Impact on Wound Healing Events After Early Conversion to Everolimus in De Novo Renal Transplant Recipients: 24-Month Results from the Randomized ELEVATE Study.
1ELEVATE Study Group, Hamburg, Germany
2Novartis, Basel, Switzerland
3Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation, East Hanover.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B106
Keywords: Calcineurin, Immunosuppression, Kidney transplantation, Safety
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Drug Minimization
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 12, 2016
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Halls C&D
Background
Wound healing events (WHE) are probably the most common type of post-transplant (Tx) surgical complication. Due to its antiproliferative properties, mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors may affect wound healing process. Here we evaluate the incidence of WHE at 24-months (M) post-Tx, from the ELEVATE study.
Methods
ELEVATE (NCT01114529) was a 24M, open-label, multicenter study, in which de novo kidney Tx recipients were randomized at 10-14 weeks post-Tx to receive either EVR (n=360; trough level [C0] 6-10 ng/mL) or continue standard CNI regimen (n=357; C0: TAC 5-10 ng/mL or CsA 100-250 ng/mL); all patients received enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium and steroids. Incidence of patients with WHE was summarized by treatment arm and baseline body mass index (BMI) quartile.
Results
At M24, incidence of WHE was similar in both the arms (EVR, 6.6 vs. CNI, 5.8%; P=0.662); although it varied within CNI arms (TAC, 7.6%; P=0.670 vs. CsA, 2.5%; P=0.085). Fluid collection was the most commonly reported WHE in EVR arm (n=5, 1.4% vs. CNI arm: n=1, 0.3%).
A total of 60 lymphocele events were reported in the run-in period prior to randomization.
The incidence of patients with WHE was similar in ≤25 percentile BMI category (EVR, 0.9 vs. CNI, 0.8%; P=0.846). However, the incidence was higher in EVR arm in >25–≤50 (2.6 vs. 1.1%; P=0.271) and significantly higher in >50–≤75 categories (2.0 vs. 0.6%; P=0.049).
Incidence of patients free from WHE was similar in both arms (EVR, Kaplan-Meier estimates 94.7%; 95%CI: 92.3, 97.1 vs. CNI, 93.7%; 95%CI: 91.0, 96.4; P=0.615).
Conclusions
Incidence of patients with WHE was low and comparable between the treatment arms. However, the combination of two anti-proliferative substances may present a risk for the development of de novo fluid collections of unknown origin more than 3M after surgery, especially for patients with a high BMI risk factor. 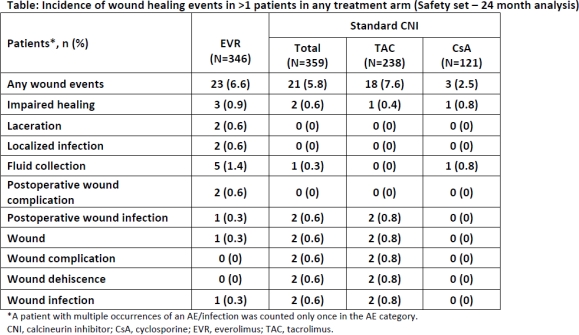
CITATION INFORMATION: Nashan B, van der Giet M, Holdaas H, Zeier M, Pascual J, Avihingsanon Y, Lopez P, Aguilar-Sanchez J, Kochuparampil J, Wang Z, Cruzado J, De Fijter J. Impact on Wound Healing Events After Early Conversion to Everolimus in De Novo Renal Transplant Recipients: 24-Month Results from the Randomized ELEVATE Study. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nashan B, Giet Mvander, Holdaas H, Zeier M, Pascual J, Avihingsanon Y, Lopez P, Aguilar-Sanchez J, Kochuparampil J, Wang Z, Cruzado J, Fijter JDe. Impact on Wound Healing Events After Early Conversion to Everolimus in De Novo Renal Transplant Recipients: 24-Month Results from the Randomized ELEVATE Study. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/impact-on-wound-healing-events-after-early-conversion-to-everolimus-in-de-novo-renal-transplant-recipients-24-month-results-from-the-randomized-elevate-study/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
