Five-Year Outcomes After Transplantation of Kidneys from Deceased Donors with Acute Kidney Injury.
1Division of Transplant Surgery, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA
2Kidney Transplant Program, Lankenau Medical Center, Wynnewood, PA
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 327
Keywords: Graft survival, Kidney transplantation, Outcome, Resource utilization
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Donors with Acute Kidney Injury
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, May 1, 2017
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:06pm-5:18pm
Presentation Time: 5:06pm-5:18pm
Location: E450a
Background: Kidneys from deceased donors with acute kidney injury (AKI) are often discarded due to a perceived higher risk of poor graft function. Kidney Donor Profile Index (KDPI) is the standard metric for donor kidney quality and a driver of organ acceptance. We examined the clinical outcomes of deceased donor kidneys with AKI across KDPI strata.
Methods: We reviewed all cases of deceased donor kidney transplant (KT) performed from January 1, 2009 to December 31, 2015 at two transplant centers. Data collected included donor terminal creatinine (Cr), donor age, KDPI, recipient age, cause of renal failure, cold ischemia time and Cr at 3 and 6 months and 1, 3, and 5 years post-transplant. Primary clinical outcomes (kidney graft function, death censored graft and patient survival) were measured for patients receiving kidneys from donors with and without AKI (terminal Cr above 2 mg/dL).
Results: A total of 498 KT were performed, of which 85 came from AKI donors. Differences between the AKI and non-AKI groups are summarized in Table 1.
| AKI
(n=85) |
non-AKI
(n=412) |
p value | |
| donor Cr | 3.89 | 0.96 | <0.05 |
| donor age (yr.) | 31.9 | 39.6 | 0.00006 |
| KDPI (%) | 39 | 50 | 0.000158 |
| CIT (min.) | 639 | 455 | 0.005 |
Comparing the groups, there was no difference in the kidney graft function at any of the chosen time-points. Across KDPI strata, there was a significant difference in kidney graft function at 3 months (p <0.05), 6 months (p <0.05), 1 year (p=0.001), and 3 years (p=0.004). Figure 1 depicts Kaplan-Meier curves for graft survival. There was no statistical differences in patient survival by donor AKI or KDPI.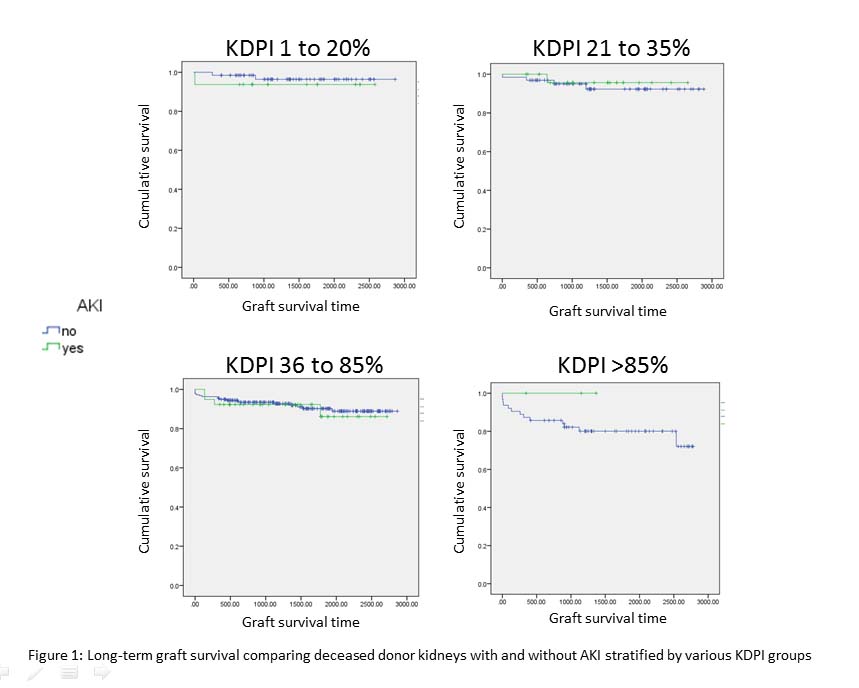 Conclusion: We found that over 5 years, AKI kidneys perform similarly to non-AKI kidneys at each KDPI strata in terms of kidney graft function, graft survival, and patient survival. Donors with AKI tended to have a lower KDPI. With judicious selection of AKI kidneys, short and long-term patient outcomes are satisfactory.
Conclusion: We found that over 5 years, AKI kidneys perform similarly to non-AKI kidneys at each KDPI strata in terms of kidney graft function, graft survival, and patient survival. Donors with AKI tended to have a lower KDPI. With judicious selection of AKI kidneys, short and long-term patient outcomes are satisfactory.
CITATION INFORMATION: Latona J, Shah A, Frank A, Maley W, Doria C, Ramirez C. Five-Year Outcomes After Transplantation of Kidneys from Deceased Donors with Acute Kidney Injury. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Latona J, Shah A, Frank A, Maley W, Doria C, Ramirez C. Five-Year Outcomes After Transplantation of Kidneys from Deceased Donors with Acute Kidney Injury. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/five-year-outcomes-after-transplantation-of-kidneys-from-deceased-donors-with-acute-kidney-injury/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
