Impact of Pretransplant Non-Donor-Specific HLA Immunization: Mainly Class 1 Immunization Leads to Poor Immunologic Outcome and Graft Loss.
Nephrology, Charite, Berlin, Germany.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 57
Keywords: Antibodies, Graft survival, Kidney transplantation, Panel reactive antibodies
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Novel Markers of Long Term Kidney Transplant Outcomes
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, June 12, 2016
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:42pm-3:54pm
Presentation Time: 3:42pm-3:54pm
Location: Ballroom A
Background Anti-HLA immunization measured as Panel Reactive Antibodies (PRA) is known to have a negative impact on patient and graft survival. The influence of pre-transplant peak PRA (pPRA) on immunologic outcome and the individual effects of anti-HLA class 1 and class 2 antibodies remain undetermined.
Methods We conducted a retrospective long-term study with inclusion of 1150 adult kidney transplant recipients (KTR) transplanted 1995-2014. None of the KTR had pretransplant donor specific antibodies (DSA). Demographics, clinical data and long-term outcomes over a period of maximal 20 years were assessed. Pretransplant peak PRA (pPRA) was determined using solid-phase essays Elisa and Luminex. HLA-immunization was defined as a pPRA >0%.
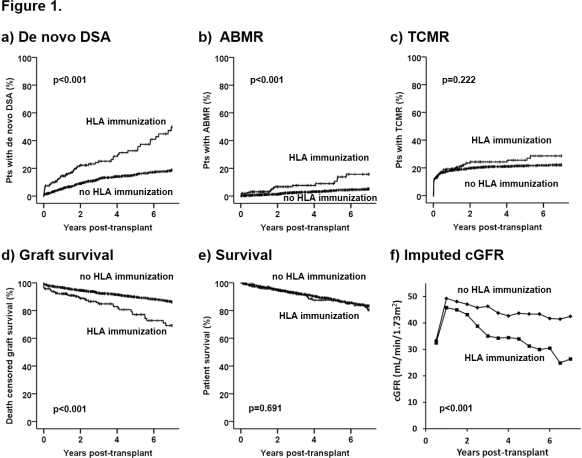
Results KTR with pre-transplant HLA immunization showed a significantly higher proportion of females, previous transplantations and longer time on dialysis. They were at a significantly higher risk for developing de novo DSA, antibody mediated rejections (ABMR), had a poorer death censored graft survival and a lower imputed cGFR. There was no significant difference in the incidence of T-cell mediated rejections (TCMR) or patient survival (Fig. 1 a-f). Cox proportional hazards models showed a significant association of pre-transplant immunization with development of de novo DSA (class 1 HR 2.57, p<0.001, class 2 HR 2.49, p<0.001), ABMR (class 1 HR 3.74, p<0.001, class 2 HR 2.36, p=0.025) and death censored graft loss (class 1 HR 2.49, p<0.001, class 2 HR 1.93, p=0.005). A multivariate model adjusted for recipient age, donor age, gender, time on dialysis, prior kidney transplantation, HLA-mismatches and cold ischemia time revealed only class 1 but not class 2 pre-transplant HLA immunization as an independent risk factor for de novo DSA, ABMR and death censored graft loss (HR 2.76, p<0.001, HR 4.16, p<0.001 and HR 2.07, p<0.001, respectively). There was no significant association with TCMR.
Conclusion Mainly non-donor-specific pre-transplant HLA class 1 immunization is an independent risk factor for the development of de novo DSA, ABMR and graft loss.
CITATION INFORMATION: Staeck O, Halleck F, Staeck A, Lehner L, Duerr M, Schrezenmeier E, Budde K, Khadzhynov D. Impact of Pretransplant Non-Donor-Specific HLA Immunization: Mainly Class 1 Immunization Leads to Poor Immunologic Outcome and Graft Loss. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Staeck O, Halleck F, Staeck A, Lehner L, Duerr M, Schrezenmeier E, Budde K, Khadzhynov D. Impact of Pretransplant Non-Donor-Specific HLA Immunization: Mainly Class 1 Immunization Leads to Poor Immunologic Outcome and Graft Loss. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/impact-of-pretransplant-non-donor-specific-hla-immunization-mainly-class-1-immunization-leads-to-poor-immunologic-outcome-and-graft-loss/. Accessed March 7, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
