Ibrutinib Suppresses Alloantibody Responses in A Mouse Model of Allosensitization: A Preliminary Report.
CTC/Surgery, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A8
Keywords: Alloantibodies, B cells, Immunosuppression, Mice
Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 11, 2016
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Halls C&D
Background Ibrutinib is a Bruton tyrosine Kinase (BTK) antagonist that inhibits B cell receptor (BCR) signaling, therefore blocking B cell activation. Ibrutinib is approved by FDA for treatment of B-cell malignancies. In considering its anti B
cell property, we recently carried out studies to evaluate whether ibrutinib has suppressive effect on alloantibody responses in mice.
Methods: A mouse model of allosensitization using a C57BL/6 mouse as the recipient of a HLA.A2+ skin allograft) was employed to examine the effects of ibrutinib (20mg/kg/day IP injection for 14 days) on de novo alloantibody responses. For the study of recall antibody suppression by ibrutinib, mice received primary SG were re-immunized with a second HLA.A2+ SG at Day 90 Ptx. Donor-specific antibody (DSA) levels were measured in a flow-cytometric antibody binding assay. Splenic T and B cell subsets and bone marrow B/plasma cells were analyzed in flow cytometry.
Results: Control mice (n=6) developed peak levels of DSA IgM at day 14 PTx while the ibrutinib treated mice (n=6) had significantly lower levels of DSA IgM (p=0.0047). Control mice developed HLA.A2-specific IgG antibodies at day 14 (230+60 MFI) and reached peak levels at day 21 (426+61 MFI). In contrast, mice in the treatment group had low levels of HLA.A2-specific IgG at day 14 (109+59 MFI, p=0.004) and day 21 (241+86 MFI, p=0.003). FACS analysis of lymphocytic cells found a reduction of B220+/CD19+ B cell population (p<0.05) and reduction of CD38dimCD138+B220– plasma cells (p<0.05) in the spleens. In addition, ibrutinib treatment reduced recall DSA IgG levels (281+119 vs. control 455+147 MFI, p=0.05) in responses to 2nd SG.
Conclusion: Ibrutinib is effective in suppressing de novo alloantibody responses through blocking BTK mediated BCR signaling, leading to reduction of B cells. Use of ibrutinib may provide benefits to HLA-sensitized transplant patients for B cell suppression. 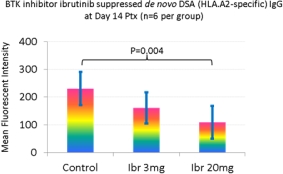
CITATION INFORMATION: Wu G, Kim I, Chai N.-N, Klein A, Jordan S. Ibrutinib Suppresses Alloantibody Responses in A Mouse Model of Allosensitization: A Preliminary Report. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wu G, Kim I, Chai N-N, Klein A, Jordan S. Ibrutinib Suppresses Alloantibody Responses in A Mouse Model of Allosensitization: A Preliminary Report. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/ibrutinib-suppresses-alloantibody-responses-in-a-mouse-model-of-allosensitization-a-preliminary-report/. Accessed March 2, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
