Hydrogen Sulfide Supplementation Helps Mitigate Effects of Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in a Murine Model of Donation After Cardiac Death Renal Transplantation.
1Microbiology & Immunology, University of Western Ontario, London, Canada
2Matthew Mailing Centre for Translational Transplant Studies, London Health Sciences Centre, London, Canada.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C177
Keywords: Donors, Ischemia, Kidney transplantation, non-heart-beating, Warm ischemia
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Kidney Transplantation: AKI/Preservation/DCD
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 13, 2016
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Halls C&D
Donation after cardiac death(DCD) renal grafts experience a combination of prolonged warm and cold ischemia leading to greater ischemia reperfusion injury(IRI) that results in higher rates of delayed graft function & failure in transplant recipients. We have previously shown that hydrogen sulfide(H2S) supplementation helps to reduce IRI in either cold or warm ischemic models. This study aims to investigate if H2S supplementation could improve renal graft outcomes that have experienced a combination of warm and cold ischemia.
Methods: Adult male Lewis syngeneic rats were used such that the sham operated rats underwent a midline incision only while the renal transplant recipients in the untreated & H2S treated group were bilaterally nephrectomized before receiving donor kidneys that had experienced 30 minutes of clamping and 18 hours of cold storage(4[ordm]C). For the H2S treated group, donor rats received D-cysteine(2mmol/kg weight of rat) intra-peritoneally 1 hour prior to the surgical procedure and the cold storage solution was supplemented with 150[mu]M sodium hydrogen sulfide. The transplant recipients were then monitored for a maximum of 30 days. Blood and urine samples were collected periodically and the grafts were recovered at the time of sacrifice or death.
Results: H2S supplementation provided survival benefit as exhibited by significantly improved survival of the H2S treated group in comparison to untreated group(p<0.05). It also improved renal graft function evident from higher urine protein to urine creatinine ratio and increased serum creatinine in the untreated group. Further, significantly greater renal injury(p<0.05) indicated by acute tubular necrosis scores is observed in the untreated group in comparison to the sham group.
Conclusions: This is the first study depicting benefits of H2S supplementation in a clinically relevant murine model of DCD renal transplantation and could potentially help to reduce IRI and improve DCD graft function in future.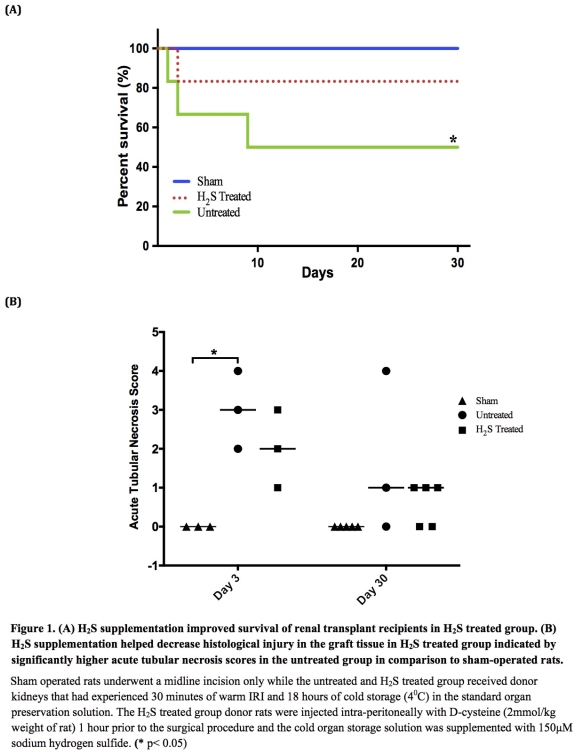
CITATION INFORMATION: Grewal J, Lobb I, Saha M, Jiang J, Haig A, Sener A. Hydrogen Sulfide Supplementation Helps Mitigate Effects of Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in a Murine Model of Donation After Cardiac Death Renal Transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Grewal J, Lobb I, Saha M, Jiang J, Haig A, Sener A. Hydrogen Sulfide Supplementation Helps Mitigate Effects of Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in a Murine Model of Donation After Cardiac Death Renal Transplantation. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/hydrogen-sulfide-supplementation-helps-mitigate-effects-of-ischemia-reperfusion-injury-in-a-murine-model-of-donation-after-cardiac-death-renal-transplantation/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
