Factors Predicting Risk for Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Highly Sensitized Pediatric Renal Transplants.
1Comprehensive Transplant Center, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA
2Biostatistics Core, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D153
Keywords: Alloantibodies, HLA antibodies, Kidney transplantation, Pediatric
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Kidney-Pediatrics
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, June 14, 2016
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Halls C&D
Introduction: Antibody-mediated rejection (ABMR) is a concern in highly sensitized (HS) patients (pts) receiving renal transplant (tx). We have previously published that a donor specific antibody (DSA) relative intensity score (RIS) of > 17 at time of tx predicted ABMR in HS adults. Here we analyzed risk factors in HS pediatric pts.
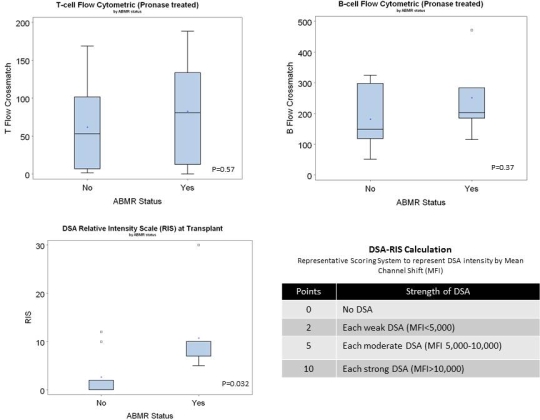
Methods: 16 HS pts underwent renal tx from 1/2009 to 10/2014. 15/16 pts received a previous tx. All pts underwent desensitization with IVIg/Rituximab. RIS scores at the time of tx were calculated for each pt (Figure 1). Risk factors for ABMR were examined in 2 groups: ABMR+ (n=7) and ABMR- (n=9) .
Results: Pt characteristics were similar and pt survival was 100%. 2 ABMR+ pts suffered graft loss, one from rejection 16 months post-tx and the other from recurrent FSGS. ABMR+ pts had higher class I and II %PRA, and higher T and B-cell flow cytometric crossmatches at the time of tx, although not statistically significant. However, ABMR+ pts had a significantly higher RIS, p=0.032.
Conclusion: DSA-RIS was the most important predictor of ABMR+ in HS patients and should be considered in both allocation strategy and post-tx monitoring for ABMR.
| Characteristics | ABMR (n=7) | No ABMR (n=9) | P-value |
| Age, yr, Mean ± SD | 21.0 ± 6.9 | 18.7 ± 3.9 | 0.42 |
| Male/female | 4/3 | 6/3 | > 0.99 |
| Deceased donor | 7 | 8 | > 0.99 |
| Sensitizing Events | > 0.99 | ||
| Blood Transfusion | 0 | 1 | |
| Previous Transplants | 7 | 8 | |
| Panel Reactive Antibody (PRA) % at tx | |||
| Class I | 73.1 ± 19.1 | 49.1 ± 28.3 | 0.075 |
| Class II | 63.7 ± 29.8 | 61.0 ± 23.8 | 0.84 |
| T-cell FCMX (Mean Channel Shift) at Tx- Pronase Treated | 82.5 ± 73.4 | 61.6±59.9 | 0.57 |
| B-cell FCMX (Mean Channel Shift) at Tx- Pronase Treated | 251.2 ± 136.8 | 181.2 ± 107.0 | 0.37 |
| DSA RIS at transplant | |||
| Class I only | 7.0 ± 5.0 | 2.4 ± 2.9 | 0.043 |
| Class II only | 5.1 ± 7.0 | 0.9 ± 1.8 | 0.16 |
| Both class I and class II | 12.1 ± 9.3 | 3.3 ± 2.6 | 0.032 |
CITATION INFORMATION: Kim I, Choi J, Vo A, Louie S, Mirocha J, Jordan S, Kamil E, Puliyanda D. Factors Predicting Risk for Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Highly Sensitized Pediatric Renal Transplants. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kim I, Choi J, Vo A, Louie S, Mirocha J, Jordan S, Kamil E, Puliyanda D. Factors Predicting Risk for Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Highly Sensitized Pediatric Renal Transplants. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/factors-predicting-risk-for-antibody-mediated-rejection-in-highly-sensitized-pediatric-renal-transplants/. Accessed February 27, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
