Evaluating Adherence to Immunosuppressive Drugs through Trackyourmed® an Innovative Qr Code-Scanner App in Renal Transplantation: Preliminary Results from i-COM Trial
1Renal Transplant Unit, Bellvitge University Hospital, L'Hospitalet de Llobregat, Spain, 2Renal Transplant Unit, Hospital Clinic, Barcelona, Spain, 3Renal Transplant Unit, Vall D'Hebron Hospital, Barcelona, Spain
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A139
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, Monitoring, Outcome, Patient education
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Biomarkers, Immune Monitoring and Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 1, 2019
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: Low adherence to chronic immunosuppressive (IS) drugs has been recognized as a major cause of premature graft loss. Although erratic trough blood IS levels may identify patients with low compliance, this approach does not allow an accurate assessment of IS adherence in the long run. Unfortunately, useful methods to improve medication adherence are scarce and not easy to implement. We developed a novel m-Health-based technology (Trackyourmed®), in which an accurate tracking of medication intakes through a novel QR code scan system is recorded in a backoffice for its ulterior evaluation.
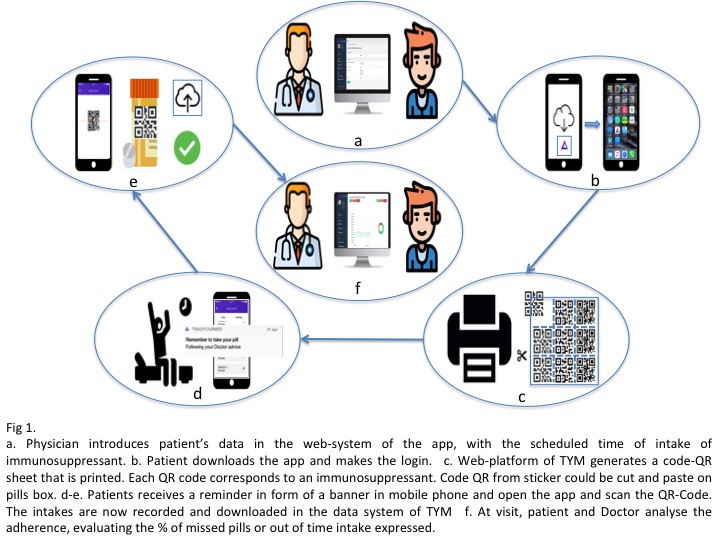
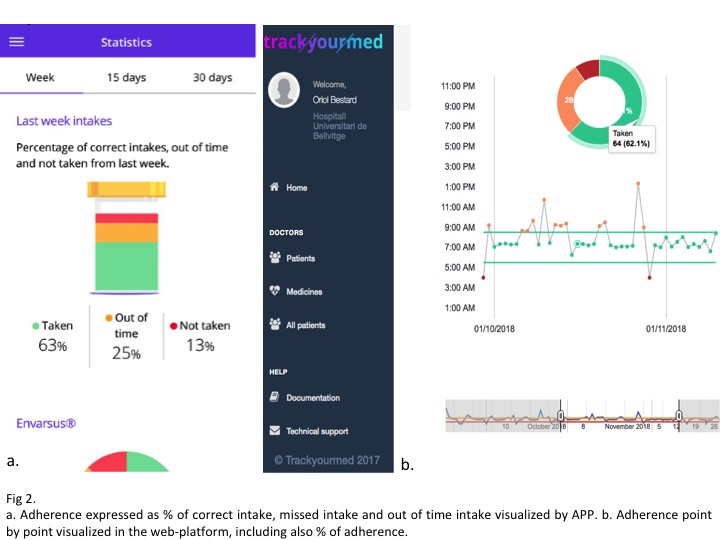
*Methods: We have conducted a 6-month follow-up prospective, non-randomized pilot study (i-COM), to evaluate the rate of implementation success of this new tool among kidney transplant recipients and characterize main factors associated to erratic or low IS compliance. As shown in Figure 1, this novel technology provides an accurate reminder, awareness and tracking of the different IS intakes done by the patient. All this information is then recorded and may be immediately visualized both by patients and transplant physician (Figure 2.) All patients had been transplanted for at least 6 months. 50% were living-donor and all received tacrolimus (TAC) and mycopheolate mofetil (MMF)-based IS, being 50% on an extended-release TAC. Medication non-adherence includes missing doses and intakes out of the prescribed time. Here we provide an interim analysis of the first 50 patients included in the study.
*Results: 10/50(20%) patients abandoned the use of the app short time its initiation (first 3 weeks), whereas 80% recognized being comfortable and happy with its use. The. Majority of patients stopping the app use were younger and had more frequently experienced acute rejection in the past as compared with active users. Patients with extended-release TAC showed significantly more regular intakes than patients with an immediate-release formulation. Notably, evening intakes, either for immediate-release TAC or MMF were significantly less on time and taken than morning intakes. Satisfaction rates among patients using this new app was very high, aiming at continuing with its use beyond the study follow-up.
*Conclusions: This preliminary analysis suggest that the use of this new m-Health technology seems to have high acceptance among kidney transplant recipients and is able to recognize patients with low IS adherence after kidney transplantation. The implementation of novel m-Health technologies such as Trackyourmed® may help reducing the incidence of IS non-adherence to ultimately improve kidney graft survival
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Melilli E, Meneghini M, Montero N, Coloma A, Revuelta I, Moreso F, Torregrosa V, Grinyo J, Bestard O. Evaluating Adherence to Immunosuppressive Drugs through Trackyourmed® an Innovative Qr Code-Scanner App in Renal Transplantation: Preliminary Results from i-COM Trial [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/evaluating-adherence-to-immunosuppressive-drugs-through-trackyourmed-an-innovative-qr-code-scanner-app-in-renal-transplantation-preliminary-results-from-i-com-trial/. Accessed March 11, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress