist) stimulation for 3 days and LPS (10ug/ml), PMA (50ng/ml), and ionomycin (1ug/ml) stimulation for the last 5 hours. In vitro, Bregs-TLR and naïve B cells w/o LPS stimulation were co-cultured for 3 days. In vivo, B6 recipients were adoptively transferred with Bregs-TLR on D-1 and transplanted with OVA skin grafts on D0. B cell subsets and markers of proliferation were measured by flow cytometry on day 21.
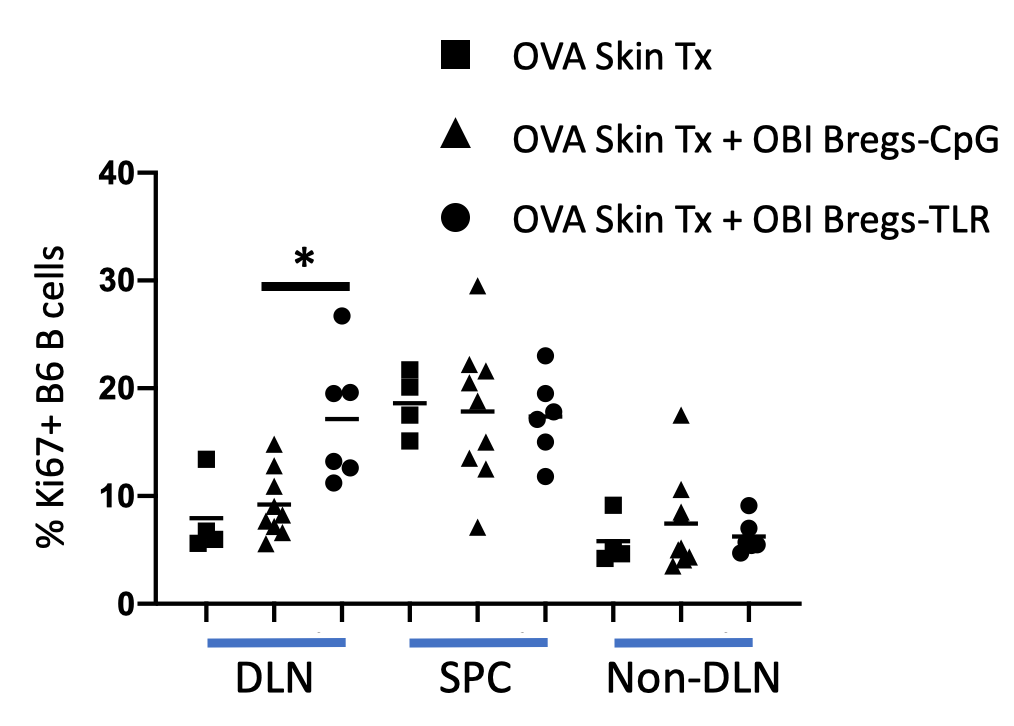
*Results: Flow cytometry found that naive B cells showed low viability and little proliferation in comparison to B cells stimulated for 96h with LPS. In the complete absence of any LPS stimulation, B cells did not survive unless Bregs-TLR or Bregs-CpG were added. Interestingly, while Bregs-CpG induced five generations of B cell proliferation, Bregs-TLR induced a comparable amount of proliferation in fewer generations (5 vs. 2). On the other hand, in vivo data showed that Bregs-TLR could induce B cell proliferation (Figure) and more CD19+IgMhiIgDloCD23loCD21hi MZ B cells in B6 recipients while Bregs-CpG could not.
*Conclusions: Bregs-TLR regulate the proliferation and differentiation of naïve B cells both in vitro and in vivo. The increase of MZ B cell percentage may indicate that the mechanism for which Bregs-TLR induce the proliferation of other B cells lies in an MZ B cell-relevant pathway.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fu Q, Lee KM, Deng K, Agarwal D, Matheson R, Press T, Lei J, Yang H, LeGuern C, Deng S, Markmann JF. Influence of Regulatory B Cells on B Cells [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/influence-of-regulatory-b-cells-on-b-cells/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress