Infectious Complications in ABO Incompatible Kidney Transplantation Recipient According to the Rituximab Dose
1Department of Transplantation Surgery, Yonsei University Health System, Seoul, Republic of Korea
2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University Health System, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C88
Keywords: Highly-sensitized, Infection, Kidney transplantation, Monoclonal antibodies
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Kidney Immunosuppression: Desensitization
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, May 4, 2015
Session Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Background
Desensitization with rituximab and intravenous immunoglobulin improves ABO incompatible (ABOi) kidney transplantation (KT) outcomes. However, infections have been noted in association with rituximab administration. In this study, we retrospectively compared infectious outcomes between ABOi KT and ABO compatible (ABOc) KT according to rituximab dose.
Methods
We analyzed 218 consecutive recipients (118 ABO compatible, 100 ABO incompatible) who underwent kidney transplantation from living donor between June 2010 and July 2014. ABOi KT patients were categorized by rituximab dose (375mg/m2 standard dose vs. 200mg reduced dose). All patients received basiliximab for induction immunosuppression and maintained on triple immunosuppression consisting of tacrolimus, prednisone, and mycophenolate mofetil.
Results
During an average follow-up of 23 months, overall patient survival was 99 and 98%, and graft survival was 99 and 96% in the ABOc and ABOi groups, retrospectively. A total of 31 patients (38.3%) in the standard rituximab group in ABOi KT and 29 patients (24.6%) in the ABOc KT group diagnosed with infection (p=0.027). There was one death in standard dose rituximab group related to infection (1%). Afterward, we reduced the dose of rituximab to 200mg to decrease the infection risk in August 2013 (n=19). Four patients (21.0%) diagnosed with infection in reduced dose group in ABOi KT. The rejection rate was not significantly different between rituximab groups in ABOi KT.
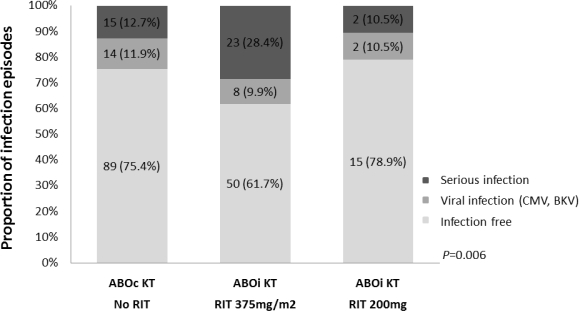
Conclusion
Standard dose of rituximab increase infection risk when used for desensitization. Reduced dose of rituximab might be sufficient for blood type incompatible desensitization without increase the risk of serious infections.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lee J, Lee J, Kim S, Ju M, Joo D, Kim M, Kim S, Kim Y, Kim H, Huh K. Infectious Complications in ABO Incompatible Kidney Transplantation Recipient According to the Rituximab Dose [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/infectious-complications-in-abo-incompatible-kidney-transplantation-recipient-according-to-the-rituximab-dose/. Accessed February 24, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
