Incidence and Effects of Posttransplant Herpes Zoster in Adult Solid Organ Transplant Recipients : A Meta-Analysis
S. H. Han, D. Kwon
Yonsei University Health System, Seoul, Korea, Republic of
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B-187
Keywords: Infection, Rejection, Vaccination
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: All Infections (Excluding Kidney & Viral Hepatitis)
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Recently, non-live recombinant subunit HZ vaccine showed highly effective for herpes zoster (HZ) in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Several observational studies reported various features of HZ among heterogeneous subjects of solid organ transplantation (SOT) recipients. We performed a meta-analysis to clarify clinical aspects of HZ in SOT recipients.
*Methods: We collected the articles using keywords of “herpes zoster” or “human herpesvirus 3” or “varicella zoster” and “transplant” in Pubmed and EMBASE database. Among total 3671 papers, 739 overlapping and 1406 irrelevant studies were removed by abstract review. The full text review deleted 1512 studies (301 in pediatrics, 956 in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, 23 of laboratory studies, 217 of case report, and 15 of non-English). Because two studies were not eligible due to insufficient data, we finally included 12 observational studies in meta-analysis. In addition, we retrospectively collected the data for 329 HZ in 3498 SOT recipients from January 2001 to December 2018 of Yonsei University Health System at South Korea to include this meta-analysis. We systemically analyzed given data according to sex and transplant organs with R package.
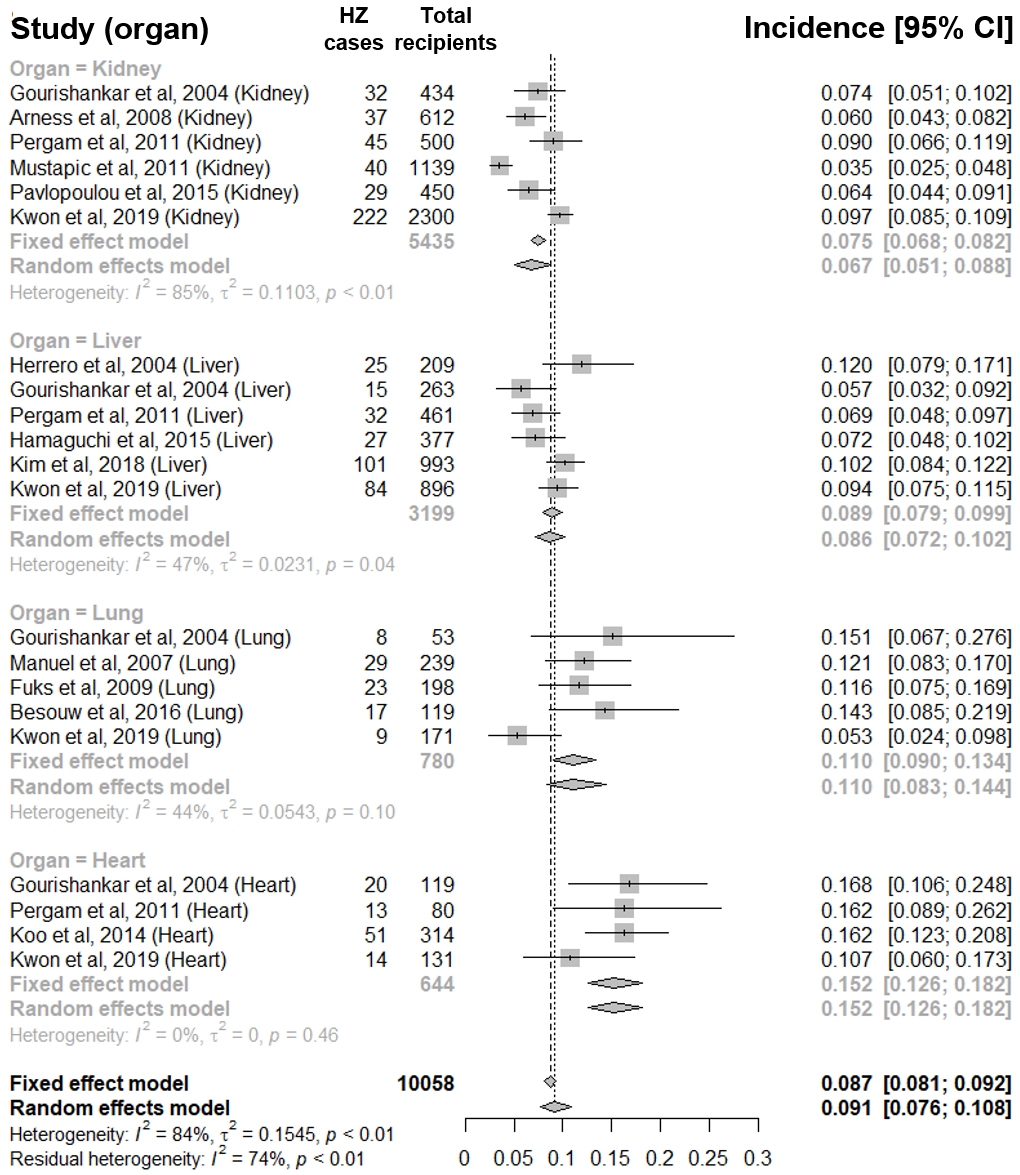
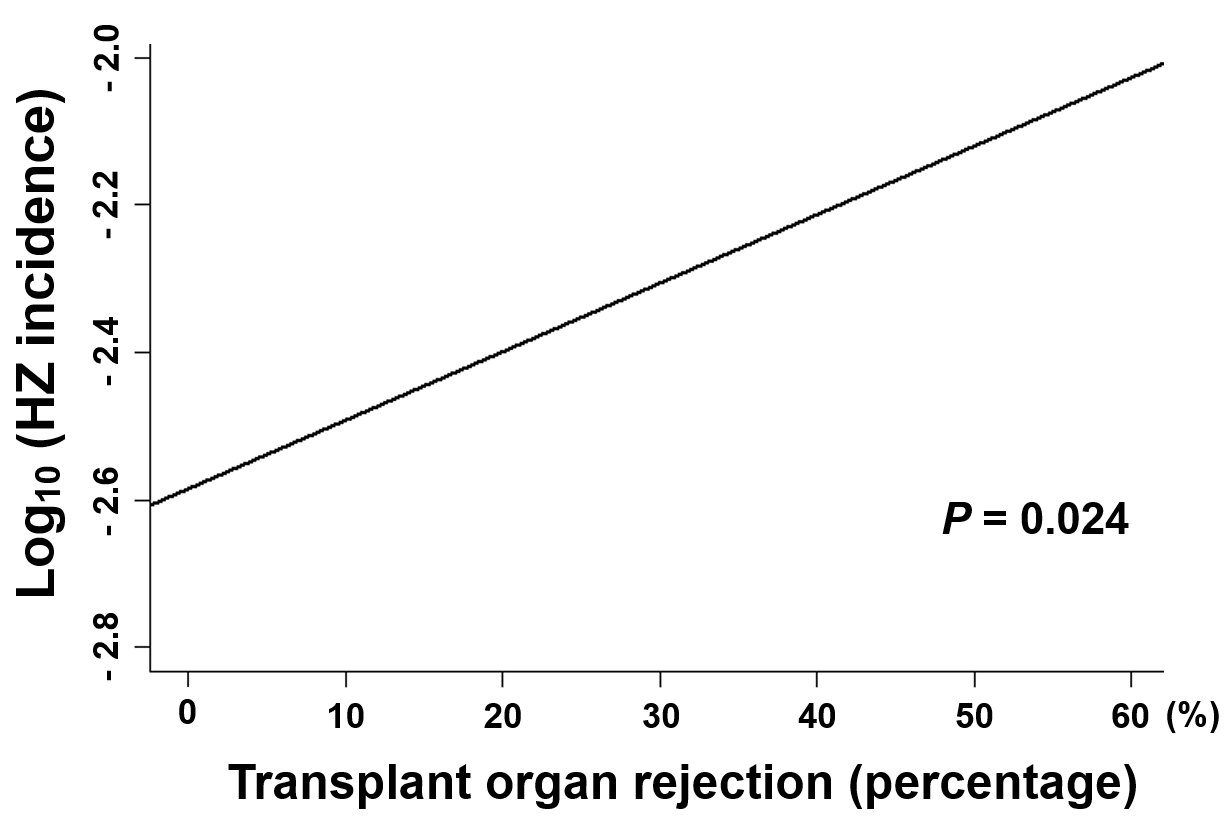
*Results: Total 873 HZ cases occurred in 10058 SOT recipients. Total pooled proportion (PP) of HZ was 0.091 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.076-0.108) in random effects model. The PP was significantly different between four transplant organs (overall P < 0.001). The PP of HZ in heart transplant (HT) recipients (N=644, 0.152, 95% CI; 0.126-0.182) was highest, followed by lung transplant (LTx) (N=780, 0.110, 95% CI; 0.083-0.144) and liver transplant recipients (LT) (3199, 0.086, 95% CI; 0.072-0.102). The kidney transplant (KT) recipients had the lowest HZ PP (N=5435, 0.067, 95% CI; 0.051-0.088) (Figure 1). Meta-regression revealed that higher PP of HZ was significantly associated with higher proportion of graft rejection (P = 0.024) (Figure 2).
*Conclusions: The HT and LTx recipients had higher PP of HZ than LT and KT recipients. The HZ development in SOT recipient had significantly association with the higher risk of graft rejection. The active program for HZ vaccination should be implemented in high risk SOT recipients
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Han SH, Kwon D. Incidence and Effects of Posttransplant Herpes Zoster in Adult Solid Organ Transplant Recipients : A Meta-Analysis [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/incidence-and-effects-of-posttransplant-herpes-zoster-in-adult-solid-organ-transplant-recipients-a-meta-analysis/. Accessed February 27, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress