Extracellular Matrix from Pancreas Improves Human Islet Function In Vitro
1Department of Surgery, School of Medicine, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond
2Department of Biomedical Engineering, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond
3Hume-Lee Transplant Center, VCU Health System, Richmond.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B77
Keywords: Islets
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Islet Cell and Cell Transplantation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 3, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Background:
Islets which are clinically transplanted into the portal vein are subjected to inflammatory insults in the peri-transplant period followed by immune assault causing long-term islet dysfunction. Within the pancreas, the islets are surrounded by Extracellular Matrix (ECM) proteins and interaction of islets with ECM has been shown to regulate essential function. Isolation of islets results in cleavage of islet-ECM network that may play an important role in islet survival, proliferation, and insulin secretion. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the role of pancreas derived ECM on islet function and viability.
Methods:
Islets and ECM were isolated using modified Ricordi's protocol from pancreas obtained from cadaveric donors for research purpose. Remnant pancreas connective tissue was harvested after complete digestion. Residual cells were lysed and connective tissue was further digested with pepsin, lyophilized and milled into powder. The powdered ECM was reconstituted in buffer solution. We co-cultured human islets with ECM (0.1, 1, 10, or 100 ug/ml, respectively) for 48hrs. Islets were then tested for viability and glucose stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) function. Protein analysis of ECM fraction was also performed.
Results:
Co-culture of islets with ECM had no significant effect on the viability of islets at the concentrations tested. A significant difference in stimulation index was found between the control and ECM at concentration of 100 ug/ml (4.3±1.3 vs. 6.5±1.2; p < 0.05). 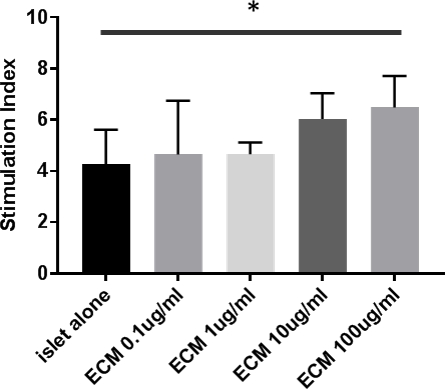 Protein analysis revealed the presence of fibronectin in the ECM fraction.
Protein analysis revealed the presence of fibronectin in the ECM fraction.
Conclusion:
Co-culture of islets with pancreatic ECM did not affect the viability, however there was a significant increase in the insulin release in response to glucose. ECM from pancreas has the potential to be used as material for encapsulation or coating for islet culture before transplantation.
CITATION INFORMATION: Shindo Y., Pouillot R., Young B., Link P., Heise R., Levy M., Kanak M. Extracellular Matrix from Pancreas Improves Human Islet Function In Vitro Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Shindo Y, Pouillot R, Young B, Link P, Heise R, Levy M, Kanak M. Extracellular Matrix from Pancreas Improves Human Islet Function In Vitro [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/extracellular-matrix-from-pancreas-improves-human-islet-function-in-vitro/. Accessed March 11, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
