Everolimus with Reduced Calcineurin Inhibitor Exposure in De Novo Kidney Transplant Recipients: Efficacy and Safety Outcomes from the TRANSFORM Study
1TRANSFORM Study Group, Livingston
2Novartis Pharma AG, Basel, Switzerland.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 597
Keywords: Efficacy, Kidney transplantation, Renal function, Safety
Session Information
Session Time: 8:30am-10:00am
 Presentation Time: 9:45am-10:00am
Presentation Time: 9:45am-10:00am
Location: Room Hall B
Purpose: Everolimus (EVR)-facilitated calcineurin inhibitor (CNI) reduction regimens help prevent long-term CNI nephrotoxicity in kidney transplant recipients (KTxRs). TRANSFORM (NCT01950819) is the largest study in de novo KTxRs to date to evaluate the efficacy and safety of EVR+reduced-dose CNI (rCNI: tacrolimus [TAC] or cyclosporine) and mycophenolic acid (MPA)+standard-dose CNI (sCNI). Here we present the 12-month (M) data from this study.
Methods: TRANSFORM is a 24M, multicenter, open-label study in which KTxRs were randomized to receive EVR+rCNI (N=1022) or MPA+sCNI (N=1015) with induction and steroids. The primary objective was M12 incidence of binary composite of treated biopsy-proven acute rejection (tBPAR) or estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) <50 mL/min/1.73m2. Other assessments included M12 incidence of donor-specific antibodies (DSA), adverse events (AEs), and infections.
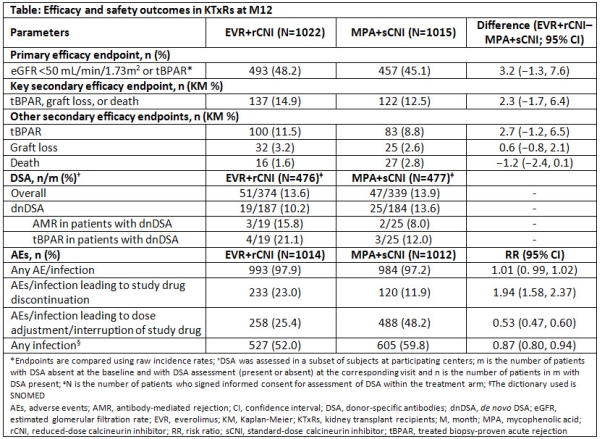
Results: Overall, 76.9% of KTxRs completed the study medication up to M12. Mean EVR trough level was within the target range (3-8 ng/mL) throughout the study. At M12, only 57.9% and 62.1% of KTxRs were within the TAC target range in the EVR+rCNI and MPA+sCNI arms, respectively. Non-inferiority margin of 10% for the primary endpoint was achieved in EVR+rCNI vs MPA+sCNI (48.2% vs 45.1%, P=0.001; Table). Mean eGFR (53 vs 54.4 mL/min/1.73m2) and incidence of the composite endpoint of tBPAR/graft loss/death were comparable between arms. Overall tBPAR rates were low and comparable between both arms (11.5% vs 8.8%). Incidence of de novo DSA (dnDSA) was numerically lower in EVR+rCNI (10.2%) vs MPA+sCNI arm (13.6%). Overall, incidence of AEs was comparable between arms; incidence of AEs leading to study drug discontinuation was higher with EVR+rCNI vs MPA+sCNI, but AEs requiring dose adjustment were higher in MPA+sCNI arm.
Conclusion: In comparison to MPA+sCNI-based regimen, EVR+rCNI-based regimen provides good and comparable efficacy, safety, and renal function in KTxRs. M24 follow-up data are awaited.
CITATION INFORMATION: Mulgaonkar S., Pascual J., Chadban S., Tedesco H., Berger S., Qazi Y., Legendre C., Basic-Jukic N., Bernhardt P., Vincenti F. Everolimus with Reduced Calcineurin Inhibitor Exposure in De Novo Kidney Transplant Recipients: Efficacy and Safety Outcomes from the TRANSFORM Study Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mulgaonkar S, Pascual J, Chadban S, Tedesco H, Berger S, Qazi Y, Legendre C, Basic-Jukic N, Bernhardt P, Vincenti F. Everolimus with Reduced Calcineurin Inhibitor Exposure in De Novo Kidney Transplant Recipients: Efficacy and Safety Outcomes from the TRANSFORM Study [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/everolimus-with-reduced-calcineurin-inhibitor-exposure-in-de-novo-kidney-transplant-recipients-efficacy-and-safety-outcomes-from-the-transform-study/. Accessed March 12, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress