Evidence of a Clinically Significant Drug-Drug Interaction between Cannabidiol and Tacrolimus: A Case Report
1University of Cinninati, Cincinnati, OH
2Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, Cincinnati, OH.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B331
Keywords: Calcineurin, Drug interaction
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Non-Organ Specific: Economics, Public Policy, Allocation, Ethics
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 3, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Cannabidiol (CBD), a major purified non-psychoactive component of marijuana with anticonvulsant properties, is being studied under an expanded access IND as an adjuvant treatment for refractory epilepsy (Epidiolex; GW Pharmaceuticals). CBD is metabolized by CYP3A4 and CYP2C19 with a growing body of evidence suggesting it is also a potent inhibitor of these pathways. We report for the first time a significant drug-drug interaction between the purified CBD product and tacrolimus (TAC).
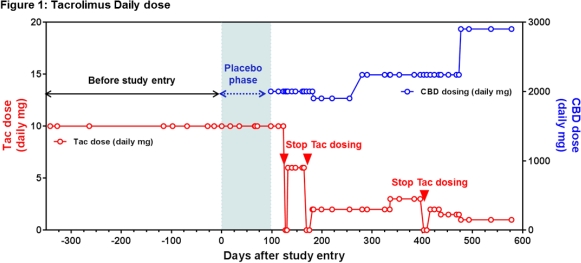
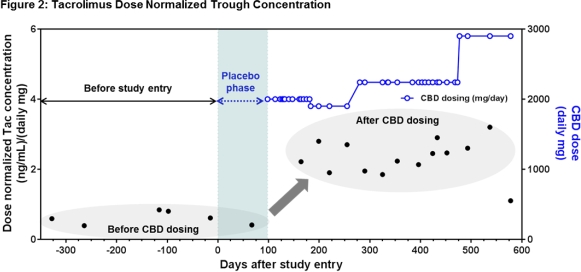
The patient was a 33 year old female with refractory epilepsy receiving TAC for interstitial nephritis. She was stable on tacrolimus 5 mg BID for a year prior to randomization in the CBD study with levels ranging from 3.9-8.4ng/mL and baseline Scr of 1.16mg/dL. She was initially randomized to the sesame oil placebo with no change in TAC levels or Scr. However, when she entered into the open label study and began receiving CBD she showed signs of TAC toxicity with Scr of 2.4mg/dL. TAC dose was reduced repeatedly while receiving CBD as in Figure 1 with a last known dose of 0.5 mg BID (a 10-fold reduction). The dose normalized TAC concentrations are in Figure 2.
Our report delineates an important concern for the transplant community with the increasing legalization of marijuana and advent of a possible FDA approved CBD product. Larger studies are needed to better understand the impact of this drug-drug interaction in solid organ transplant recipients.
CITATION INFORMATION: Leino A., Emoto C., Fukuda T., Privitera M., Vinks A., Alloway R. Evidence of a Clinically Significant Drug-Drug Interaction between Cannabidiol and Tacrolimus: A Case Report Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Leino A, Emoto C, Fukuda T, Privitera M, Vinks A, Alloway R. Evidence of a Clinically Significant Drug-Drug Interaction between Cannabidiol and Tacrolimus: A Case Report [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/evidence-of-a-clinically-significant-drug-drug-interaction-between-cannabidiol-and-tacrolimus-a-case-report/. Accessed February 23, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress