Hospital Readmissions Following Discharge After Liver Transplantation (LT).
E. Minja, S. Chinnakotla, K. Yadav, A. Pugalenthi, O. Serrano, R. Kandaswamy, W. Payne, T. Pruett, V. Kirchner.
Surgery, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B177
Keywords: Kidney/liver transplantation, Liver transplantation, Living-related liver donors, Outcome
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Kidney Issue in Liver Transplantation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 12, 2016
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Halls C&D
Background:
Our objective was to describe incidence and causes readmissions within 30 days of discharge following liver transplantation (LT).
Methodology:
Medical records of 1027 consecutive patients who underwent OLT from 1/1/1997 and 12/31/2014 at our center were reviewed and causes of readmission analyzed. Pediatric transplants were excluded.
Results:
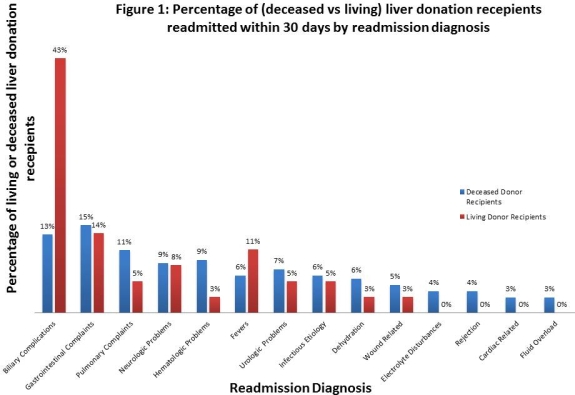
155 (15.1%) patients received living donor (LD) grafts and 873 (84.9%) patients received decease donor (DD) grafts. A total of 473 (46%) patients had readmission within 30 days of discharge following a liver transplantation. The three most common causes of readmission following a hospital discharge after a liver transplant were biliary complications (18%), gastrointestinal complaints (15%) and pulmonary complications (10%).The readmission diagnoses between DD and LD recipients are differient.(Figure 1). 43% of LD recipients who were readmitted within 30 days of discharge had biliary complications, compared to 13% for DD recipients [ p=<0.05]. Of these LD recipients with biliary complications, 50% had bile leaks and 31% had bilomas. Compared to LD recipients, pulmonary problems (11% vs. 5%) and hematologic problems (9% vs.3%) were most common causes of readmissions for DD liver recipients.
Conclusion:
Readmissions after LT represent a significant health care burden, with 46% of patients readmitted within 30 days of discharge. These data confirm that further efforts are needed to predict and circumvent treatable causes for readmission to improve health care costs and quality.
CITATION INFORMATION: Minja E, Chinnakotla S, Yadav K, Pugalenthi A, Serrano O, Kandaswamy R, Payne W, Pruett T, Kirchner V. Hospital Readmissions Following Discharge After Liver Transplantation (LT). Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Minja E, Chinnakotla S, Yadav K, Pugalenthi A, Serrano O, Kandaswamy R, Payne W, Pruett T, Kirchner V. Hospital Readmissions Following Discharge After Liver Transplantation (LT). [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/hospital-readmissions-following-discharge-after-liver-transplantation-lt/. Accessed February 23, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
