Impact of Pre- and Post-transplant Outcomes on Patient-reported Outcomes in a Prospective Multicenter Trial in Kidney Transplantation
J. M. Rohan1, J. P. Leone2, E. Woodle3, D. Kaufman4, A. R. Shields3, A. Wiseman5, A. J. Matas6, P. West-Thielke7, E. King3, R. R. Alloway3
1Children's Hospital Richmond VCU, Richmond, VA, 2Tampa General, Tampa, FL, 3U Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH, 4U Wisconsin, Madison, WI, 5Centura Transplant, Denver, CO, 6U Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, 7UIC, Chicago, IL
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 883
Keywords: Adverse effects, Post-transplant diabetes, Psychosocial, Risk factors
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » Kidney Psychosocial
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney Psychosocial
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: BEST Trial (Belatacept-based Early Steroid-withdrawal Trial) compared belatacept (BELA)-based early steroid withdrawal (ESW) regimens with a tacrolimus (TAC)-based ESW regimen across 2years. CNI free/ESW bela groups revealed improved patient-reported outcomes (PROs) in kidney transplant (KTx) patients (pts). GI distress in TAC group increased across 2-years. Neurologic, GI, and mobility symptoms were reported less frequently in BELA groups. Previous trials did not examine predictive models investigating longitudinal differences in PROs between BELA- and TAC-groups. We attempt to determine if clinically relevant pre- and post-transplant outcomes [e.g., chronic dialysis vs. pre-emptive, acute rejection, diabetes (preexisting, new onset diabetes after transplant (NODAT), death, death censored graft loss (DCGL), and eGFR<45] predicted worse PROs over two years
*Methods: This longitudinal, multisite study was conducted across 8 sites. All pts received mycophenolate and 5 days of steroids. Pts were randomized to 3 groups: alem+BELA, r-ATG+BELA, r-ATG+TAC. Pts completed 2 PRO measures at baseline, 1-, and 2-years (MEMPHIS, MTSOSD-59R). Intent to treat analyses (n=316) using a multivariate analysis (MVA) framework examined pre- and post-transplant outcomes, randomization assignment, time since KTx, gender, and race
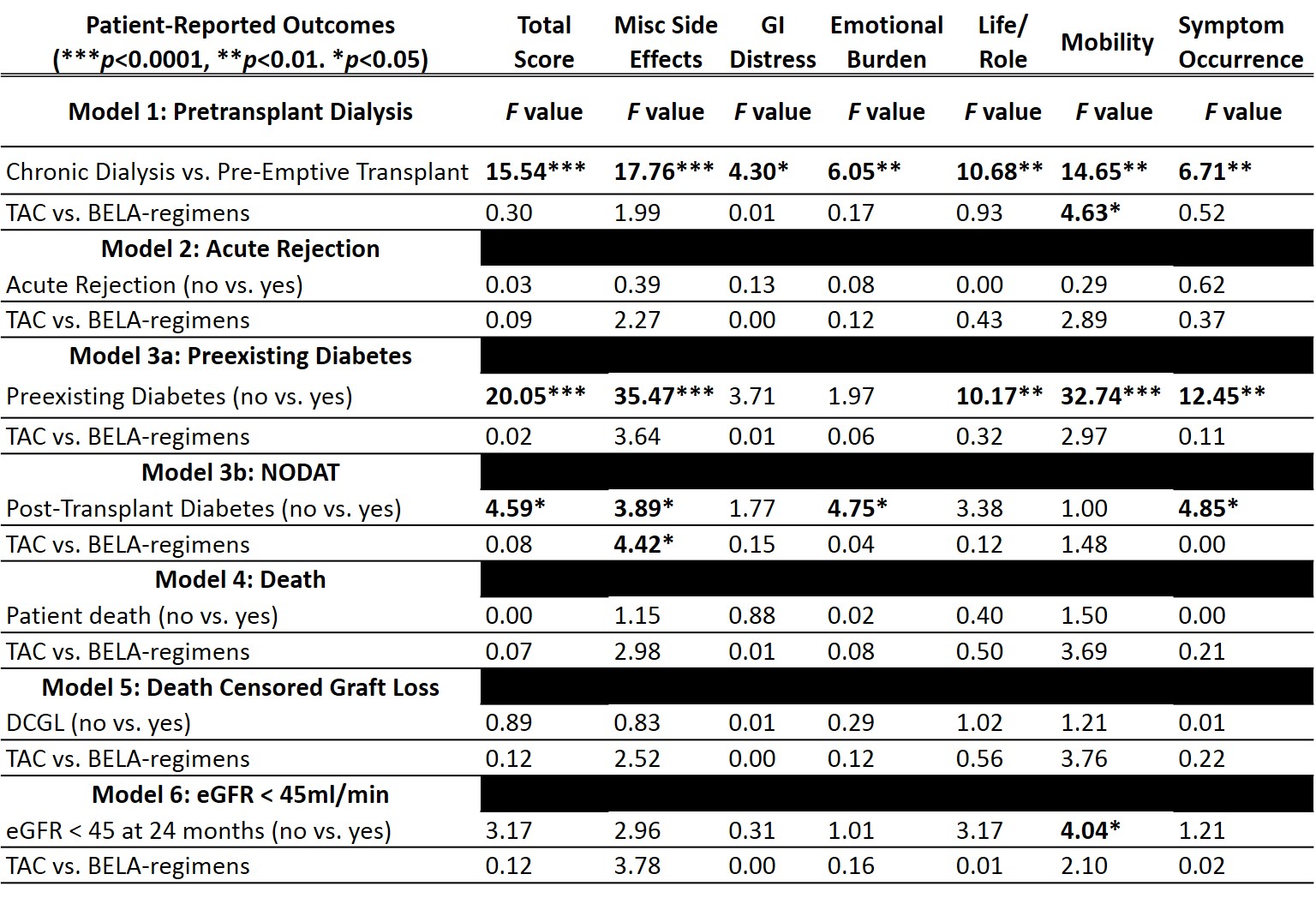
*Results: MVA (Table 1) indicated pts receiving pre-emptive transplant reported worse PROs across 2-years. Preexisting diabetes and NODAT predicted worse PROs over time. Death, DCGL, rejection, and eGFR<45 was not predictive of PROs with exception of mobility; those with eGFR<45 reported worse mobility. Controlling for gender, race, and time post KTx, medication regimen only significantly influenced the relationship between PROs in pts who developed NODAT and received TAC; these pts reported significantly worse miscellaneous symptoms than BELA-treated pts.
*Conclusions: Predictive models indicated pre-emptive transplant, preexisting diabetes, NODAT, and eGFR<45 significantly predicted worse PROs. Rejection did not predict PROs. TAC pts with NODAT reported worse miscellaneous symptoms. These findings support utilization of PROs in drug trials to highlight the value of regimens with lower NODAT and improved eGFR.Table 1. Multivariate Analyses for Predictive Models of PROs
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rohan JM, Leone JP, Woodle E, Kaufman D, Shields AR, Wiseman A, Matas AJ, West-Thielke P, King E, Alloway RR. Impact of Pre- and Post-transplant Outcomes on Patient-reported Outcomes in a Prospective Multicenter Trial in Kidney Transplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/impact-of-pre-and-post-transplant-outcomes-on-patient-reported-outcomes-in-a-prospective-multicenter-trial-in-kidney-transplantation/. Accessed March 8, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress