Infections Requiring Hospitalization After Simultaneous Pancreas-Kidney Transplantation Compared to Kidney Transplantation Alone
J. Grasberger1, F. Ortiz2, A. Ekstrand2, V. Sallinen1, M. Lempinen1, I. Helanterä1
1Transplantation and Liver Surgery, Helsinki University Hospital, Helsinki, Finland, 2Nephrology, Helsinki University Hospital, Helsinki, Finland
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1626
Keywords: Infection, Kidney, Outcome, Pancreas
Topic: Clinical Science » Infection Disease » 24 - All Infections (Excluding Kidney & Viral Hepatitis)
Session Information
Session Name: All Infections (Excluding Kidney & Viral Hepatitis) IV
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Tuesday, June 7, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: Although infections related to surgical complications are more common after simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation (SPK) compared to kidney transplantation alone (KTA), the burden of infections after transplantation has not been compared in detail between these groups. The aim of this study is to compare the frequency of infections requiring hospitalization between SPK and KTA patients after transplantation
*Methods: We analyzed retrospectively all 163 patients undergoing SPK in our institution during 2010-2019. The control group consisted of 155 with end-stage renal disease secondary to type 1 diabetes who received KTA from a deceased donor before the routine implementation of the SPK program in our institution during 2004-2013. The inclusion criteria for the controls included donor and recipient age <60 and BMI <30. All hospital admissions for infections were included.
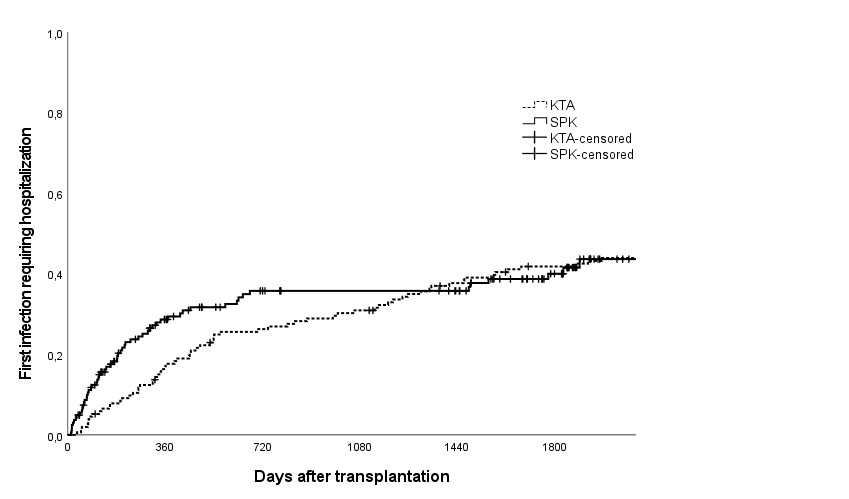
*Results: For SPK patients, immunosuppression comprised of tacrolimus, mycophenolate and steroids. All SPK patients received induction with single-dose antithymocyte globulin (ATG). From KTA patients, only 3.9% (6/155) received induction (all with basiliximab) and 87% (135/155) were on cyclosporine-based immunosuppression. The time from transplantation to the first infection during 5-year follow-up is demonstrated in the Kaplan Meier estimate (Figure 1.). The majority of infections were pyelonephritis in 40% and 13%, pneumonia in 10% and 31%, gastroenteritis in 21% and 17%, and erysipelas in 20% and 19% of the SPK and KTA recipients, respectively.
*Conclusions: In SPK patients, majority of first infections requiring hospitalization after transplantation occurred within the first year, which could be related to ATG induction and more intensive immunosuppression. Although infections seemed to occur later in KTA patients, at the end of the 5-year follow-up, no significant difference was detected between groups.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Grasberger J, Ortiz F, Ekstrand A, Sallinen V, Lempinen M, Helanterä I. Infections Requiring Hospitalization After Simultaneous Pancreas-Kidney Transplantation Compared to Kidney Transplantation Alone [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/infections-requiring-hospitalization-after-simultaneous-pancreas-kidney-transplantation-compared-to-kidney-transplantation-alone/. Accessed March 11, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress