Ex Vivo Assessment of Marginal Human Kidneys Using Computed Tomography
1Surgery, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, CT, 2Surgery, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom, 3Yale Translational Research Imaging Center, New Haven, CT, 4Radiology, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, CT
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D385
Keywords: Bioengineering, Donors, marginal, Kidney transplantation, Radiologic assessment
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Late Breaking
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, June 4, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: Thousands of ‘marginal’ organs are discarded each year despite a severe organ shortage. This has motivated development of new technologies, such as ex vivo organ perfusion, to revitalize marginal organs. Currently, tools to assess organ viability ex vivo are limited to gross measures like urine production. We adapted computed tomography to enable quantitative whole organ assessments of human kidneys ex vivo.
*Methods: 6 transplant-declined human kidneys were obtained in partnership with New England Donor Services under an approved ethical protocol. CT was performed at the Yale Translational Research Imaging Center on a GE Medical Systems CT scanner. Organs were flushed with cold preservation solution and stored on ice until imaging. DICOM images were reconstructed in Horos and analyzed with custom MATLAB code.
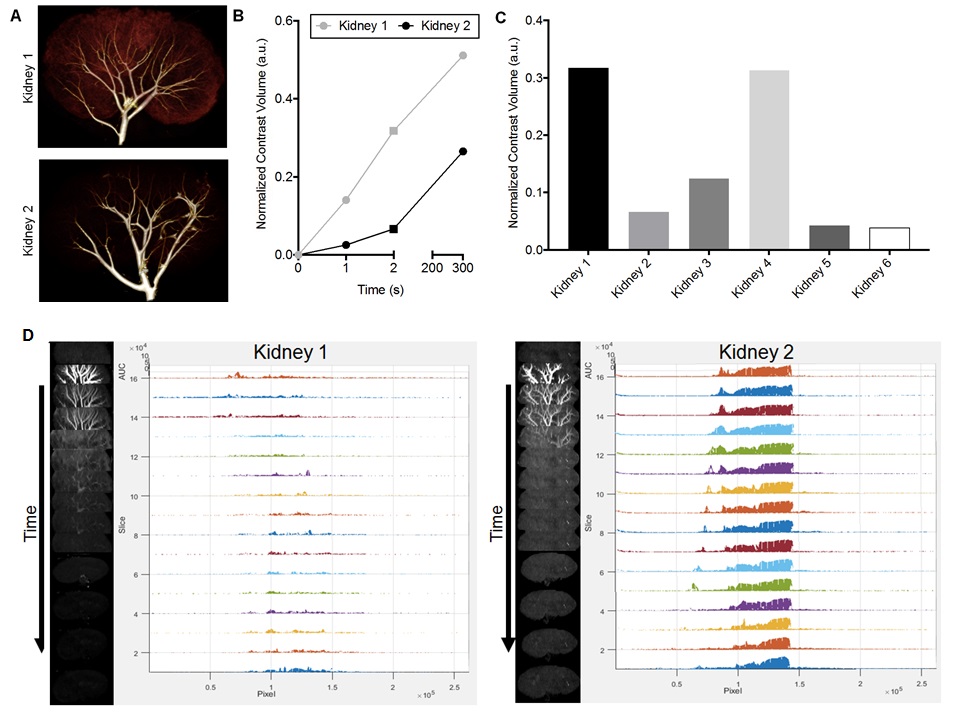
*Results: We performed a pilot study of 6 transplant-declined human kidneys to assess feasibility and establish our ex vivo imaging methods. Contrast enhanced CT was performed ex vivo using a constant pressure infusion with crystalloid solution. Fig. 1A shows 3D renderings of a 22 year old DCD donor kidney declined for suspected air embolism (but otherwise transplantable) compared to a 39 year old DCD donor with suspected fibrosis. These organs, representing opposite ends of the marginal quality spectrum, displayed stark differences in the normalized volume of contrast enhancement (Fig. 1B). Fig. 1C shows a comparison of contrast volumes for each of the 6 kidneys. Dynamic analysis of physiologic function was performed by assessing washout rates of iohexol following bolus administration. Custom MATLAB code provided 3D voxel by voxel assessment of contrast clearance rate, a parameter related to the quality of glomerular filtration (Fig. 1D).
*Conclusions: We demonstrated that ex vivo whole-organ imaging is feasible and can enable dynamic, quantitative assessments of marginal human organs. Our approach can be used for repeat measurements before and after therapeutic interventions to provide robust quantification that controls for the inherent variability of human organs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Harris MK, DiRito JR, Liu H, Boutagy N, Liu C, Hosgood S, Mulligan D, Nicholson ML, Sinusas A, Haakinson D, Tietjen GT. Ex Vivo Assessment of Marginal Human Kidneys Using Computed Tomography [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/ex-vivo-assessment-of-marginal-human-kidneys-using-computed-tomography/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress