Evaluation of Immunosuppression and Infection after Desensitization in Lung Transplantation
University of Maryland Medical Center, Baltimore.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C255
Keywords: Antibodies, Immunosuppression, Lung transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Lung: All Topics
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 4, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Purpose: To reduce waitlist time for sensitized lung transplant recipients (LTR), our center used peri-operative desensitization for LTR with a positive virtual crossmatch (P-VXM). We aimed to examine immunosuppression, infection and survival in our desensitized P-VXM LTR compared to negative virtual crossmatch (N-VXM) LTR.
Methods: This was an IRB-approved, single-center retrospective study of LTR transplanted between 01/2015-05/2017. Multi-organ transplants or those with no virtual crossmatch available were excluded. Variables for analysis included induction agents, tacrolimus levels, mycophenolate mofetil daily doses, infections and patient survival.
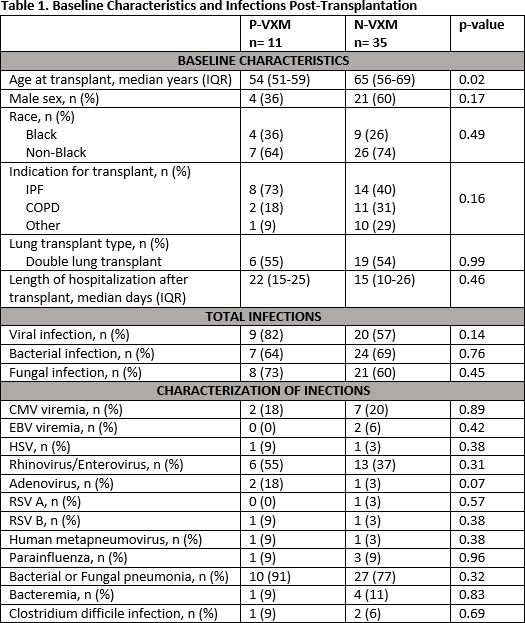
Results: Seven LTR (20%) in the N-VXM group received induction, 6 of which received a lymphocyte depleting agent. Desensitization therapy for all P-VXM LTR included rabbit anti-thymocyte globulin (median total dose of 3 mg/kg, IQR 2.7-4.8), intravenous immunoglobulin G (median total dose of 1 g/kg, IQR 1-1) and plasmapheresis (3 sessions intra-op and a median of 4 sessions post-op, IQR 4-5) within 7 days of transplant. Maintenance immunosuppression appeared similar between groups, with no significant difference in tacrolimus trough levels (p=0.96). There were no significant differences in infections (Table 1) or patient survival (100% in the P-VXM group vs. 94% in the N-VXM group, p=0.26) at a median time to follow-up of 685 days (IQR 602-697) vs. 359 days (IQR 262-502), respectively; p= 0.008. 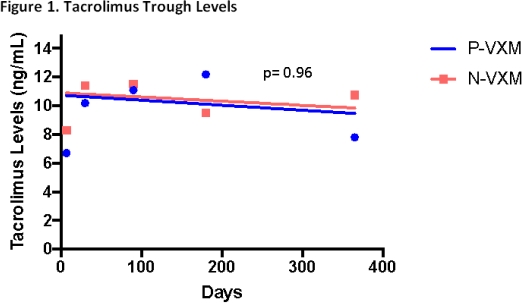
Conclusion: Our study has shown no differences in maintenance immunosuppressive regimens, infections and survival in P-VXM LTR who underwent desensitization when compared to N-VXM LTR, despite more use of lymphocyte depleting agents and plasmapheresis. Based off our single-center study, P-VXM LTR may be safely transplanted, although more studies are warranted.
CITATION INFORMATION: Hammad S., Ravichandran B., Kim J., KuKuruga D., Cipriano S., Kon Z. Evaluation of Immunosuppression and Infection after Desensitization in Lung Transplantation Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hammad S, Ravichandran B, Kim J, KuKuruga D, Cipriano S, Kon Z. Evaluation of Immunosuppression and Infection after Desensitization in Lung Transplantation [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/evaluation-of-immunosuppression-and-infection-after-desensitization-in-lung-transplantation/. Accessed March 6, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
