Evaluation of the Toxicity Profile of Proteasome Inhibitor-Based Therapy for Antibody Mediated Rejection.
1U of Cinncinati, Cincinnati
2The Christ Hospital, Cincinnati.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 411
Keywords: Adverse effects, Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney AMR: Predicting the Patient at Risk
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Tuesday, June 14, 2016
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:42pm-3:54pm
Presentation Time: 3:42pm-3:54pm
Location: Ballroom B
Background: Experience with bortezomib (BTZ) antibody mediated rejection (AMR) therapy has progressively increased over the past few years. The BTZ toxicity profile in the transplant population has been previously described in a modest-sized population with intermediate follow up. The purpose of this study was to evaluate toxicities associated with BTZ AMR therapy in a large kidney and/or pancreas transplant population with long term follow up.
Methods: Pts were evaluated at baseline, during therapy, and following completion of BTZ therapy. Gastrointestinal and hematologic adverse effects were graded in accordance with the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE). The Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Neurotoxicity (FACT/GOG-Ntx) questionnaire was used to evaluate peripheral neuropathy. AMR was diagnosed according to the Banff criteria.
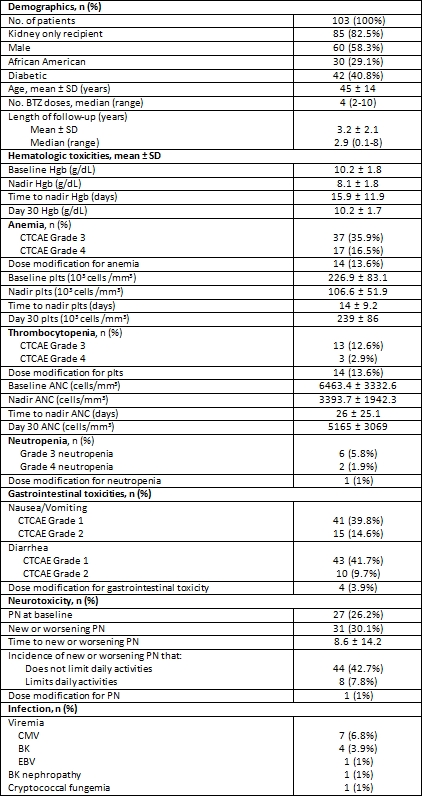
Results: 103 pts received BTZ for AMR treatment. 78 pts (75.7%) completed 1 cycle of BTZ. The most common toxicity was gastrointestinal; symptoms were generally mild only requiring dose adjustment in 4 pts (3.9%). Grade 3 and 4 hematologic toxicity occurred in 61 pts (59.2%). However, resulted in dose modifications in only 29 pts (28.2%): 14 for anemia, 14 for thrombocytopenia, 1 for neutropenia. New or worsening PN was also common, occurring in 42.7%. Peripheral neuropathy (PN) resolved in all patients; median time to resolution was 13 days (range 3-461). BTZ dose adjustments for PN were required in only 1 (1%) pt. CMV viremia was observed in 7 (6.8%) pts. BK viremia in 4 (3.9%) of pts and 1 case of BK nephropathy was noted. One pt with grade 4 neutropenia expired with cryptococcal fungemia. Malignancy was not observed.
Conclusion: Overall, toxicities associated with BTZ are relatively low in severity and appear to be transient. This large series with longer follow-up further defines the adverse event profile of BTZ AMR therapy in kidney and/or pancreas transplant recipients.
 .
.
CITATION INFORMATION: Leino A, Lichvar A, Abu-Jawdeh B, Govil A, Mogilishetty G, Cardi M, Kremer J, Cuffy M, Paterno F, Alloway R, Shields A, Woodle E. Evaluation of the Toxicity Profile of Proteasome Inhibitor-Based Therapy for Antibody Mediated Rejection. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Leino A, Lichvar A, Abu-Jawdeh B, Govil A, Mogilishetty G, Cardi M, Kremer J, Cuffy M, Paterno F, Alloway R, Shields A, Woodle E. Evaluation of the Toxicity Profile of Proteasome Inhibitor-Based Therapy for Antibody Mediated Rejection. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/evaluation-of-the-toxicity-profile-of-proteasome-inhibitor-based-therapy-for-antibody-mediated-rejection/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
