Impact of Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Inhibitors on Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence after Liver Transplant
1Pharmacy, NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital, New York, NY
2Surgery, Weill Cornell Medical College, New York, NY.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B268
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma, Liver transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Liver: Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Other Malignancies
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 3, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Despite limited benefit to patients within Milan criteria on explant, mTORi are routinely utilized for prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) recurrence after liver transplantation (LT). The objective of this study was to determine the impact of mTORi on HCC recurrence after LT risk-stratified by the Model of Recurrence After Liver Transplant (MORAL) score, a novel risk stratification incorporating tumor characteristics.
All adult liver transplant recipients (LTR) with HCC between 2001-2012, at a single institution, were assessed. LTR who died within 90 days of LT or with preoperative signs of sepsis or steroid use were excluded. LTR were stratified into high- and low-risk groups for HCC recurrence based on MORAL score and Milan criteria. The primary outcome was recurrence-free survival (RFS) at 3 years between groups (no mTORi vs. mTORi) stratified by MORAL score. Secondary outcomes included time to recurrence (TTR) and RFS at 5 years.
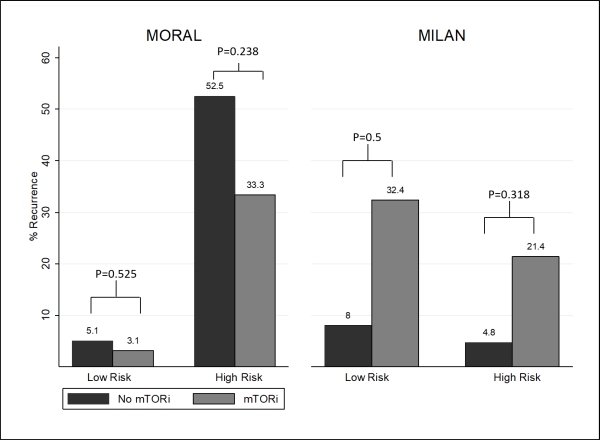
A total of 336 LTR were included; 41 LTR received mTORi therapy. Median age was 59 years, 80% were male, and 69% had HCV cirrhosis. Of the LTR who received mTORi, 54% received a CNI concomitantly. HCC recurrence was 10% (n=4) in the mTORi group and 15% (n=43) in the no mTORi group, p=0.4 [figure 1]. RFS at 3 and 5 years for mTORi vs. no mTORi was 91% vs. 86% (p=0.004) and 85% vs. 80% (p=0.1), respectively. In those at high risk of recurrence based on MORAL, RFS at 3 and 5 years for mTORi vs. no mTORi was 61% vs. 48% (p=0.2) and 61% vs. 36% (p=0.2), respectively. Median TTR was 628 days (IQR 350-1080) in LTR who received mTORi and 321 days (IQR 165-605) with no mTORi, p=0.2. Median time from LT to initiation of mTORi was 700 days (IQR 217-896); median duration was 666 days (IQR 108-1666).
There was a numerically lower HCC recurrence and longer TTR, and significantly greater RFS at 3 years in LTR who received mTORi vs. no mTORi. Additional years of follow-up and recurrence events may better describe the impact of mTORi on HCC recurrence post-LT and help elucidate specific patient and/or tumor characteristics that may portend benefit from mTORi therapy.
CITATION INFORMATION: Hendon N., Salerno D., Sammons C., Halazun K. Impact of Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Inhibitors on Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence after Liver Transplant Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hendon N, Salerno D, Sammons C, Halazun K. Impact of Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Inhibitors on Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence after Liver Transplant [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/impact-of-mammalian-target-of-rapamycin-inhibitors-on-hepatocellular-carcinoma-recurrence-after-liver-transplant/. Accessed March 12, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress