Identification of Antibody-Mediated Rejection After Kidney Transplantation by Specific MicroRNAs.
1University Medicine Charité-Nephrology, Berlin, Germany
2German Rheumatism Research Centre DRFZ, Berlin, Germany
3University Medicine Charité-Pathology, Berlin, Germany
4University Medicine Charité-Transfusion Medicine, Berlin, Germany
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A15
Keywords: Gene expression, Kidney, Kidney transplantation, Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Antibody Mediated Rejection in Kidney Transplant Recipients I
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, April 29, 2017
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall D1
Antibody-mediated rejection (ABMR) is the major cause for allograft failure, since a curative therapy is lacking. There are also still challenges in ABMR diagnosis. The identification of specific microRNAs as biomarker and as basis for functional studies might improve these crucial problems after kidney transplantation.
Total RNA from blood of 6 patients with biopsy-proven ABMR at the time of biopsy, of 6 matched control patients with stable graft function and of 4 patients with T-cell mediated rejection (TCMR) at the time of biopsy was isolated. The small RNA fraction was isolated and libraries were prepared for single end sequencing with 50 bp by HiSeq2500 Illumina Next Generation Sequencing Device. Raw data was mapped by the miRDeep2.0.0.8 algorithm script to detect the expression of microRNAs. Differentially expressed microRNAs were determined with deseq2 using the Wald test (p value<=0.05; fold change>=1.5). The identified candidate microRNAs were validated with RT-PCR.
301 microRNAs were detected. From these, 61 microRNAs were differentially expressed between the three patient cohorts. The expression of 31 microRNAs distinguished ABMR from control patients, 18 differentiated ABMR from TCMR. Two of these microRNAs were able to discriminate ABMR from controls and from TCMR. 32 microRNAs were differentially expressed between control patients and TCMR, whereas 11 of these differentiated controls from ABMR and from TCMR. Eight specific microRNAs distinguished TCMR from ABMR and controls. Ultimately the expression of 1 microRNA discriminated all three patient groups from each other.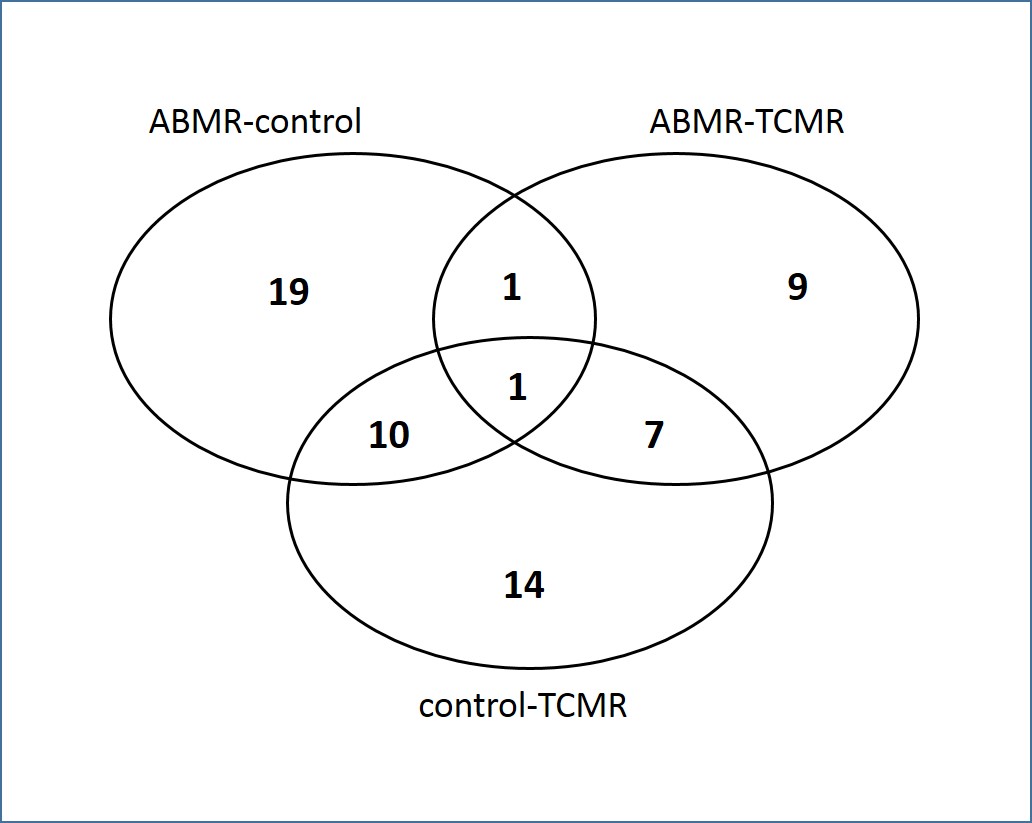 The identification of ABMR specific microRNAs in blood allows the evaluation of these potentially diagnostic markers in studies with high numbers of patients with different etiologies like ABMR, TCMR, infections and IFTA after kidney transplantation.
The identification of ABMR specific microRNAs in blood allows the evaluation of these potentially diagnostic markers in studies with high numbers of patients with different etiologies like ABMR, TCMR, infections and IFTA after kidney transplantation.
CITATION INFORMATION: Matz M, Heinrich F, Durek P, Lorkowski C, Wu K, Lachmann N, Budde K, Mashreghi M.-F. Identification of Antibody-Mediated Rejection After Kidney Transplantation by Specific MicroRNAs. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Matz M, Heinrich F, Durek P, Lorkowski C, Wu K, Lachmann N, Budde K, Mashreghi M-F. Identification of Antibody-Mediated Rejection After Kidney Transplantation by Specific MicroRNAs. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/identification-of-antibody-mediated-rejection-after-kidney-transplantation-by-specific-micrornas/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
