Exploring the Correlation with Donor Hepatitis C Viral Load and Viral Kinetics in Naïve Kidney Transplantation Recipients
A. Brooks1, A. Rechnitzer1, R. Teo1, D. Y. Goldstein2, M. Narlieva2, J. P. Rocca1, M. Ajaimy1, L. Liriano-Ward1, Y. Azzi1, C. Pynadath1, P. Loarte-Campos1, E. Akalin1, M. E. Le1, H. Yaffe1, S. Greenstein1, J. Torabi1, M. M. Kinkhabwala1, J. A. Graham1
1Montefiore-Einstein Center for Transplantation, Montefiore Medical Center, Bronx, NY, 2Pathology, Montefiore Medical Center, Bronx, NY
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: LB 70
Keywords: Area-under-curve (AUC), Hepatitis C, Kidney, Kidney transplantation
Topic: Clinical Science » Infectious Disease » Non-Organ Specific: Viral Hepatitis
Session Information
Session Name: Non-Organ Specific: Viral Hepatitis
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: The transplantation of Hepatitis C viremic (HCV) kidneys into uninfected recipients was made possible by effective direct acting anti-viral (DAA) therapy. This study aims to analyze the relationship between the donor HCV viral load and recipient HCV viral kinetics.
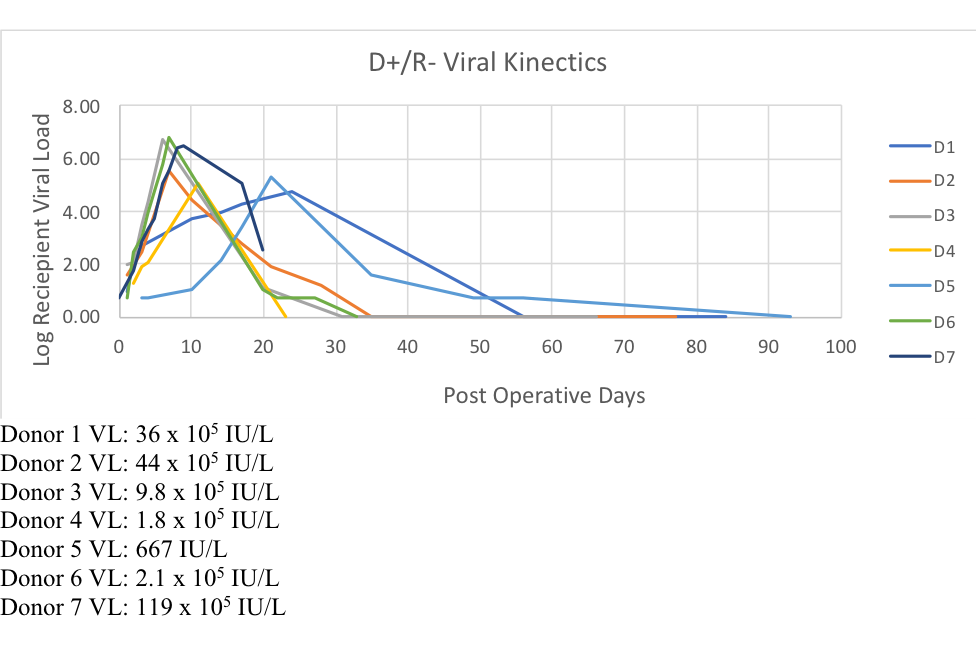
*Methods: A single center retrospective study of HCV naïve patients that received HCV nucleic acid test positive kidneys (D+/R-) was performed. Seven donors had documented donor HCV viral loads at time of transplantation. Recipient viral loads were measured at regular intervals following transplantation. Area under the curve (AUC) was calculated to represent the extent of viral burden in the recipients. Recipient peak viral load, viral load AUC, recipient age, date of DAA initiation, and type of induction were analyzed using a linear regression model. D+/R- patients were monitored post-operatively for development of viremia and were all subsequently treated with DAAs.
*Results: The average age in the D+/R- group was 43.4 years. The mean donor age was 36.5 years. KDPI was 57.1%. The mean donor viral load was found to be 3.05 x 106 UI/L. The mean peak recipient viral load was 2.23 x 106 IU/L. The mean AUC was 16.13 x 106 (IU/L x days). The linear regression model showed no correlation between the donor viral load and the recipient peak viral load or the recipient viral load AUC (p = 0.7 and 0.6). DAA initiation and induction was also non-predictive.
*Conclusions: D+/R- transplantation offers patients an alternative strategy to increase access to kidney transplantation. Although, donor viral load did not correlate with the degree of recipient viremia, future studies may find this association significant with a larger cohort.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Brooks A, Rechnitzer A, Teo R, Goldstein DY, Narlieva M, Rocca JP, Ajaimy M, Liriano-Ward L, Azzi Y, Pynadath C, Loarte-Campos P, Akalin E, Le ME, Yaffe H, Greenstein S, Torabi J, Kinkhabwala MM, Graham JA. Exploring the Correlation with Donor Hepatitis C Viral Load and Viral Kinetics in Naïve Kidney Transplantation Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/exploring-the-correlation-with-donor-hepatitis-c-viral-load-and-viral-kinetics-in-naive-kidney-transplantation-recipients/. Accessed March 12, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress