Incidence of Chronic Kidney Disease after Liver Transplantation Using Measured GFR
1Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Northwestern University, Chicago, IL, 2Transplant Hepatology, Baylor University Medical Center Dallas, Dallas, TX, 3Transplant Surgery, Baylor University Medical Center Dallas, Dallas, TX
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 370
Keywords: Liver transplantation, Renal dysfunction, Renal function, Risk factors
Session Information
Session Name: Liver Retransplantation and Other Complications
Session Type: Oral Abstract Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:45pm
 Presentation Time: 3:27pm-3:39pm
Presentation Time: 3:27pm-3:39pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Historical rates of ESRD after LT are 8% (1 year) and 18% (5 years) (Ojo NEJM 2003). However, these rates were based older estimates and estimated GFR using serum creatinine. We examined the true natural history of CKD using a protocolized collection of measured GFR (mGFR) in the current era.
*Methods: We examined all patients that underwent LT Alone (1997-2015) and underwent protocol mGFR measurement using iothalamate clearance. The primary outcome was incident CKD stage 3 or higher (mGFR<60 ml/min/1.73 m2) and incident ESRD (defined as mGFR <20 ml/min/1.73 m2 > 90 days post LT, hemodialysis, or kidney transplantation). We also stratified by mGFR pre-transplant and MELD-Na at LT. Hazard of ESRD was determined using the Fine-Gray method after adjustment for pre-transplant mGFR, MELD-Na at LT, gender, and age at LT treating death and LT graft loss as competing risks.
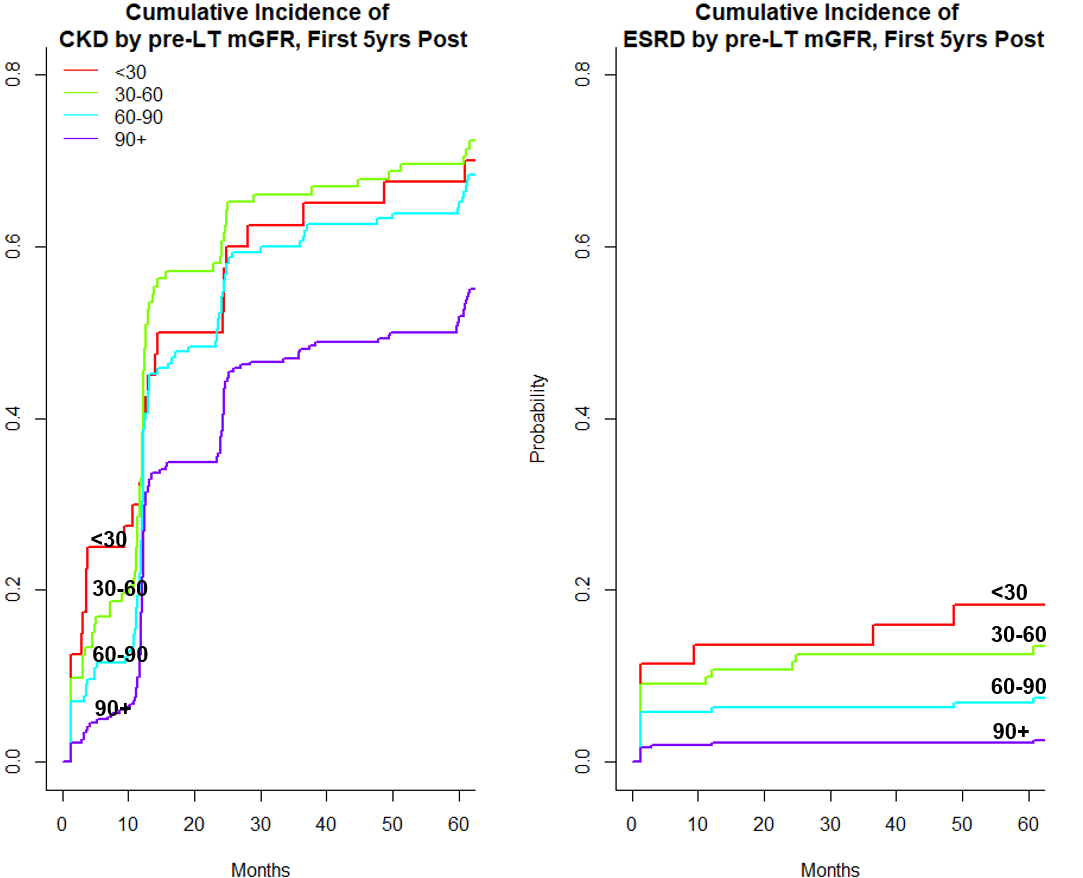
*Results: Overall 1,147 LTA recipients underwent a total of 4,704 mGFR measurements (median of 4 mGFR per patient, IQR 2-5) over a median follow up of 7 years. Mean age was 52 yrs, 74% Caucasian, 36% female, MELD-Na at LT 18.5. The average mGFR in the first month post LT was 57.0 ml/min/1.73 m2. The average drop in mGFR was 12% (57.0 to 50.8 ml/min/1.73 m2). The cumulative incidence of CKD stage ≥3 and ESRD was 24.1% and 5.1% (1y), 57.3% and 5.8% (3y), and 61.2% and 6.0% (5y). When limited only to the current era (2006-2015), rates of ESRD were unchanged. A pre LT cutoff of 40ml/min, 38 and 30 was associated with a 3.7%, 4.1% and 4.5% incidence of ESRD in the first year.When stratified by pre LT mGFR, the cumulative incidence of post-LT ESRD at 5 years was 3.9% (GFR 60+ ml/min/1.73 m2), 12.5%(mGFR 30-60 ml/min/1.73 m2), and 18.3% (mGFR <30 ml/min/1.73 m2), (Figure) Rates of ESRD were higher by MELD score at LT: 3.0% (MELD<15), 6.0% (MELD 15-25) 7.7% (MELD 25-35) 32.2% (MELD 35+). On competing risk analyses, a 10 ml/min/1.73 m2 decrease in mGFR pre-LT was associated with a 20% increased subdistribution hazard of ESRD (sHR per 10 ml/min/1.73 m2: 1.20, 95% CI 1.12-1.28, p<0.001) after adjustment for MELD-Na, sex, and age.
*Conclusions: In a cohort with true measures of renal function, rates of CKD and ESRD are much lower than reported despite transplantation of sicker patients in modern times. CKD and ESRD are still common with ESRD in 1 in 16 patients after 5 years. Re-evaluation of GFR cutoffs at time of LT is needed for consideration of dual organ transplantation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mazumder NR, Levitsky J, Saracino G, Klintmalm G, Trotter J, Asrani S. Incidence of Chronic Kidney Disease after Liver Transplantation Using Measured GFR [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/incidence-of-chronic-kidney-disease-after-liver-transplantation-using-measured-gfr/. Accessed February 23, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress