Induction Therapy With either Anti-Thymocyte Antibodies or Il2 Receptor Inhibitors Appears to Decrease the Risk of Graft Loss in DCD Liver Transplantation Compared to No Induction Therapy
University of Washington, Seattle.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C109
Keywords: Donors, Immunosuppression, Liver transplantation, non-heart-beating, Outcome
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Liver Donation and Allocation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, May 4, 2015
Session Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Location: Exhibit Hall E
An analysis of our center's outcomes in DCD liver transplants suggested that induction with anti-thymocyte antibody preparations (ATG) may reduce the risk of graft loss in DCD livers and that their effects may be significantly greater than that of IL2 receptor inhibitors (IL2R). Given this finding, we sought to see if there is a similar effect detectable using national data. Methods: All 2275 adult DCD liver transplants from the beginning of the MELD era through October 2013 were analyzed using UNOS STAR data. The SSDMF was used to correct patient survival data. The 296 patients who received ATG induction, the 385 who received IL2R induction, and the 2067 who received no induction were compared (22 who received alemtuzumab were excluded due to the small n). Results: The use of either ATG or IL2R induction appeared to increase graft survival in DCD livers. There was no difference in graft survival between recipients receiving ATG or IL2R (p = 0.8). In the multivariate model, ATG or IL2R induction, CIT ≥ 9 hours (and CIT as a continuous variable), donor age ≥ 50 (and donor age as a continuous variable), DCD WIT ≥ 20 min (and DCD wit as a continuous variable), recipient age and gender, and year of transplantation were significant risk factors. Recipient HCV, recipient weight, and donor weight and gender were not significant risk factors in the multivariate model. Conclusions: Induction with ATG or an IL2R appeared to increase graft survival after DCD liver transplantation compared to no induction therapy. Unlike the findings from our center, the present findings do not suggest that there is a difference in the magnitude of the protective effect from ATG or IL2R induction.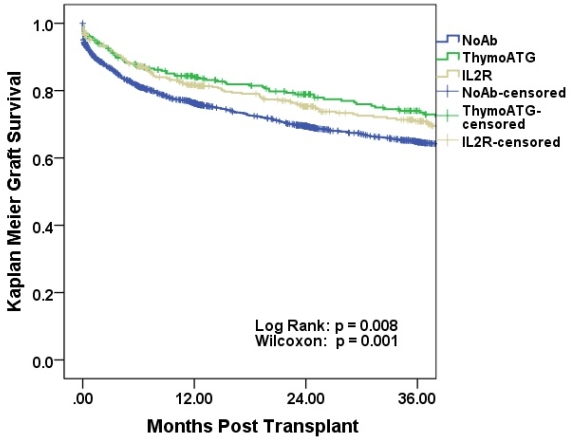
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rayhill S, Haldorson J, Dick A, Nazarian S, Sibulesky L, Montenovo M, Yu L, Javid I, Pearson T, Bakthavatsalam R, Healey P, Perkins J, Reyes J. Induction Therapy With either Anti-Thymocyte Antibodies or Il2 Receptor Inhibitors Appears to Decrease the Risk of Graft Loss in DCD Liver Transplantation Compared to No Induction Therapy [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/induction-therapy-with-either-anti-thymocyte-antibodies-or-il2-receptor-inhibitors-appears-to-decrease-the-risk-of-graft-loss-in-dcd-liver-transplantation-compared-to-no-induction-therapy/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
